O rinovírus é um vírus de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de sentido positivo, lábil em ácido, da família Picornavirus. O vírus, que causa a constipação comum, é mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente adquirido nas vias aéreas através da inalação de aerossóis que contêm rinovírus e fomites Fomites Inanimate objects that carry pathogenic microorganisms and thus can serve as the source of infection. Microorganisms typically survive on fomites for minutes or hours. Common fomites include clothing, tissue paper, hairbrushes, and cooking and eating utensils. Adenovirus. Como o rinovírus é inativado pelo ácido gástrico, o vírus só consegue afetar a mucosa nasal e a conjuntiva, causando edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema dos tecidos subepiteliais e resultando na constipação comum 1 a 3 dias após a transmissão. O diagnóstico é clínico e a doença é tipicamente ligeira e autolimitada. O tratamento é de suporte e pode incluir o aumento da ingestão de fuidos, AINEs e descongestionantes nasais.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificação do vírus RNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias maneiras. A maioria dos vírus tem um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus do genoma de RNA podem ser ainda caracterizados por um RNA de cadeia simples ou dupla. Os vírus “envelopados” são cobertos por uma fina camada de membrana celular (geralmente retirada da célula hospedeira). Se a camada estiver ausente, os vírus são chamados de vírus “nus”. Os vírus com genomas de cadeia simples são vírus de “sentido positivo” se o genoma for usado diretamente como mRNA, que é traduzido em proteínas. Os vírus de “sentido negativo” de cadeia simples usam a RNA polimerase dependente de RNA, uma enzima viral, para transcrever o seu genoma em mRNA.
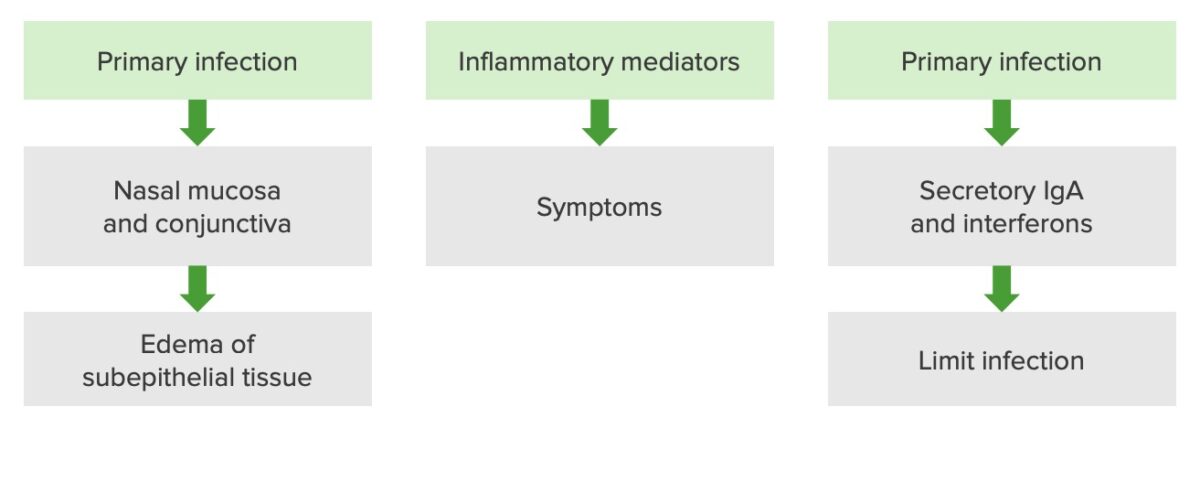
Fisiopatologia de uma infeção por rinovírus
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Sintoma | Coronavírus ( COVID-19 COVID-19 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that mainly affects the respiratory system but can also cause damage to other body systems (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, and central nervous systems). ) | Influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza (Vírus da gripe) | Rinovírus (constipação comum) | Alergias sazonais |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Febre | Frequentemente | Frequentemente | Rara | Rara |
| Fadiga | Frequentemente | Frequentemente | Às vezes | Frequentemente |
| Tosse | Frequentemente | Frequentemente | Às vezes | Frequentemente |
| Esternutos | Rara | Não | Frequentemente | Frequentemente |
| Mialgias | Às vezes | Frequentemente | Às vezes | Não |
| Rinorreia ou congestão nasal | Rara | Às vezes | Frequentemente | Frequentemente |
| Dor de garganta | Às vezes | Às vezes | Frequentemente | Não |
| Diarreia | Rara | Às vezes | Não | Não |
| Cefaleia | Às vezes | Frequentemente | Frequentemente | Às vezes |
| Dispneia | Frequentemente | Rara | Rara | Rara |
| Perda de paladar e olfato | Frequentemente | Rara | Às vezes | Rara |