A neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita grave (SCN, pela sigla em inglês) afeta a mielopoiese e tem muitos subtipos diferentes. A SCN manifesta-se na infância por infeções bacterianas com risco de vida. O tratamento comprovadamente eficaz é a administração do fator estimulador de colónias de granulócitos, que eleva a contagem diminuída de neutrófilos. A doença de Kostmann (SCN3) tem um padrão de transmissão autossómico recessivo, enquanto o subtipo mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comum, SCN1, tem transmissão autossómica dominante.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Em 50%–60% casos, neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia congénita grave (SCN) é devido a uma mutação do gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics ELANE autossómico dominante. No entanto, a mutação inicial descrita por Kostmann foi em HAX1, transmitida num padrão autossómico recessivo. A transmissão recessiva ligada ao X é devida a mutações na proteína do gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics da síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich (WASP).
A tabela a seguir resume cada subtipo de SCN, os genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure envolvidos e a sua função, bem como o seu modo de transmissão.
| Tipo | Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics mutado | Proteína afetada | Modo de transmissão |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCN1 | ELANE (19p13.3) | Elastase Elastase A protease of broad specificity, obtained from dried pancreas. Molecular weight is approximately 25, 000. The enzyme breaks down elastin, the specific protein of elastic fibers, and digests other proteins such as fibrin, hemoglobin, and albumin. Proteins and Peptides de neutrófilos (a mutação leva a proteína mal dobrada, o que leva ao aumento da apoptose) | AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives |
| SCN2 | GFI1 (1p22.1) | Repressor dos processos transcricionais (a mutação leva à perda da repressão) | AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives |
| SCN3 | HAX1 (1q21.3) | Proteína X-1 associada a HCLS1 (funciona no controlo da apoptose) | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCN4 | G6PC3 (17q21.31) | G6Pase – a mutação leva à abolição da atividade enzimática, glicosilação aberrante e apoptose aumentada de células mieloides | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCN5 | VPS45 (1q21.2) | Proteína mediada por vesícula (controla o tráfego vesicular) | AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation |
| SCNX | WAS (Xp11.23)—implicado na síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich | WASP – regulador do citoesqueleto de actina (a mutação é uma mutação de ganho de função que leva à perda da autoinibição) | Recessiva ligada ao X |
A neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia pode surgir de qualquer uma das 3 vias patogénicas:
Hereditária:
Adquirida:
Autoimune:
Infeções:
Mista: neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia benigna crónica
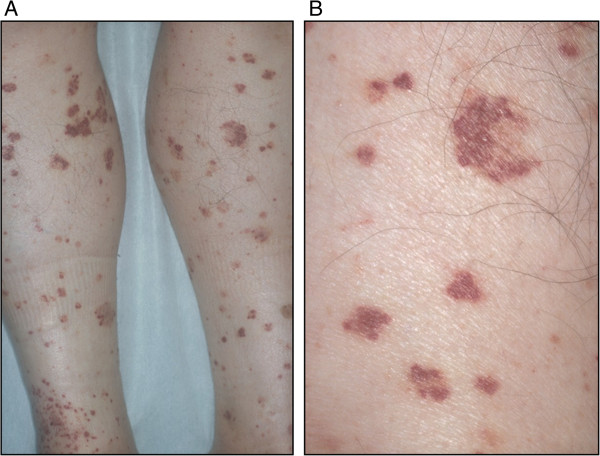
Hemorragias petequiais são uma das várias apresentações clínicas na neutropenia congénita grave (SCN)
Imagem : “Purpura” por Oshikata C, Tsurikisawa N, Takigawa M, Omori T, Sugano S, Tsuburai T, Mitomi H, Takemura T, Akiyama K. Licença: CC BY 2.0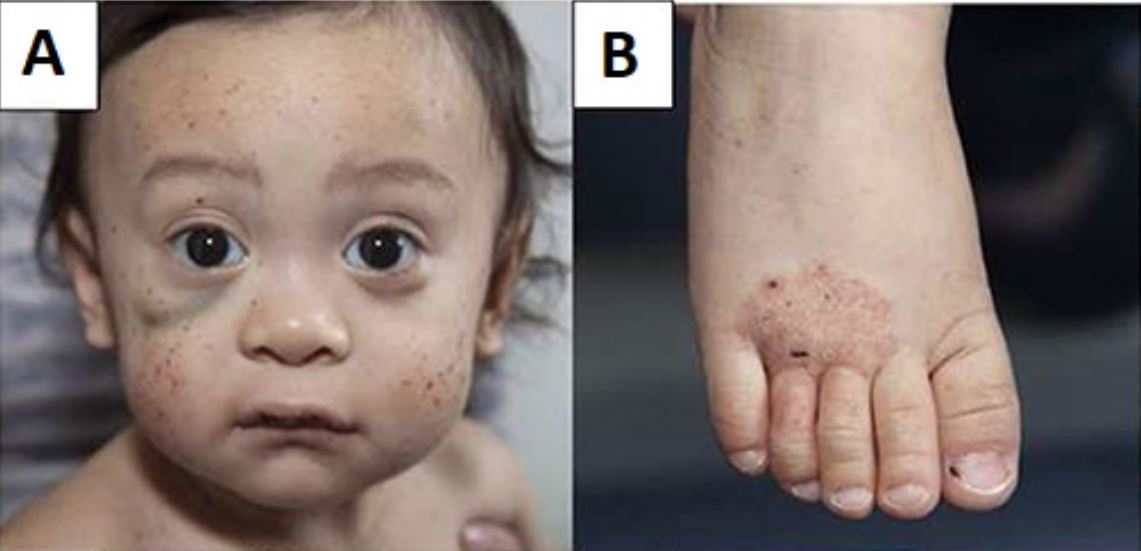
Menino com síndrome de Wiskott-Aldrich que apresenta múltiplas petéquias faciais e hematoma sob o olho direito (A) e eczema do pé (B)
Imagem : “Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome petechiae, hematoma and eczema” por Michael H. Albert and Alexandra F. Freeman. Licença: CC BY 4.0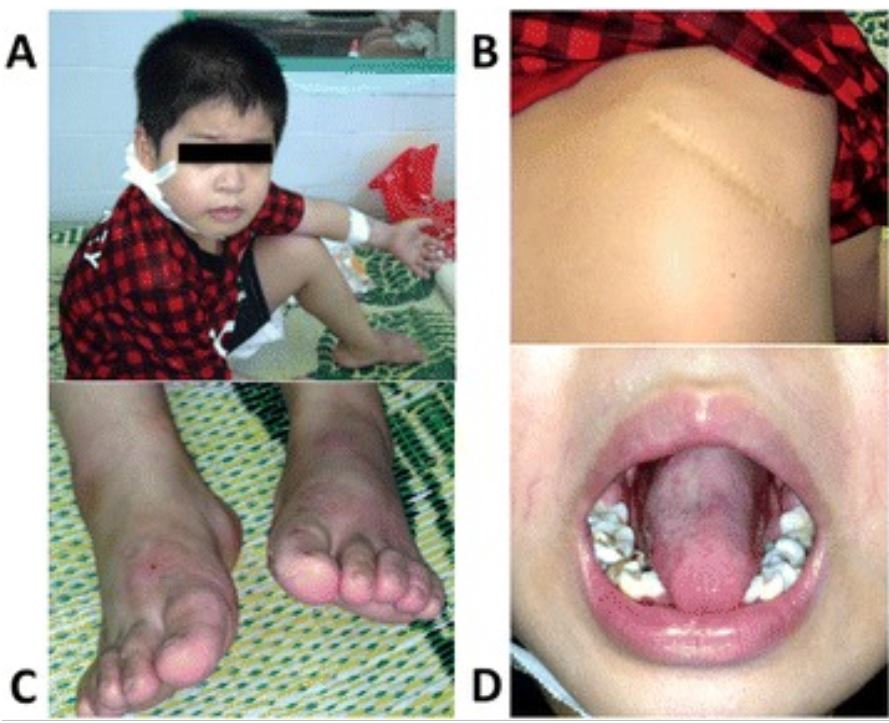
Neutropenia congénita grave causada pela mutação do gene ELANE. As imagens mostram uma série de lesões causadas por infeção.
A: Abcesso cutâneo atrás da orelha direita
B: Pneumonia grave com necessidade de lobectomia pulmonar
C: Infeção fúngica
D: úlcera oral
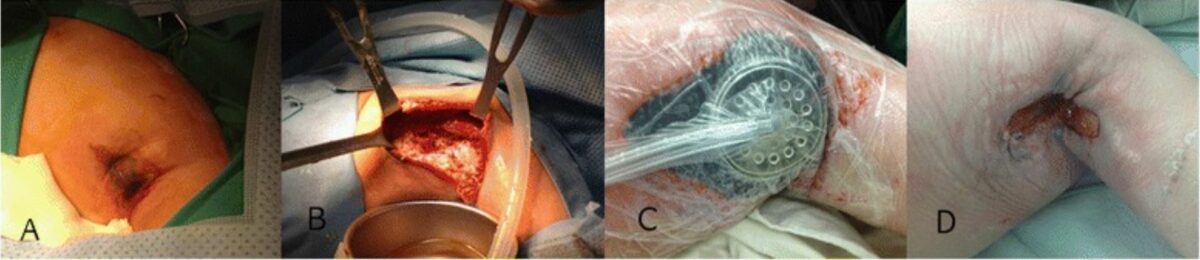
A neutropenia cíclica com uma nova mutação genética apresenta uma infeção necrotizante dos tecidos moles e sépsis grave. Tratamento bem sucedido da ferida axilar:
A: A lesão inicial na axila era de pele edemaciada com alteração azulada no centro.
B: Notar a necrose maciça da área subcutânea, músculos e fáscia com secreção contaminada encontrada na cirurgia inicial.
C: Visualização após tratamento de feridas por pressão negativa
D: Após 1 mês, o tecido de granulação cresceu rapidamente para permitir a reparação primária.

Como calcular ANC com um exemplo
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0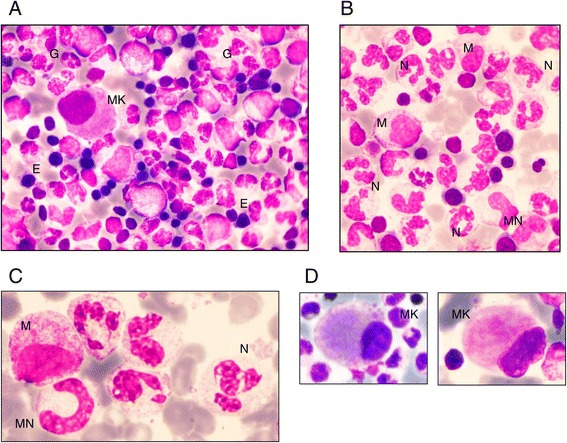
Morfologia da medula óssea em doentescom neutropenia congénita G6PC3 :
A: Morfologia típica da medula óssea global: celularidade rica com granulopoiese predominante (G), alguns eritroblastos (E) e 1 micromegacariócito (MK)
B: Granulopoiese predominante com alguns mielócitos (M), muito poucos metamielócitos (MN) e um alto número de neutrófilos maduros (N)
C: Detalhes dos neutrófilos: aspeto hipersegmentado com abertura fina entre os lobos e aglomerados de cromatina
D: Exemplos de micromegacariócitos
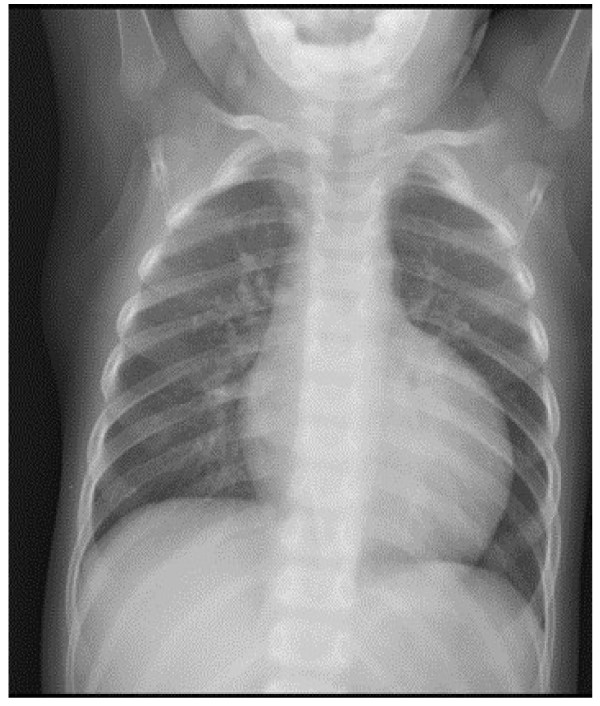
Radiografia de tórax que mostra cardiomegalia grave em doente do sexo masculino com neutropenia e atraso de crescimento
Imagem : “Cardiomyopathy in a male patient with neutropenia and growth delay” por Folsi, V., et al. Licença: CC BY 4.0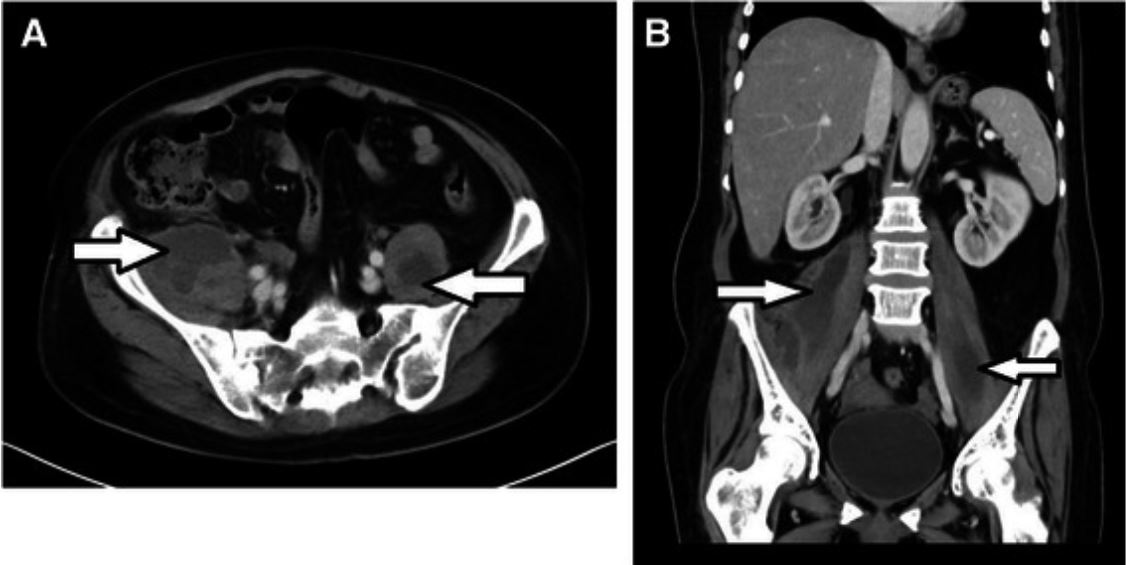
Abcessos primários bilaterais do psoas por Staphylococcus aureus resistente à meticilina em doente neutropénico.
Corte axial (A) e coronal (B) TC do abdómen e pelve com contraste IV que mostra abcessos bilaterais do músculo psoas (setas)
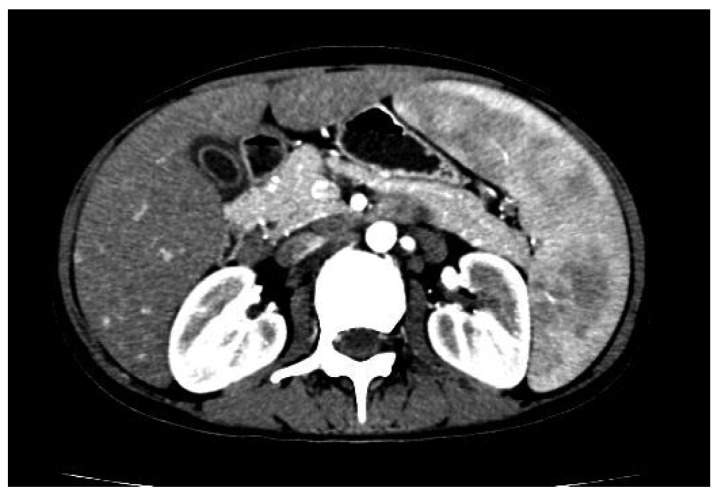
A síndrome de Felty (SF) é uma subcategoria específica da artrite reumatoide (AR) caracterizada pela tríade de AR, doença extra-articular grave e neutropenia inexplicada.
A imagem mostra uma TC abdominal de um doente com SF demonstrando esplenomegalia com atenuação heterogénea devido ao tempo de contraste angiográfico e múltiplos gânglios linfáticos aumentados distribuídos ao longo do espaço retroperitoneal, bolsa omental, raiz do mesentério e hilo hepático circundante
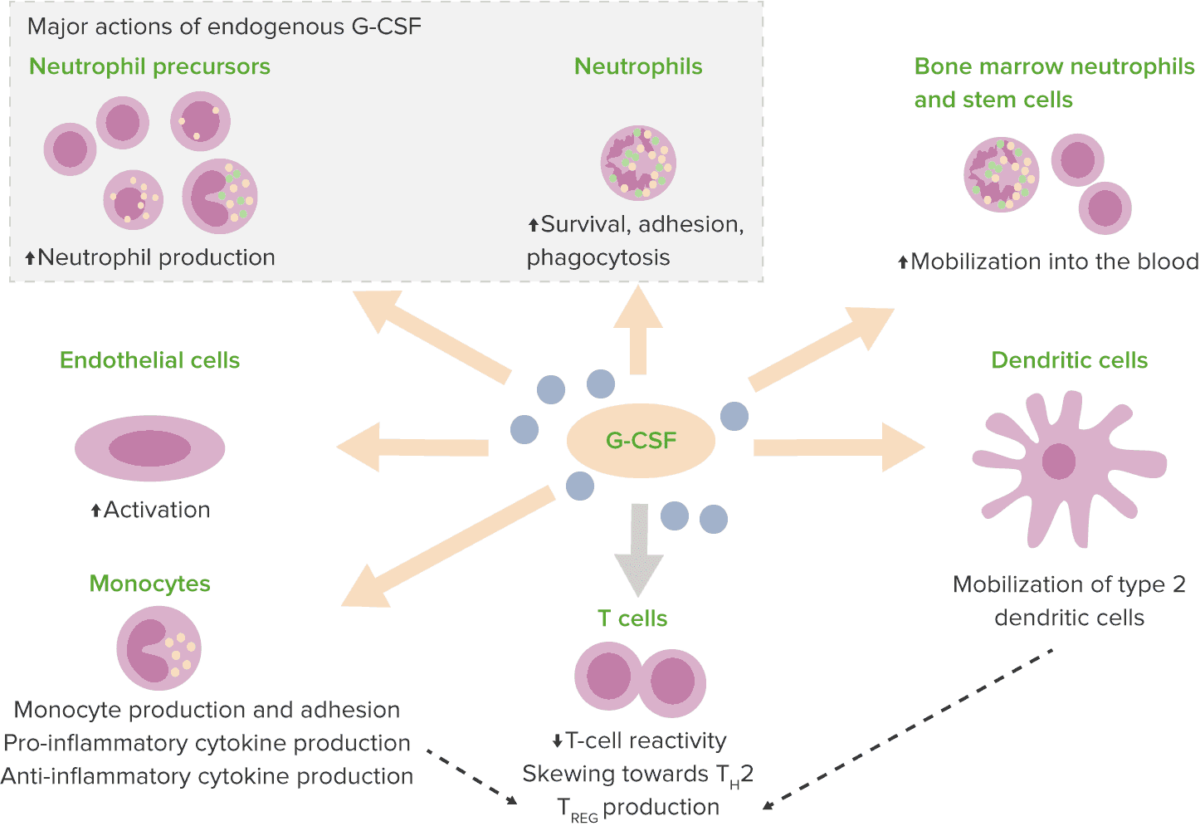
Efeitos do fator estimulador de colónias de granulócitos (G-CSF, pela sigla em inglês)
Th2: célula auxiliar T tipo 2
T REG : células T reguladoras