Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or "walking" pneumonia. Mycoplasma é uma espécie de bactéria pleomórfica que não possui parede celular, o que as torna difíceis de erradicar com antibióticos convencionais (nomeadamente penicilinas e outros antibióticos beta-lactâmicos que possuem como alvo a síntese da parede celular) e de difícil demonstração utilizando a técnica de Gram. As bactérias da espécie Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or "walking" pneumonia. Mycoplasma exprimem como alvo o epitélio respiratório e urogenital. A espécie clinicamente mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome relevante é Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Short filamentous organism of the genus mycoplasma, which binds firmly to the cells of the respiratory epithelium. It is one of the etiologic agents of non-viral primary atypical pneumonia in man. Mycoplasma (M. pneumoniae), agente etiológico da pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia atípica ou “ambulante”. A terapêutica mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome eficaz baseia-se na antibioterapia com macrólidos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Aparência em “ovo estrelado” das colónias de Mycoplasma hominis
Imagem: “Gram-negative Mycoplasma hominis” por CDC/Dr. E. Arum. Licença: Public domain.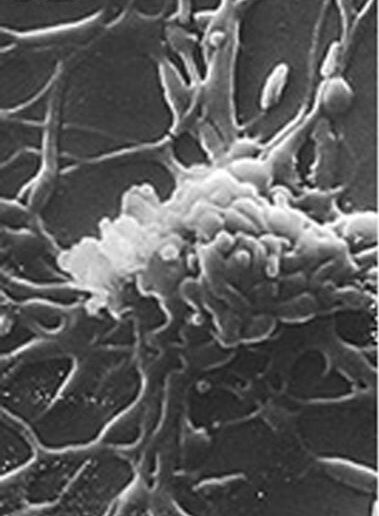
Imagem de microscopia eletrónica de varredura de M. pneumoniae, uma bactéria pleomórfica sem parede celular, observada na sua forma filamentosa
Imagem: “Mycoplasma pneumoniae” por Rottem et al. Licença: CC BY 3.0, editado por Lecturio.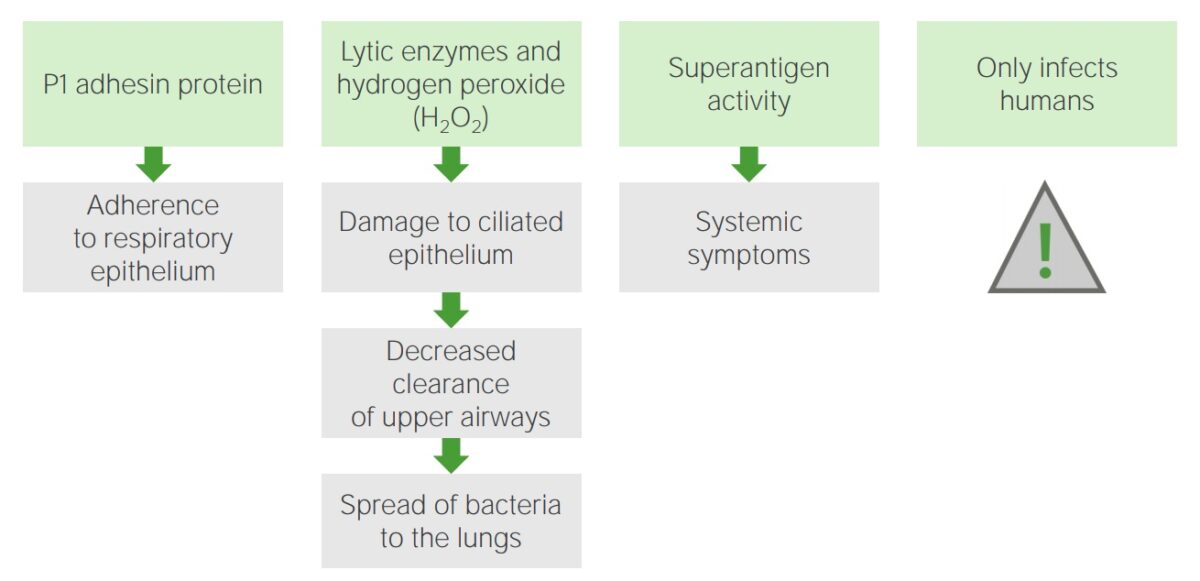
Mecanismos de patogénese: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0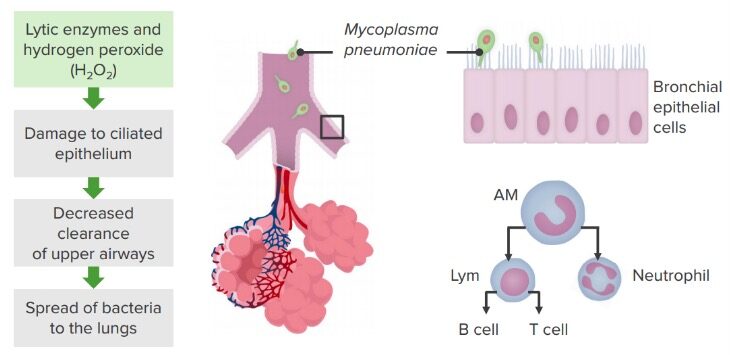
Mecanismos de patogénese: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0A patologia causada pela bactéria M. pneumoniae é variada; no entanto, o diagnóstico e o tratamento não se alteram:
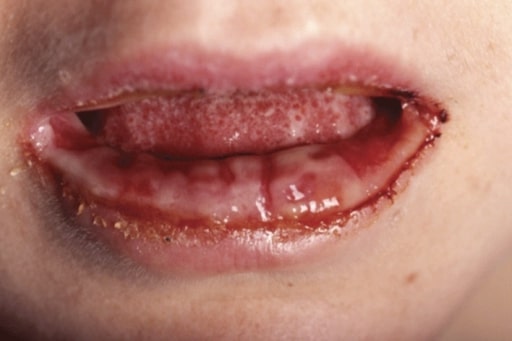
Mucosite associada a M. pneumoniae (MPAM): As lesões orais erosivas são limitadas à mucosa na forma de MPAM, numa mulher de 24 anos.
Imagem: “MPAM” por Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Erasmus MC-Sophia Children’s Hospital, University Medical Center Rotterdam, Netherlands. Licença: CC BY 4.0.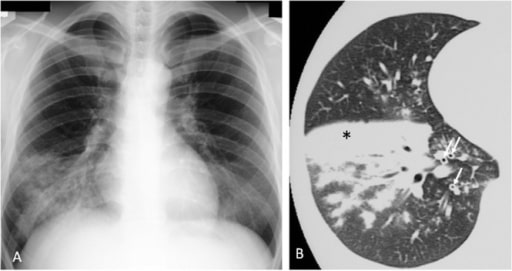
Pneumonia por Mycoplasma pneumoniae num humano. A: Radiografia do tórax com infiltrados no lobo inferior direito.
B: consolidação (∗) e espessamento dos feixes broncovasculares (↑) na tomografia computadorizada (TC)
| Características | Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia por Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or “walking” pneumonia. Mycoplasma | Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia pneumocócica |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia | Atípica (intersticial) | Típica (alveolar) |
| Precedida por faringite | Comum | Nunca |
| Início | Gradual | Súbito com arrepios |
| Febre | Baixa | Alta |
| Tosse | Não produtiva, paroxística | Produtiva |
| Dor torácica pleurítica | Ausente | Presente |
| Leucocitose | Ausente | Presente |
| Idade de maior incidência | Adultos jovens <<30 anos | Adultos mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome velhos |
| Complicações | Otite média, eritema multiforme, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica, miocardite, pericardite, miringite bolhosa | Bacteriemia, meningite, otite média |