Os defeitos do tubo neural ( NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects, pela sigla em inglês) são o segundo tipo mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comum de defeitos congénitos ao nascimento. Os defeitos do tubo neural podem variar de assintomáticos (NTD fechado) a malformações muito graves da coluna ou do cérebro (NTD aberto). Os defeitos do tubo neural são causados pela falha no encerramento adequado do tubo neural durante a 3ª e 4ª semana de desenvolvimento embriológico. O tipo mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comum de NTD aberto é o meningomielocelo, que envolve tanto as meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy como o tecido neural. As etiologias dos NTD são multifatoriais, variando desde a nutrição materna até aos determinantes genéticos. É comum o diagnóstico pré-natal por ecografia e níveis de α-fetoproteína materna. O tratamento dos NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects abertos é principalmente cirúrgico.
Last updated: Dec 17, 2025
Um defeito do tubo neural (NTD, pela sigla em inglês; disrafismo espinhal) é um defeito congénito no revestimento do sistema nervoso central, resultante de uma falha no encerramento espontâneo do tubo neural durante a 3ª ou 4ª semana de desenvolvimento embrionário.
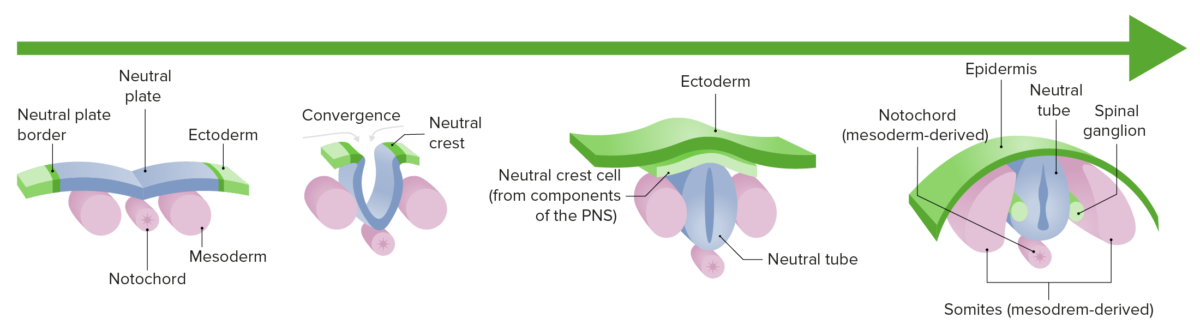
Neurulação: diferenciação e crescimento da placa neural no tubo neural durante o primeiro trimestre de gestação.
SNP: Sistema nervoso periférico
A maioria dos NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects são descobertos durante o rastreio pré-natal. Os NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects abertos são evidentes ao nascimento, mas os NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects fechados podem ter apresentações mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome subtis.
| Nome | Descrição | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Mielomeningocelo | Herniação meníngea e da medula espinhal | Quanto
mais
MAIS
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome alta a lesão na coluna,
mais
MAIS
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome grave são os sintomas:
|
| Meningocelo | Herniação meníngea sem envolvimento da medula espinhal |
|
| Encefalocelo | Meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy ± protrusão de tecido cerebral do defeito craniano |
|
| Anencefalia | Ausência da componente principal do cérebro e do crânio. |
|
| Espinha bífida oculta | Defeito de fusão do corpo vertebral na linha média sem protrusão da dura-máter ou tecido neural |
|
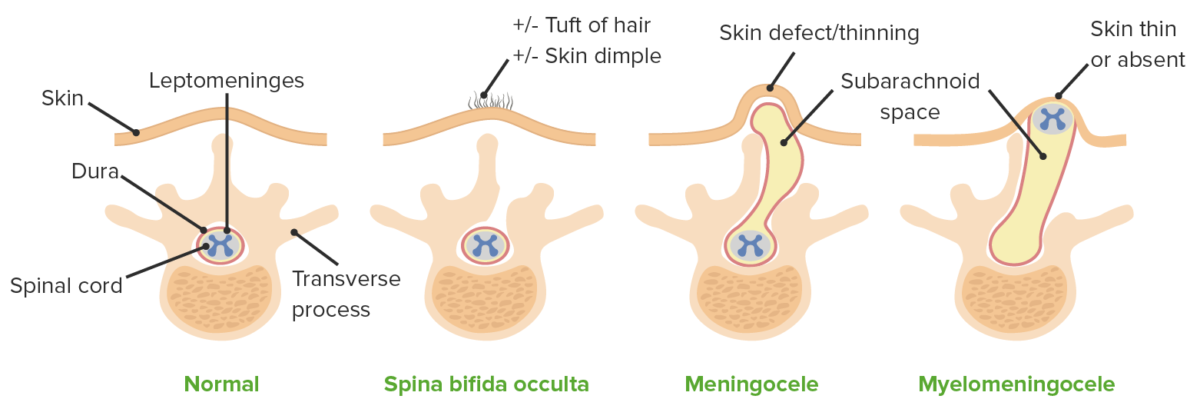
Tipos de NTD e os seus respetivos defeitos
Imagem por Lecturio.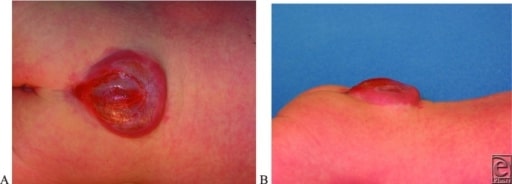
A e B: Fotografias posterior e lateral que demonstram um mielomeningocelo lombossacral
Imagem : “Lumbosacral Myelomeningocele” por US National Library of Medicine. Licença: CC BY 2.0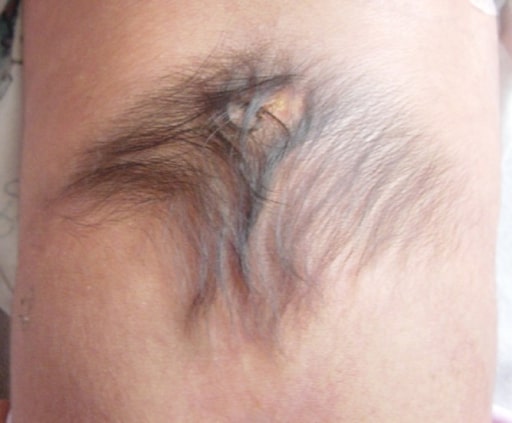
Tufo de pelo na parte inferior das costas num doente com espinha bífida
Imagem : “Hypertrichiosis” por Department of Pediatric Surgery, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi. Licença: CC BY 3.0