Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology son parásitos intracelulares obligados infecciosos compuestos por ácidos nucleicos rodeados por una cápside proteica. Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology pueden ser desnudos (sin envoltura) o con envoltura. La clasificación de los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology es compleja y se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchos factores, como el tipo y la estructura del nucleoide y de la cápside, la presencia de una envoltura, el ciclo de replicación y la variedad de hospederos. El ciclo de replicación difiere entre los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology que infectan bacterias (bacteriófagos) y los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology que infectan células eucariotas. Los LOS Neisseria bacteriófagos tienen un ciclo de replicación lítico o lisogénico, mientras que los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology eucariotas tienen un proceso de replicación definido de 6 pasos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology son parásitos intracelulares obligados, infecciosos, compuestos por ácidos nucleicos (ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) o ácido ribonucleico (ARN)) rodeado por una cápsula proteica; a veces, los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology también están rodeados por una envoltura derivada de las membranas de la célula huésped.
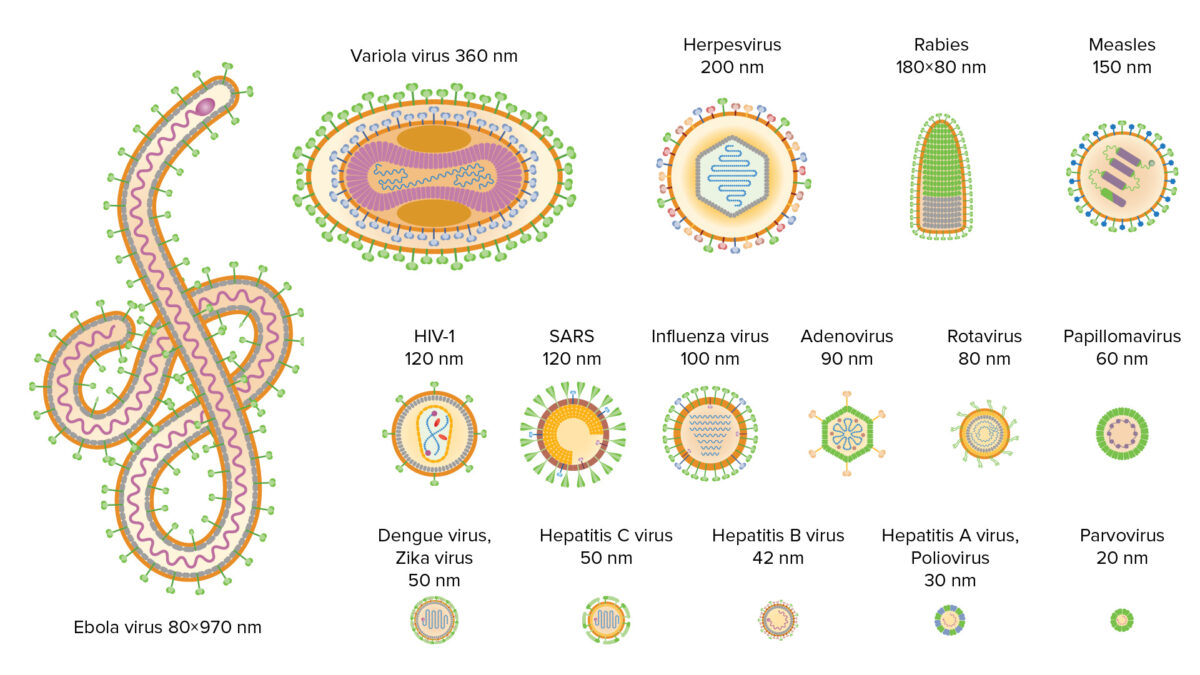
Variedad de virus existentes, incluyendo el tamaño y la morfología
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La estructura básica consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
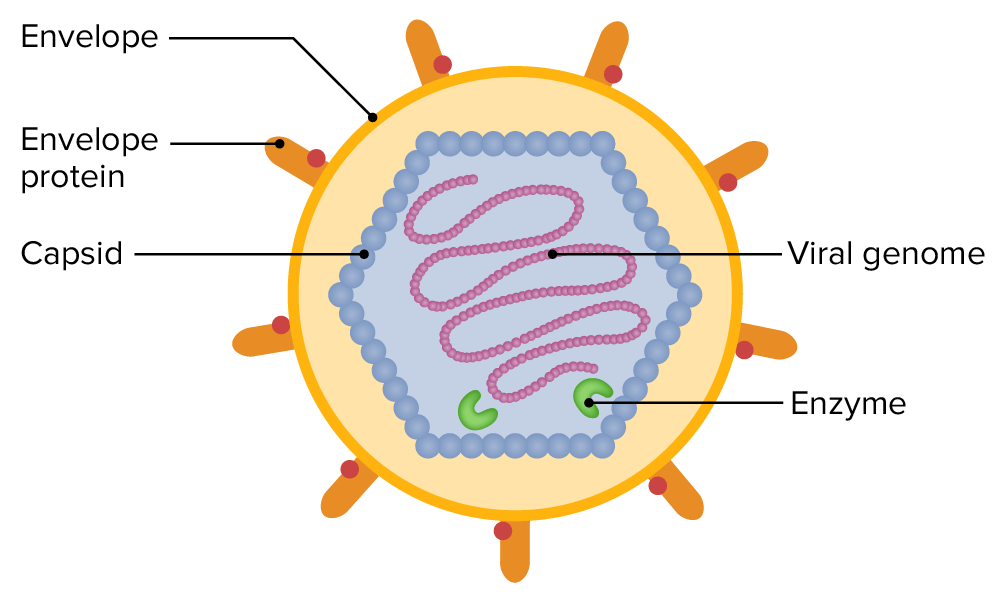
Anatomy of a virus
Image by Lecturio.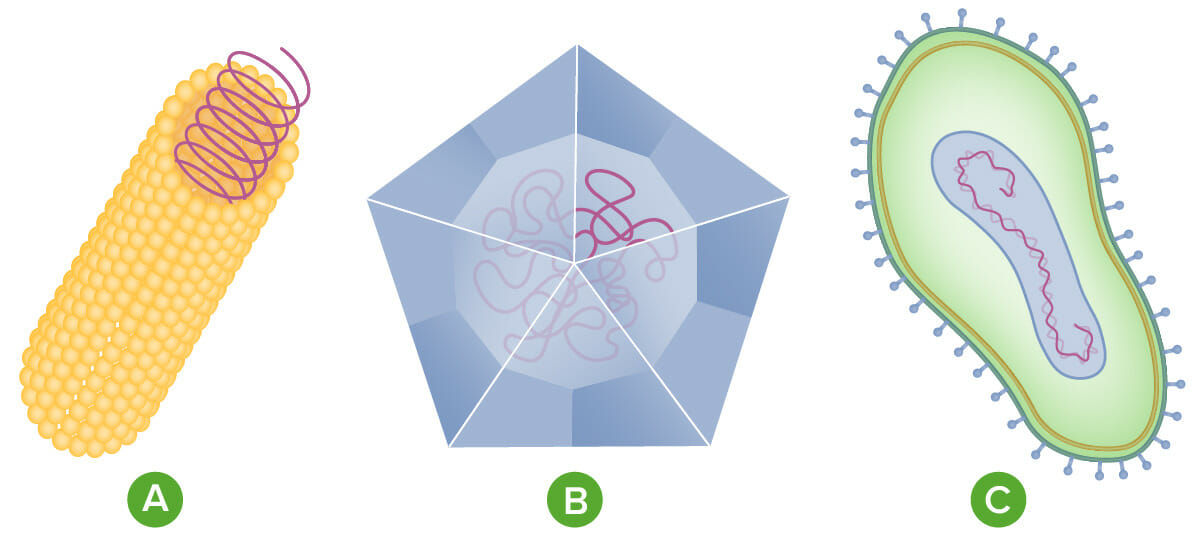
La cápside viral puede ser (a) helicoidal, (b) poliédrica, o (c) tener una forma compleja
Imagen por Lecturio.
Identificación de los virus de ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma de ARN pueden caracterizarse además, por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son positivos si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
Existen múltiples esquemas de categorización para los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology, basados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum características físicas y estrategias de replicación.
| Clasificación por: | Tipos |
|---|---|
| Tipo y estructura del nucleoide |
|
| Estructura de la cápside |
|
| Presencia de envoltura |
|
| Ciclo de replicación (para los LOS Neisseria bacteriófagos) |
|
| Otro |
|
Es importante diferenciar entre la replicación de los LOS Neisseria bacteriófagos ( virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology que infectan bacterias) y los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology eucariotas ( virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology que infectan células eucariotas).
Hay 2 vías de replicación una vez que el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology está dentro de la célula huésped bacteriana:
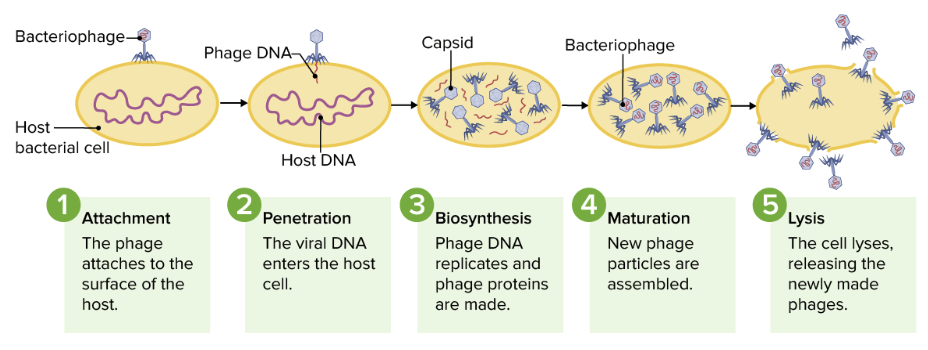
Representación del ciclo lítico
Imagen por Lecturio.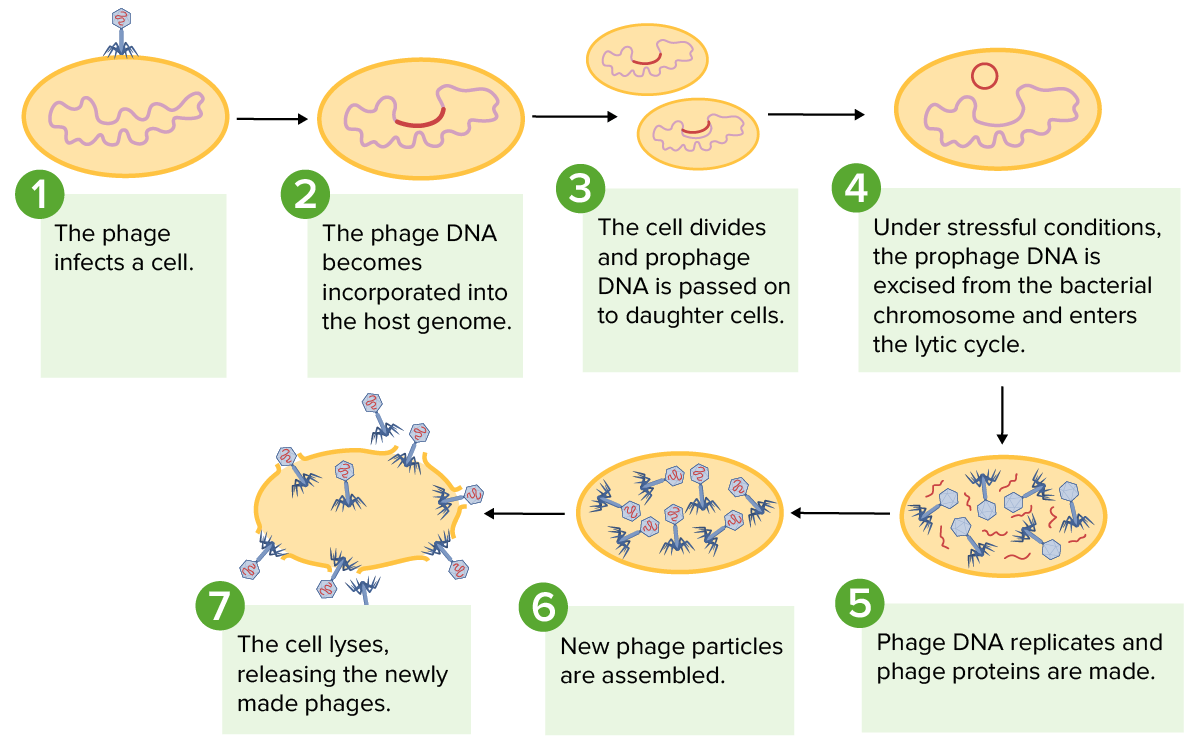
Representación de los ciclos lisogénico y lítico de los bacteriófagos: Durante el ciclo lisogénico, el ADN del bacteriófago se incorpora al genoma del huésped, que puede pasar a las células hijas. Los factores de estrés de una célula pueden provocar la entrada en el ciclo lítico, donde el ADN del fago se replica, forma nuevas partículas de fago y provoca la lisis de la célula.
Imagen por Lecturio.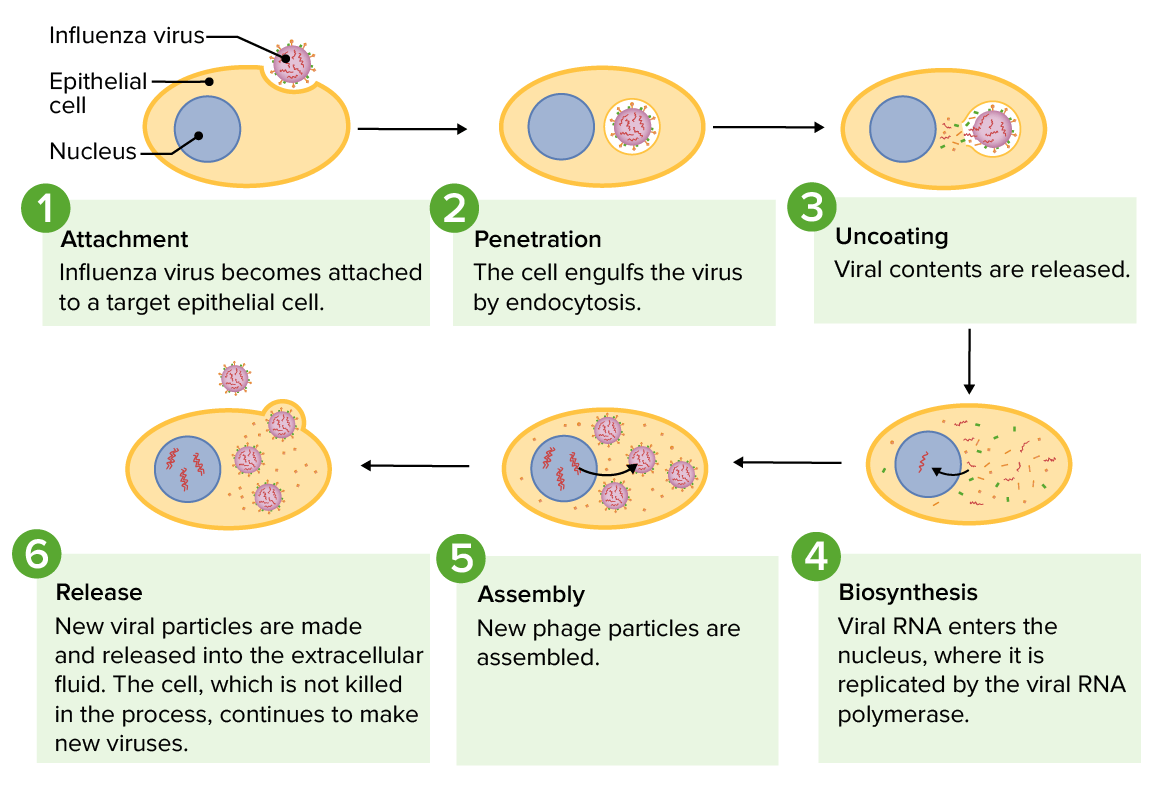
El ciclo de replicación del virus de la gripe, desde la infección de una célula huésped hasta la liberación de virus recién formados
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology han desarrollado muchos procesos para aumentar su diversidad genética:
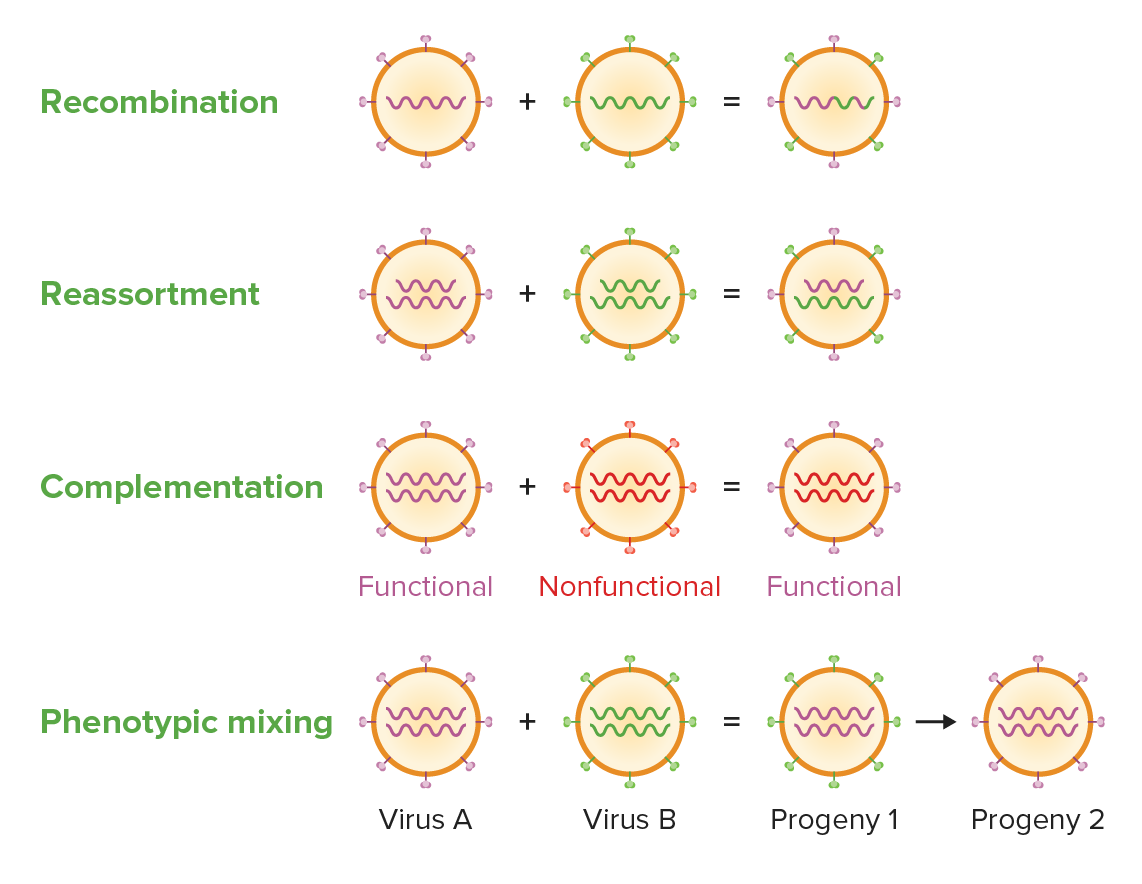
Los virus han desarrollado diversas estrategias para aumentar la diversidad genética, entre ellas la recombinación (el intercambio de genes entre 2 cromosomas por cruce en regiones homólogas), el reordenamiento (intercambio de segmentos de cromosomas), la complementación (el intercambio de material genético de un virus funcional con otro no funcional para convertir este último en funcional) y la mezcla fenotípica (mezcla de 2 genomas virales una célula huésped infectada simultáneamente dando lugar a una progenie con genomas mezclados).
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0