El traumatismo craneoencefálico se produce cuando se dirigen fuerzas externas al AL Amyloidosis cráneo y las estructuras cerebrales, lo que provoca daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cráneo, el cerebro y las estructuras intracraneales. Los LOS Neisseria traumatismos craneoencefálicos se pueden clasificar como abiertos (penetrantes) o cerrados (contusos) y primarios (del traumatismo inicial) o secundarios (traumatismo craneoencefálico indirecto) y varían de leves a graves y potencialmente mortales. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son leves, pero la presentación puede variar desde una conmoción cerebral leve hasta un estado de coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma, según la gravedad de la lesión. El tratamiento abarca desde la observación hasta la monitorización en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuidados intensivos y las intervenciones neuroquirúrgicas. El pronóstico es bueno para las lesiones leves, pero los LOS Neisseria traumatismos graves pueden provocar la muerte o daños permanentes.
Last updated: Jan 26, 2026
El traumatismo craneoencefálico es una lesión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cráneo, el cerebro y/o las estructuras intracraneales.
| Características | Respuesta | Puntuación |
|---|---|---|
| Apertura ocular | Apertura espontánea | 4 |
| Apertura órdenes verbales | 3 | |
| Apertura al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation | 2 | |
| Sin apertura | 1 | |
| Respuesta verbal | Orientado y apropiado | 5 |
| Desorientado pero habla | 4 | |
| Palabras sin sentido | 3 | |
| Quejidos | 2 | |
| Silencio | 1 | |
| Respuesta motora | Sigue comandos | 6 |
| Localiza el dolor Dolor Inflammation | 5 | |
| Se retira del dolor Dolor Inflammation | 4 | |
| Postura flexora | 3 | |
| Postura extensora | 2 | |
| Flacidez | 1 |
| Criterios | Leve | Moderado | Severo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imagenología estructural | Normal | Normal o anormal | Normal o anormal |
| Pérdida del conocimiento (LOC) | 0-30 minutos | > 30 minutos y < 24 horas | > 24 horas |
| Alteración de la conciencia/estado mental (AOC) | Por un momento, hasta 24 horas | > 24 horas significa severidad basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otros criterios | |
| Amnesia postraumática ( PTA PTA A peritonsillar abscess (PTA), also called quinsy, is a collection of pus between the capsule of the palatine tonsil and the pharyngeal muscles. A pta is usually a complication of acute tonsillitis, an infection caused by group a streptococci. Patients often present with a sore throat, trismus, and a muffled voice. Peritonsillar Abscess) | 0–1 día | > 1 y < 7 días | > 7 días |
| GCS GCS A scale that assesses the response to stimuli in patients with craniocerebral injuries. The parameters are eye opening, motor response, and verbal response. Coma | 13–15 | 9–12 | < 9 |
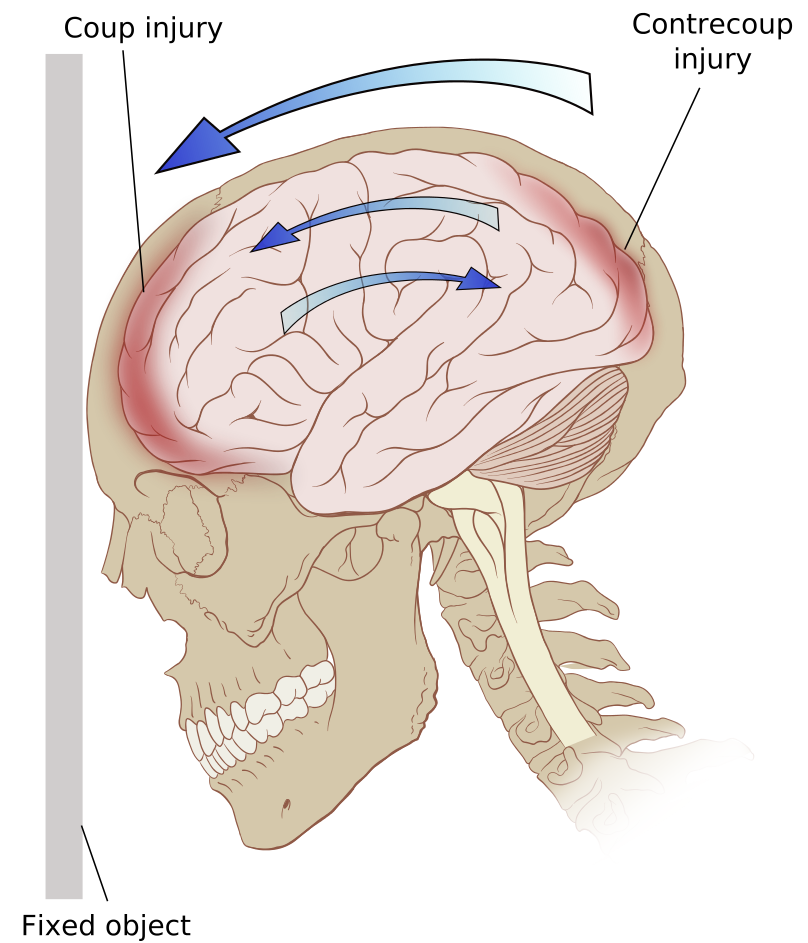
Traumatismo craneoencefálico por golpe y contragolpe
Imagen: “Contrecoup” por Patrick J. Lynch. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Fracturas lineales:
Fracturas conminutas:
Fracturas deprimidas:
Fracturas elevadas:
Fracturas de cráneo basilar:
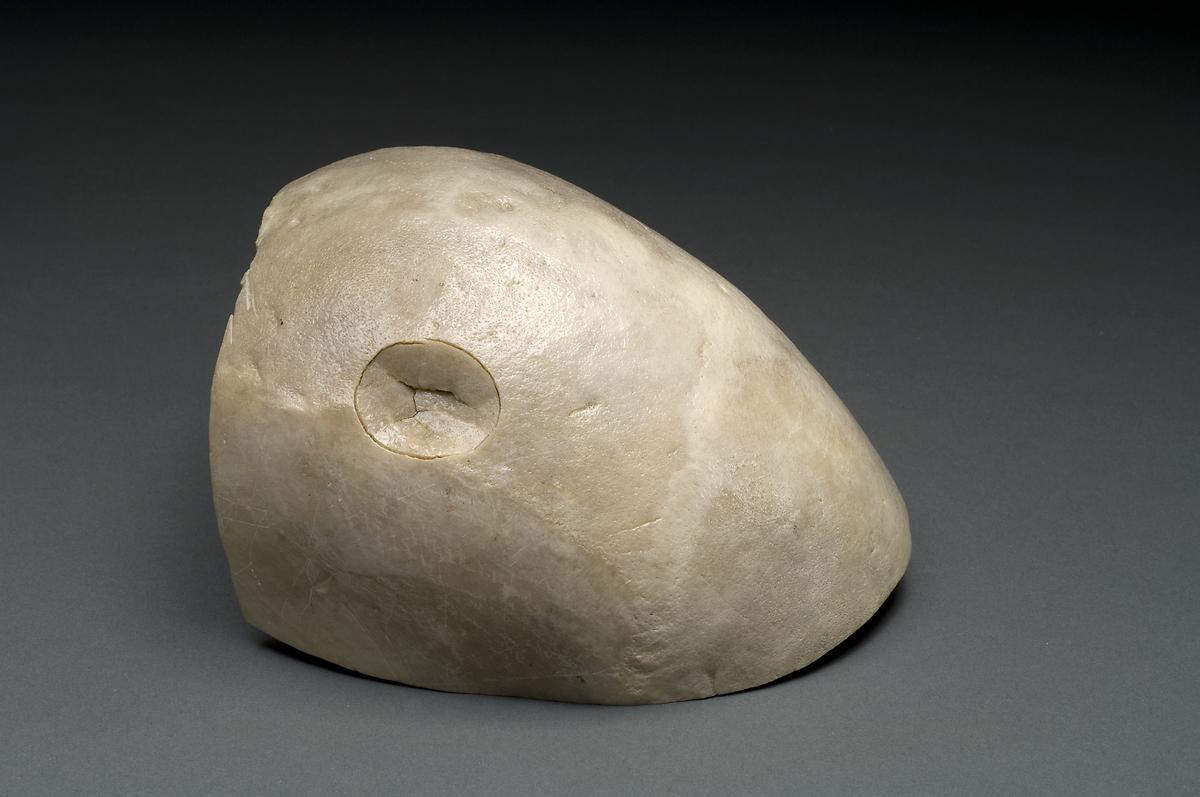

Fractura de cráneo deprimida: cráneo que muestra un traumatismo por un martillo de bola
Imagen : “Depressed skull fracture” por National Institutes of Health, Health & Human Services. Licencia: Dominio Público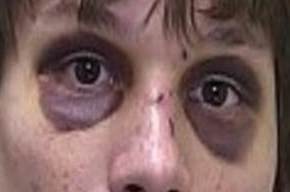
Equimosis periorbitaria bilateral: manifestación de la fractura basilar del cráneo
Imagen : “Bilateral periorbital ecchymosis (raccoon eyes)” por Marion County Sheriff’s Office.Licencia: Dominio PúblicoContusiones cerebrales focales:
Hemorragia extraaxial:
El CCHR se utiliza para determinar la necesidad de TC en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes adultos del departamento de emergencias con lesiones menores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cabeza. Su sensibilidad es cercana al AL Amyloidosis 100 % para identificar traumatismos cerebrales clínicamente significativos (i.e., traumatismos que requieren intervención neuroquirúrgica).
Requisitos:
Criterios de inclusión:
Criterios de exclusión:
Factores de alto riesgo:
Factores de riesgo intermedio:
Interpretación:
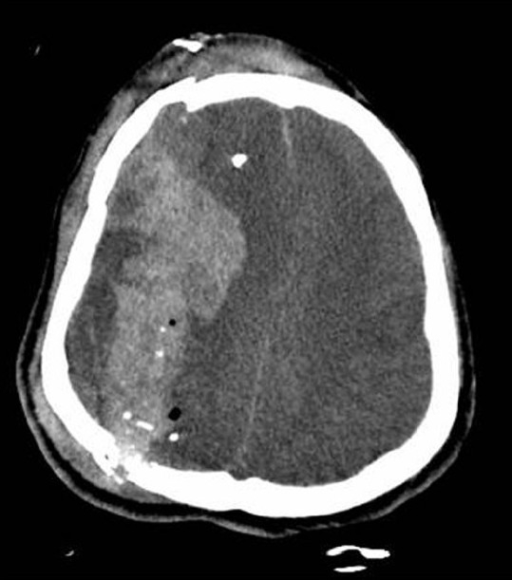
Imagen de TC de las fracturas y fragmentación del cráneo de un paciente con hemorragia intracerebral aguda y desplazamiento de la línea media
Imagen: “Traumatic brain injury complicated by environmental hyperthermia” por Hermstad E, Adams B. Licencia: CC BY 2.0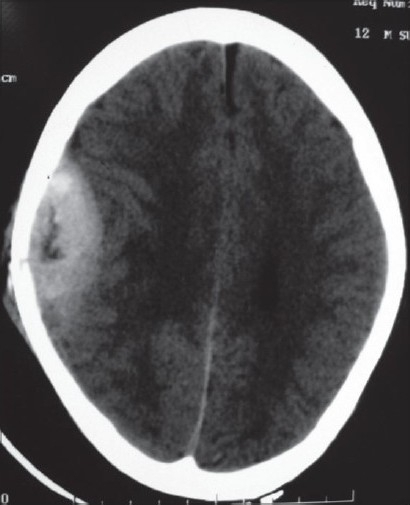
TC de un hematoma epidural parietal derecho
Imagen: “Pathological intracranial extradural hematoma in a 10-year-old child” por Bhat AR, Jain AK, Kirmani AR, Nizami F. Licencia: CC BY 2.0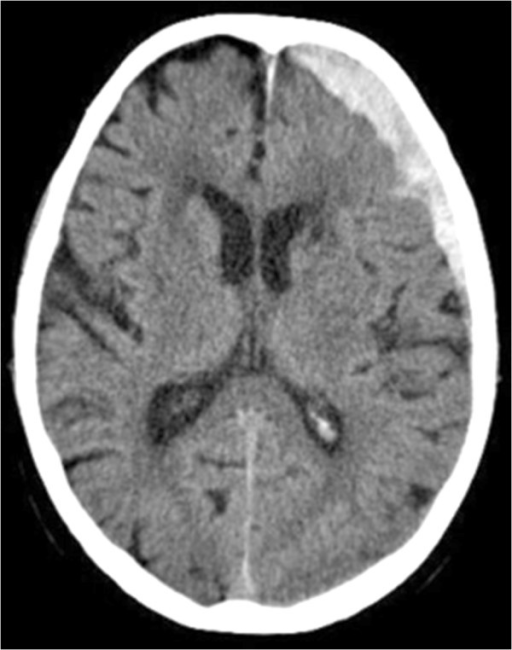
TC que demuestra el hematoma subdural fronto-temporal sobre el hemisferio izquierdo
Imagen: “Lactococcus garvieae endocarditis presenting with subdural haematoma” por Rasmussen M, Björk Werner J, Dolk M, Christensson B. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Tratamiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuidados intensivos (generalmente requerido):
Control de la PIC:
Cirugía: