Una cantidad anormal de lípidos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre se denomina dislipidemia, que incluye niveles anormales de colesterol, triglicéridos y/o lipoproteínas. La dislipidemia puede ser primaria (familiar) o secundaria (adquirida). Tanto las causas primarias como las secundarias pueden conducir al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de una enfermedad cardiovascular prematura (aterosclerosis). Las causas familiares se clasifican según el sistema de Fredrickson, que analiza la patología y los LOS Neisseria lípidos que se encuentran elevados. Ciertos tipos no aumentan el riesgo de enfermedad aterosclerótica prematura, pero aún afectan el riesgo cardíaco general y la posibilidad de eventos cardiovasculares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el futuro. El tamizaje, diagnóstico precoz y control y tratamiento estrictos son las claves para la prevención de eventos cardiovasculares.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Dislipidemia: cantidades anormales de lípidos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sangre
Las causas de la dislipidemia se pueden dividir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum causas primarias (familiares) y secundarias (adquiridas).
Causas primarias:
Causas secundarias (adquiridas):
| Tipo | Condición, modo de herencia (autosómica dominante ( AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives), autosómica recesiva ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation)), anomalía lipídica | Patología | Hallazgos |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Hiperquilomicronemia familiar (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Quilomicrones elevados |
Deficiencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lipoproteinlipasa o apolipoproteína C-II (ApoC-II) |
|
| IIa | Hipercolesterolemia familiar (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) LDL elevado |
Mutación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proproteína subtilisina/kexina convertasa tipo 9, receptores LDL defectuosos o apolipoproteína B-100 (ApoB-100) |
|
| IIb | Hipercolesterolemia familiar combinada (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) VLDL y LDL elevados |
|
|
| III | Hiperlipoproteinemia familiar (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Restos de VLDL y quilomicrones |
Apolipoproteína E (ApoE) defectuosa |
|
| IV | Hipertrigliceridemia familiar (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) VLDL elevado |
Producción excesiva de VLDL por el hígado | |
| V | Hiperlipidemia mixta (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Quilomicrones elevados y VLDL |
Apolipoproteína A5 (ApoA5) defectuosa |
|
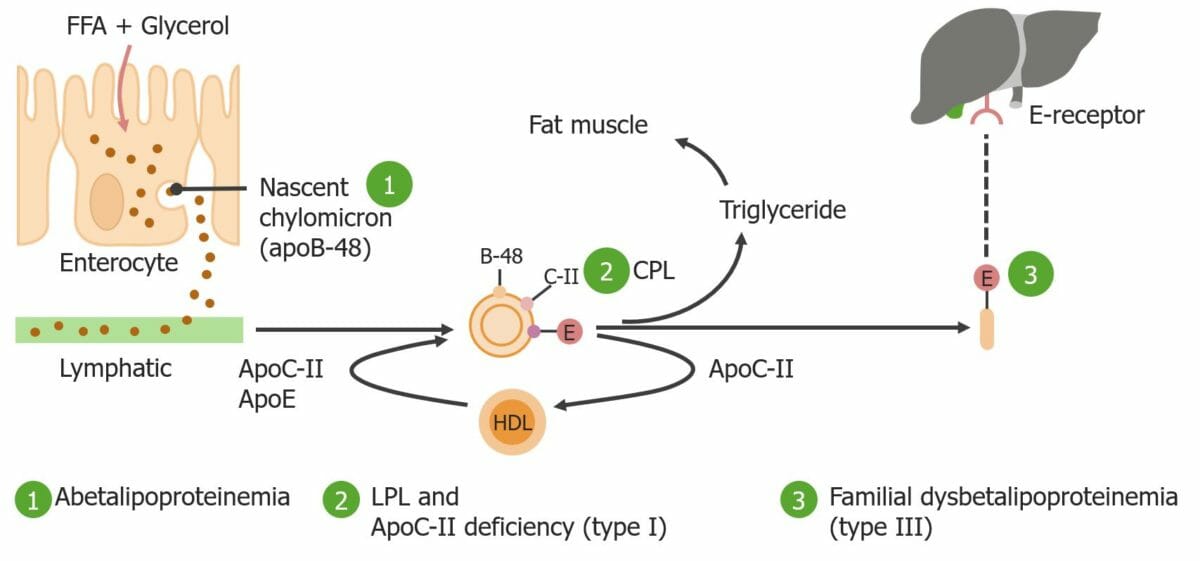
Representación esquemática de los tipos I y III según la clasificación de Fredrickson
FFA: ácido graso libre
ApoB-48: apolipoproteína-B-48
ApoC-II: apolipoproteína C-II
ApoE: apolipoproteína E
LPL: lipoproteinlipasa
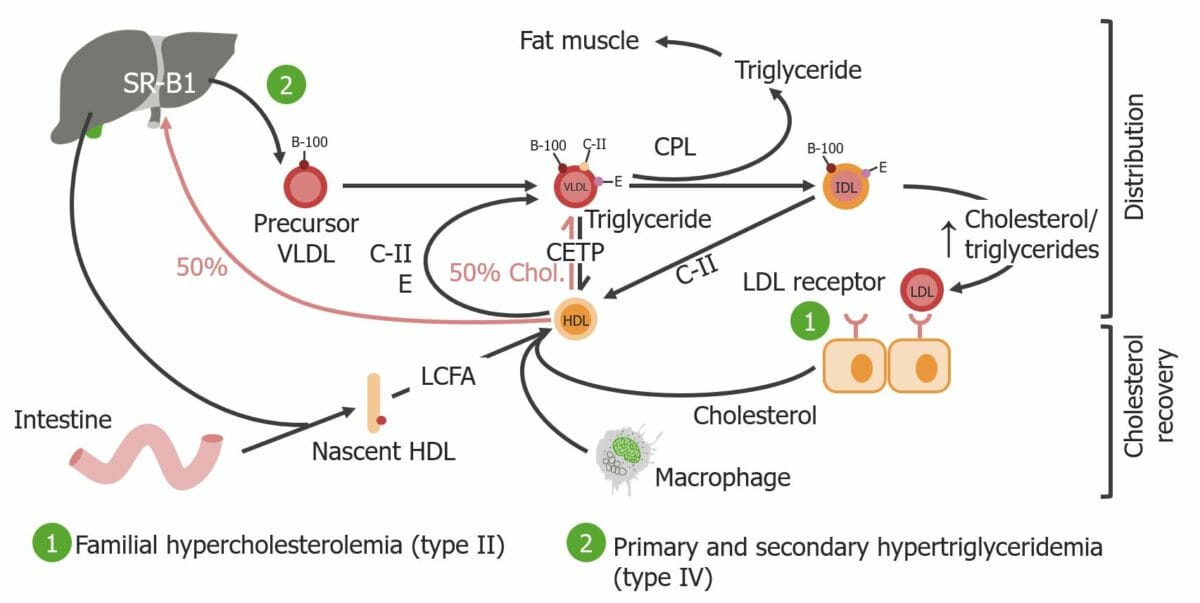
Representación esquemática de los tipos II y IV según la clasificación de Fredrickson
Imagen por Lecturio.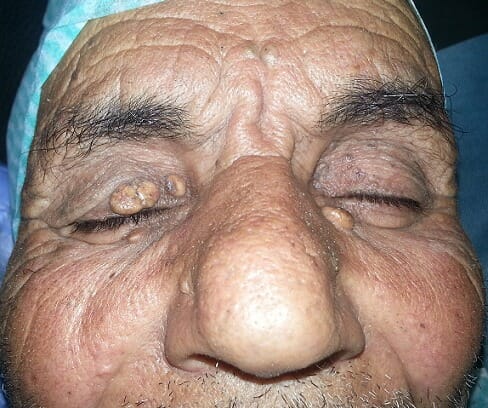
Un paciente de edad avanzada con depósitos amarillos alrededor de los párpados, muy probablemente indicativos de xantelasma
Imagen: “Les différentes lésions jaunâtres au niveau des deux paupières en rapport avec le xanthélasma” por Elghazi, T. y Hafidi, Z. Licencia: CC BY 2.0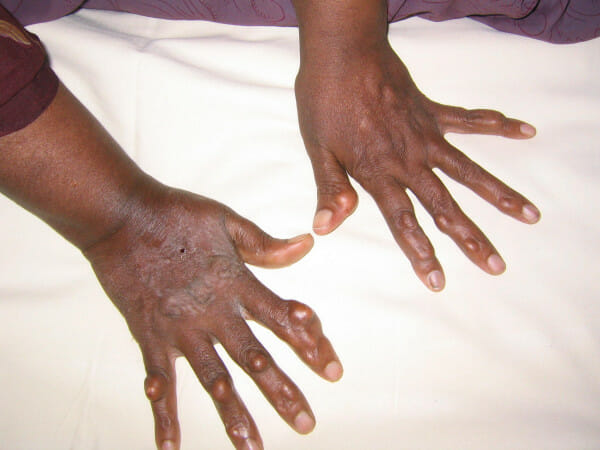
Múltiples xantomas en manos
Imagen: “Xanthomas” por Kumar, AA et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0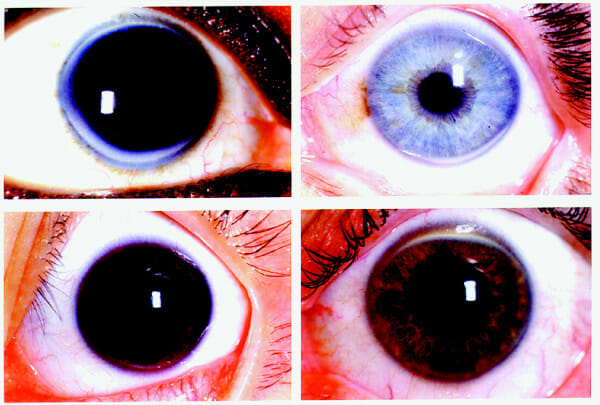
Los depósitos tienden a comenzar a las 6 y las 12 en punto y continúan hasta volverse completamente circunferenciales.
Imagen: “Corneal arcus” por Zech LA y Hoeg JM Licencia: CC BY 2.0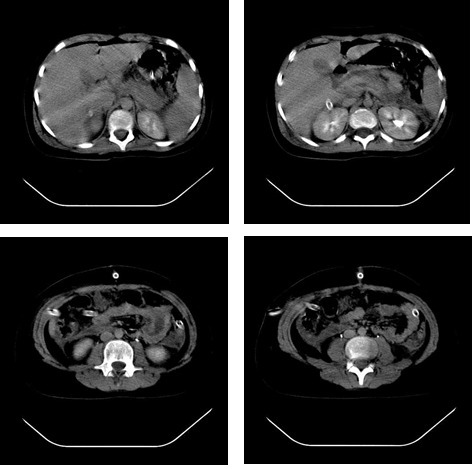
TC de pancreatitis aguda secundaria a hiperlipidemia en una niña de 11 años: La gammagrafía muestra un páncreas muy dimensionado, sobre todo en la cabeza, con estructura heterogénea y colecciones peripancreáticas.
Imagen: “Acute pancreatitis secondary to hyperlipidemia in an 11-year-old girl” por Department of Pediatric Surgery, “Grigore Alexandrescu” Clinical Emergency Hospital for Children, Bucharest. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.| Lípido | Valor normal |
|---|---|
| Colesterol total | < 200 mg/dL |
| Colesterol HDL | > 60 mg/dL |
| Colesterol LDL | < 100 mg/dL |
| Triglicéridos | < 150 mg/dL |
| Fórmula de Friedewald: LDL= colesterol total – HDL – (triglicéridos/5) | |
El objetivo del tratamiento es reducir el riesgo de enfermedades cardiovasculares.