La torsión testicular es la rotación repentina del testículo, concretamente del cordón espermático, alrededor de su eje en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el canal inguinal o por debajo de él. La rotación aguda da lugar a que el flujo sanguíneo hacia y desde el testículo se vea comprometido, lo que pone al AL Amyloidosis testículo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum riesgo de necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage. El diagnóstico y la intervención rápida son la clave para salvar el testículo afectado. Se requiere una exploración quirúrgica urgente con orquidopexia subsecuente. El intento de destorcedura manual o guiada por ultrasonido no debe retrasar la atención definitiva.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
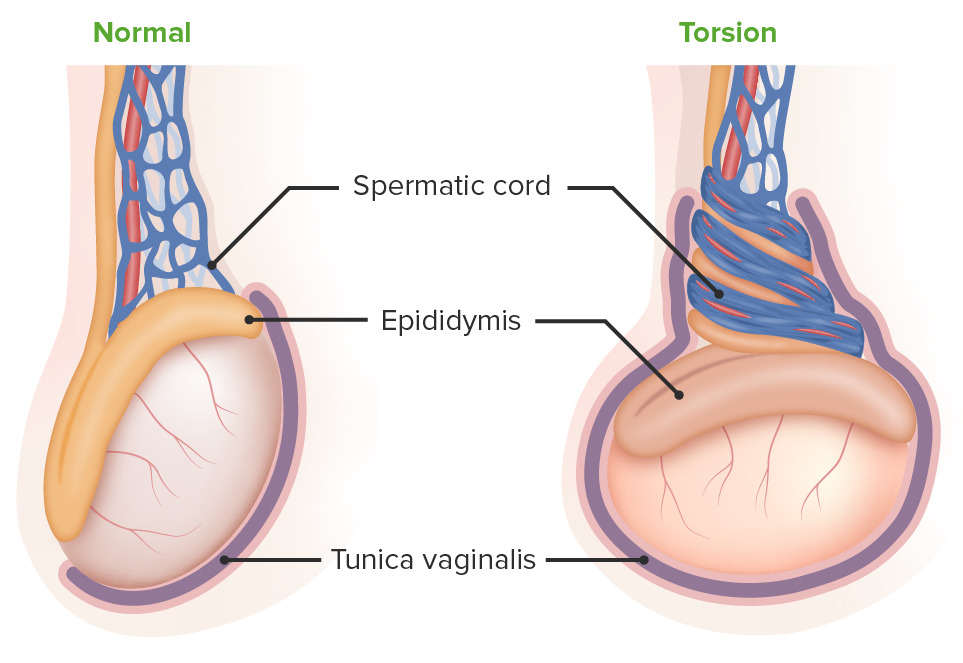
Torsión testicular:
La imagen de la izquierda muestra un testículo normal. A la derecha se ve una torsión testicular: El testículo se encuentra en posición horizontal, lo que aumenta el riesgo de torsión de los vasos espermáticos.
| Característica clínica | Puntos |
|---|---|
| Hinchazón testicular | 2 |
| Testículo duro | 2 |
| Ausencia de reflejo cremastérico | 1 |
| Testículo elevado | 1 |
| Náuseas/vómitos | 1 |
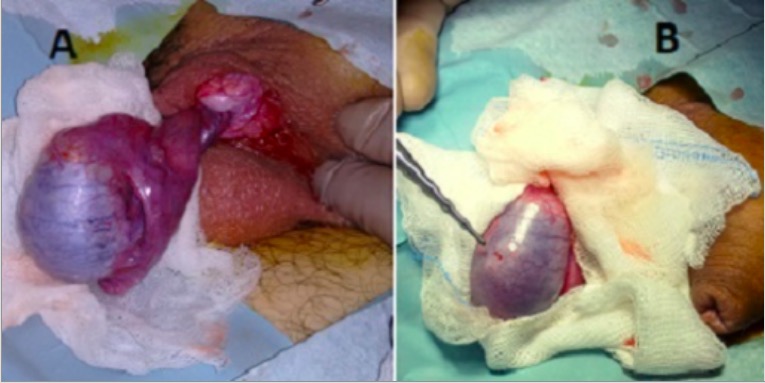
Exploración escrotal intraoperatoria para la torsión testicular:
A: testículo azul decolorado sin riego sanguíneo y cordón espermático retorcido
B: suturas previas de orquidopexia que denotan una torsión testicular recurrente
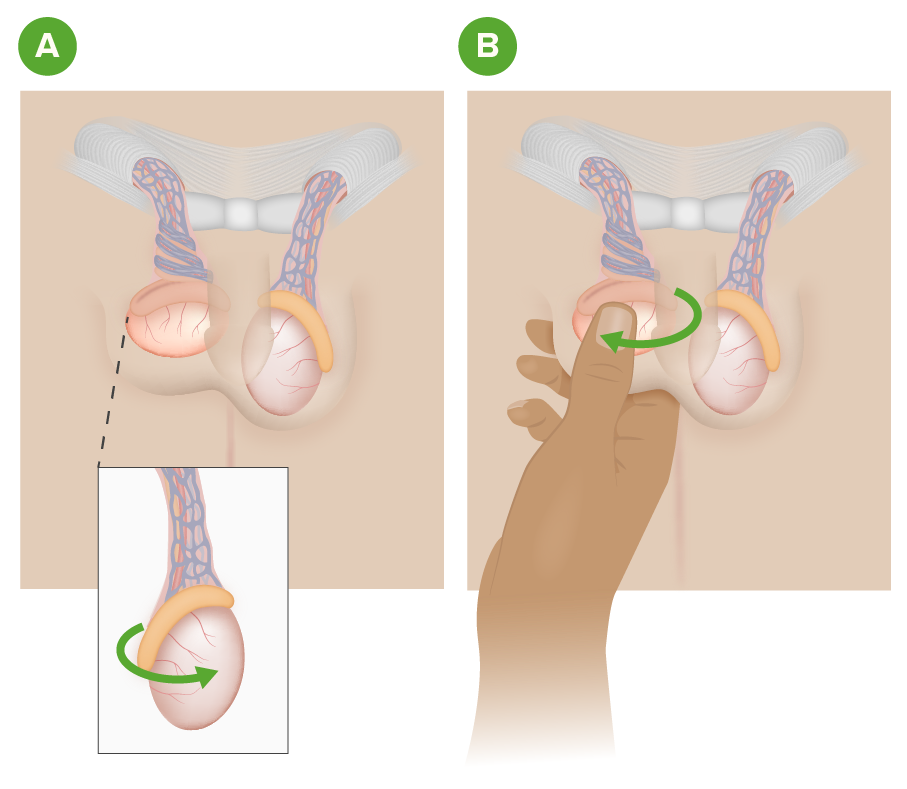
Destorcedura testicular manual:
La imagen A muestra una torsión testicular derecha.
La imagen B ilustra el método de destorcedura manual de tomar y rotar el testículo afectado con la “técnica del libro abierto” desde la posición medial a la lateral.