El síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers (SPJ) es un trastorno hereditario autosómico dominante que se caracteriza por la presencia de pólipos gastrointestinales y máculas mucocutáneas pigmentadas. El síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers es uno de los LOS Neisseria síndromes de poliposis, un grupo de afecciones heredadas o adquiridas que se caracterizan por el crecimiento de pólipos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal y que se asocian a otras características extracolónicas. Los LOS Neisseria síndromes están causados por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure específicos asociados a la supresión de tumores o a la regulación del ciclo celular. El síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers es causado por alteraciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen STK11 y se asocia a cánceres colónicos (colorrectales) y no colónicos (pancreáticos, gástricos, de mama, uterinos, cervicales, de pulmón, de ovarios y de testículos). El manejo es con vigilancia estrecha y cirugía.
Last updated: Jan 18, 2026
El síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers (SPJ) es un trastorno hereditario autosómico dominante caracterizado por pólipos hamartomatosos gastrointestinales y máculas melanóticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum piel y mucosas.
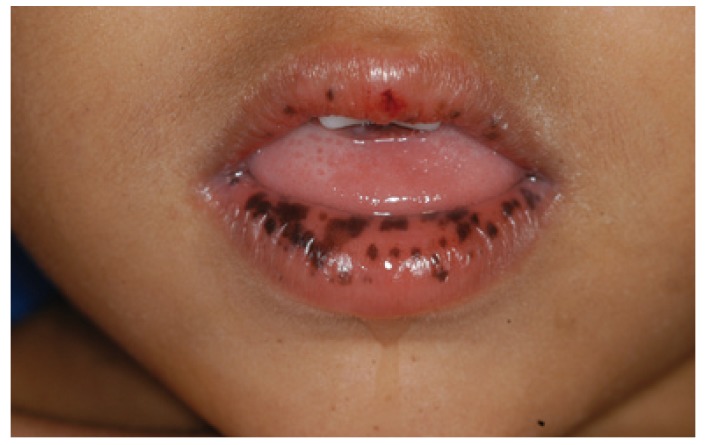
Máculas pigmentarias mucocutáneas en un paciente joven
Imagen: “Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: black spots localized in the perioral area” por Rogério O. Gondak, et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0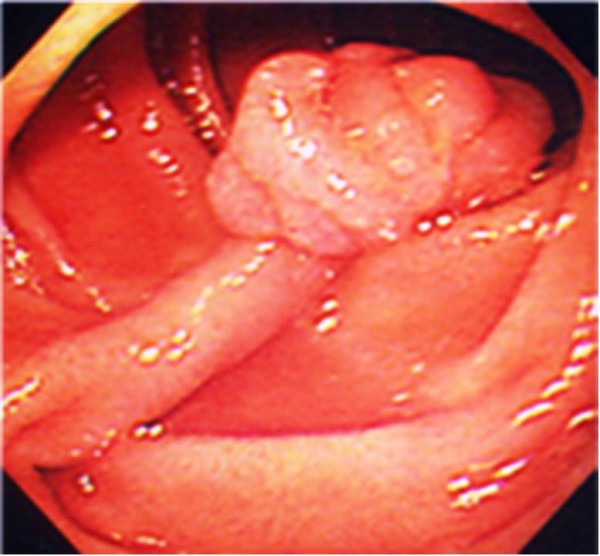
Pólipo hamartomatoso solitario típico del síndrome de Peutz-Jeghers
Imagen: “Pedunculated duodenal polyp measuring 15 mm in diameter in the second part of the duodenum” por Yusuke Sekino, et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0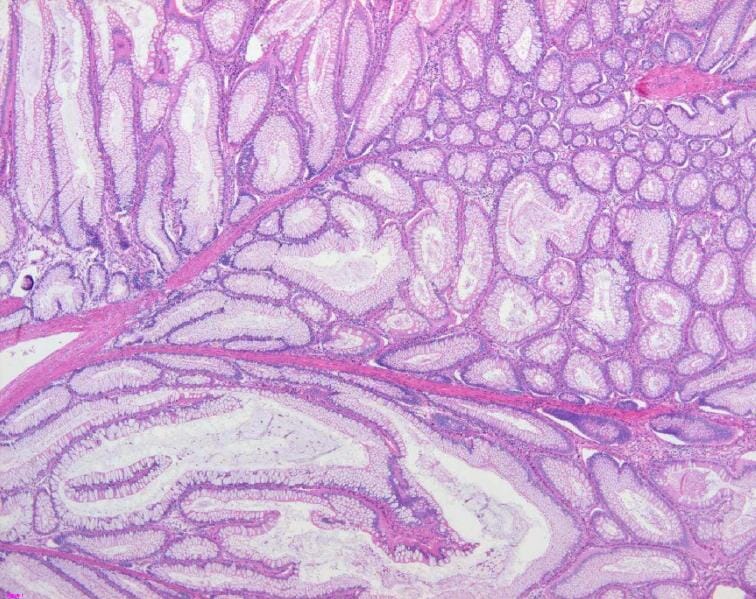
Hallazgos patológicos de un pólipo de Peutz-Jeghers: El pólipo colónico muestra un epitelio mucoso hiperplásico y un patrón arborizante de músculo liso, consistente con un pólipo hamartomatoso (tinción H&E, 200x).
Imagen: “Colon histology with Peutz-Jeghers polyp” por Jong-Ha Yoo et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0