El hueso, aunque aparentemente inerte, es una parte activa, creciente y cambiante del cuerpo humano, además de ser el principal reservorio de calcio del organismo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum condiciones homeostáticas correctas, el hueso puede remodelarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta al AL Amyloidosis daño, al AL Amyloidosis estrés o a la señalización hormonal (hormona paratiroidea y calcitonina). Los LOS Neisseria osteocitos situados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la profundidad del hueso detectan el daño y envían una señal a las células de revestimiento del hueso para que inicien el proceso de remodelación. Este proceso es vital no solo para reparar los LOS Neisseria daños, sino también para adaptarse a un nuevo entorno y condiciones.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
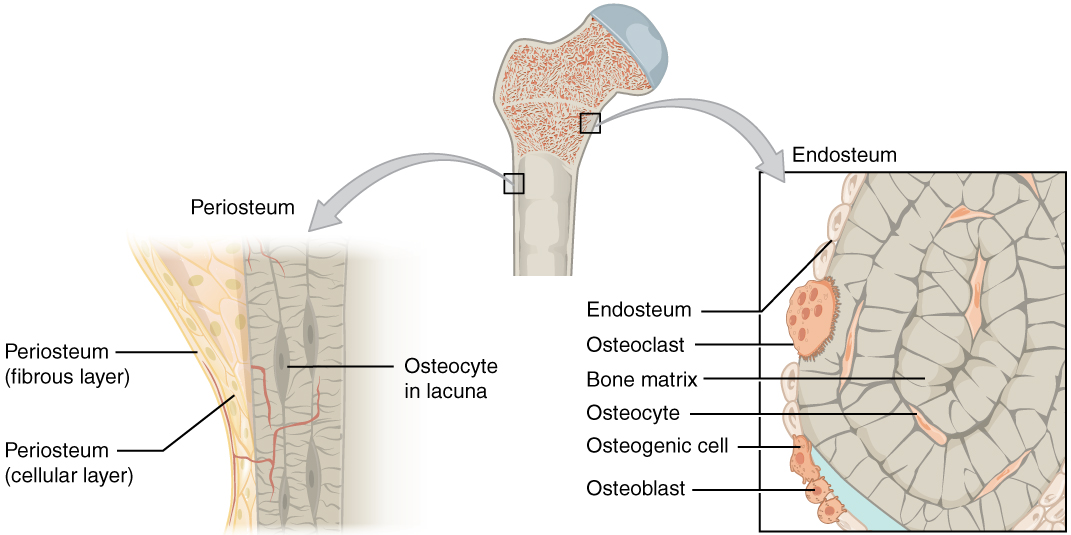
Anatomía ósea:
Los huesos están cubiertos por una capa llamada periostio, compuesta por capas fibrosas y celulares. Por debajo del periostio se encuentra el endostio, una arquitectura compleja construida sobre un andamio mineral (la matriz ósea) y compuesta por osteocitos, osteoclastos y osteoblastos.
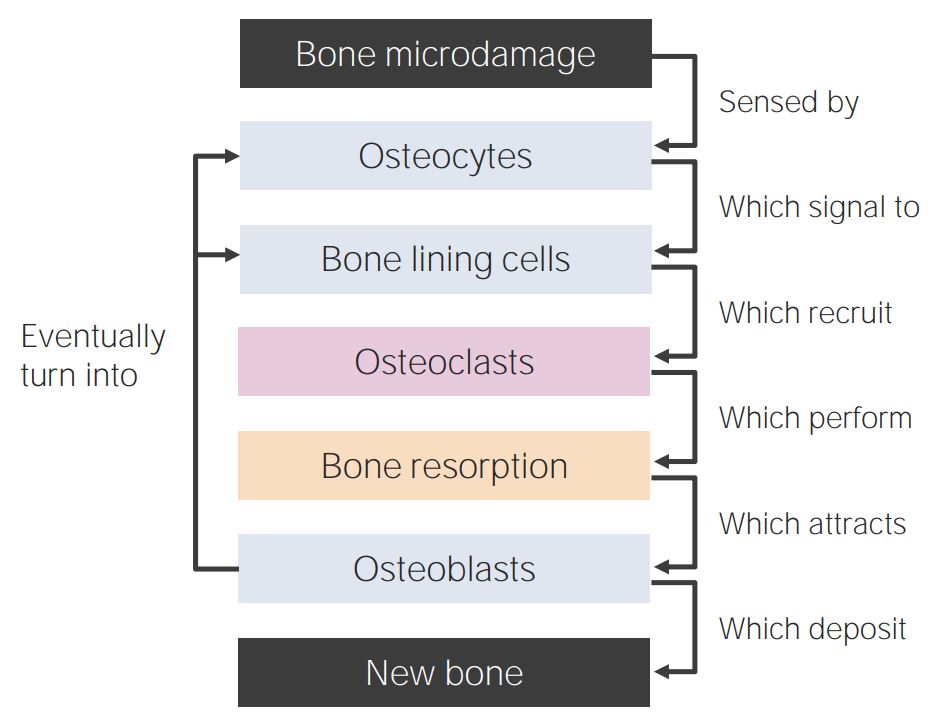
Diagrama de remodelación ósea
La remodelación ósea comienza con los osteocitos que detectan los microdaños. Este proceso provoca su apoptosis, que es percibida simultáneamente por las células de revestimiento del hueso. Estas células liberan quimioatrayentes y los osteoclastos se agrupan en la zona dañada para liberar calcio y fosfato. En cuanto los osteoclastos terminan su trabajo, los osteoblastos comienzan a reclutar el tejido óseo. El proceso también atrapa algunas de las células y forma un nuevo revestimiento al convertir los osteoblastos en osteocitos y células de revestimiento óseo.
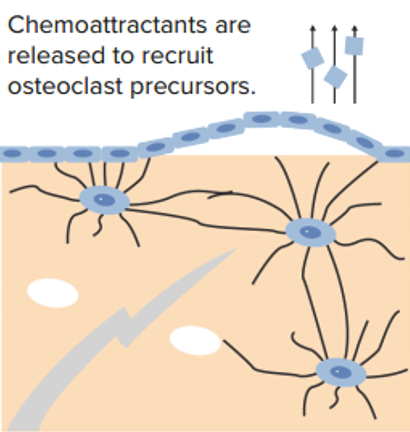
Señalización de microdaños y activación:
Los osteocitos que se encuentran en el lugar de los microdaños sufren apoptosis.
A continuación, las células del revestimiento óseo digieren el osteoide subyacente para exponer el mineral y levantar la superficie.
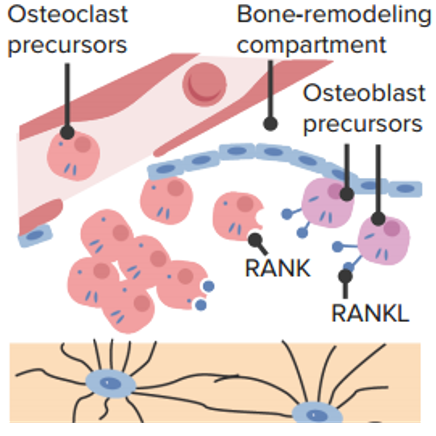
Reclutamiento de precursores de osteoclastos:
Los precursores de los osteoclastos se unen al ligando del activador del factor nuclear kappa B y se unen para formar un osteoclasto.
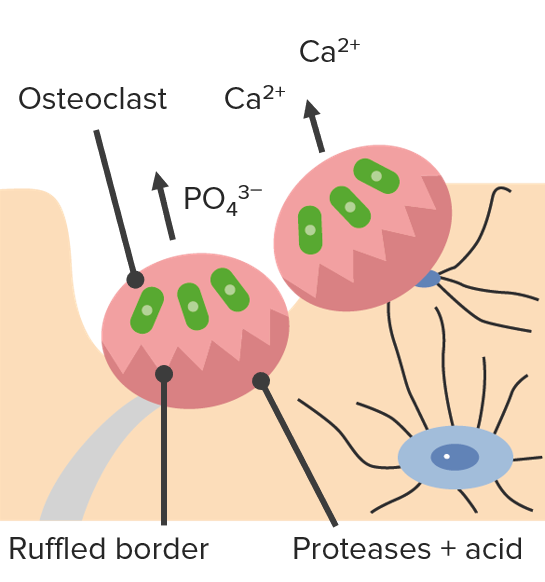
Absorción:
Los osteoclastos digieren los minerales con ácido, liberando Ca2+ y PO43-.
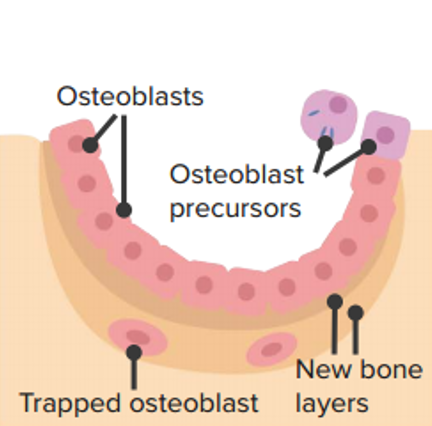
Deposición ósea:
Los precursores de los osteoblastos se convierten en osteoblastos y depositan nuevo osteoide. El osteoide se mineraliza y forma hueso nuevo.
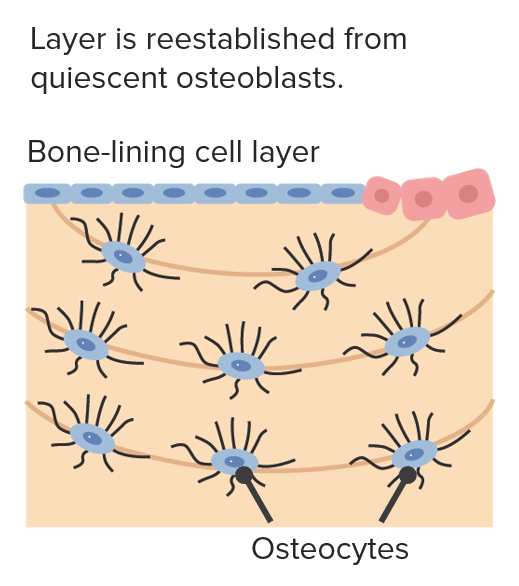
Hueso nuevo:
Los osteoblastos atrapados se convierten en osteocitos y extienden las dendritas.