La reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es una técnica que amplifica exponencialmente fragmentos de ADN para su análisis. El proceso es altamente específico, lo que permite la selección de secuencias genómicas específicas, incluso con cantidades de muestra minúsculas. La PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) cicla múltiples veces a través de 3 fases: desnaturalización del ADN molde, hibridación de un cebador específico con las hebras de ADN individuales y síntesis/elongación de nuevas moléculas de ADN. A partir de ahí, el ADN se puede visualizar con técnicas de análisis como la electroforesis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gel. La velocidad, el bajo costo, la facilidad de uso y la alta sensibilidad y especificidad hacen que esta técnica sea muy útil para las ciencias básicas y biomédicas, y se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia vuelto fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchas aplicaciones, incluido el análisis forense, el diagnóstico de enfermedades infecciosas y el diagnóstico y tamizaje de anomalías genéticas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es una técnica que amplifica secuencias de ADN específicas in vitro y de manera exponencial y se utiliza para el diagnóstico, la identificación de virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology y el análisis.
Para amplificar el ADN o el ARN, las siguientes etapas se repiten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciclos (a menudo hasta 30–40 veces):
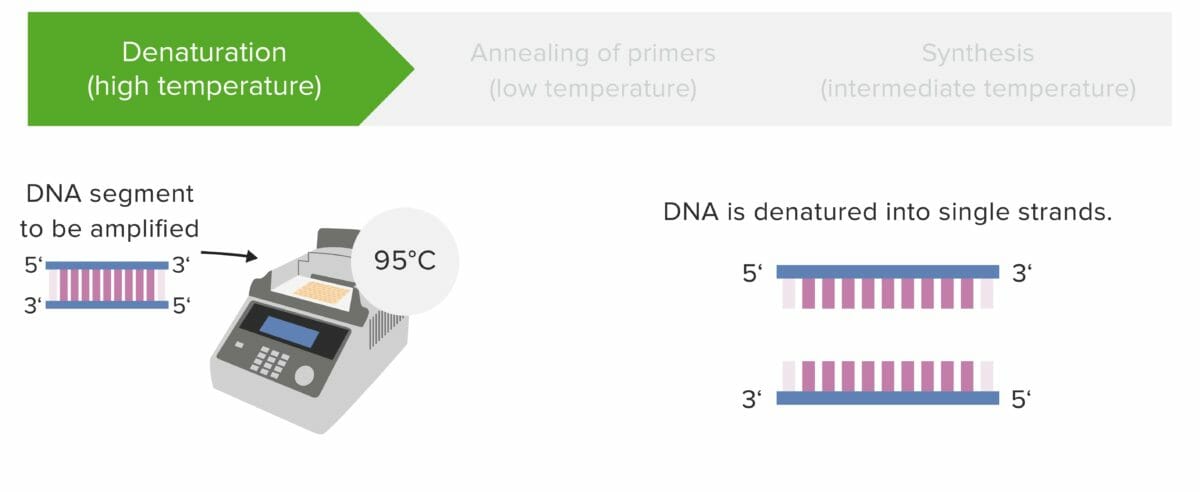
Etapa 1: Desnaturalización
El ADN se desnaturaliza a altas temperaturas, provocando la separación en hebras únicas.
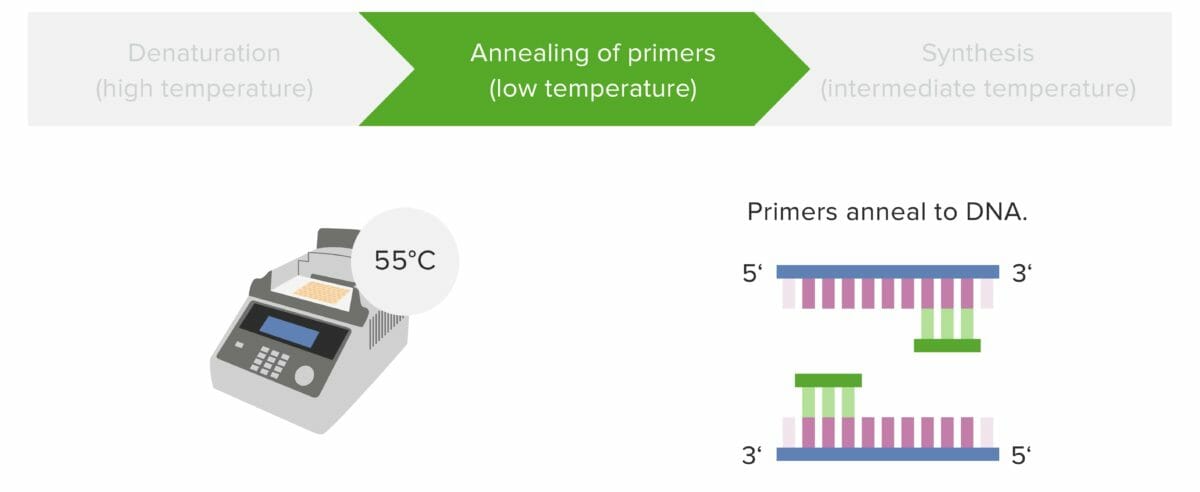
Etapa 2: Hibridación de los cebadores
Los cebadores se hibridan con el extremo 3′ de las hebras de ADN molde al enfriar la muestra.
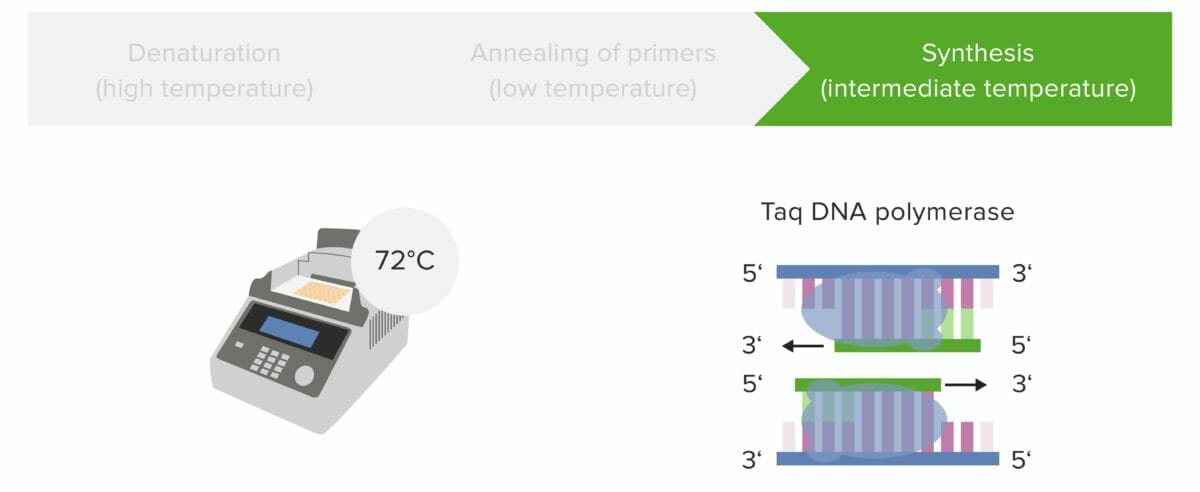
Paso 3: Síntesis/elongación
La elongación del ADN es catalizada por una ADN polimerasa termoestable, que agrega nucleótidos libres disponibles complementarios a la hebra del ADN molde, lo que da como resultado una molécula de ADN recién sintetizada. El ADN se calienta a 72°C, la temperatura adecuada para que la ADN polimerasa Taq pueda elongar los cebadores.
Hay muchas variaciones de la técnica básica de PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Algunos de los LOS Neisseria más comunes incluyen:
La PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia mejorado significativamente el potencial diagnóstico de enfermedades infecciosas.