La perforación de víscera hueca o perforación gastrointestinal representa una afección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que se pierde la integridad de la pared gastrointestinal con la consiguiente fuga del contenido entérico hacia la cavidad peritoneal, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury. Entre las causas de perforación de víscera hueca se encuentran los LOS Neisseria traumatismos, la isquemia intestinal, las infecciones o las afecciones ulcerosas, todas las cuales acaban provocando una ruptura de espesor total de la pared intestinal. La perforación de víscera hueca se presenta como una aparición súbita de dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, distensión, náuseas, vómitos, estreñimiento y síntomas de peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes e imagenología, incluyendo la TC abdominopélvica y radiografía. El tratamiento incluye reposo intestinal, uso de una sonda nasogástrica, antibióticos para evitar infecciones graves o sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock, analgésicos y reparación quirúrgica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una perforación de víscera hueca, también conocida como perforación intestinal, es una ruptura de espesor total de la pared intestinal, con la subsiguiente fuga del contenido entérico a la cavidad peritoneal, lo que provoca una respuesta inflamatoria sistémica, peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury y posiblemente sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock.
Signos vitales:
Examen abdominal:
Presentación atípica:
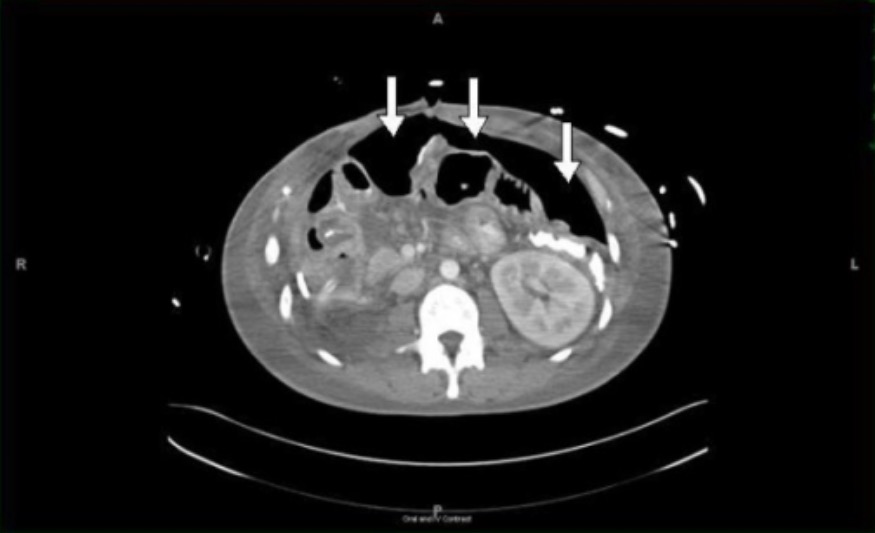
TC postoperatoria que muestra un neumoperitoneo de gran volumen debido a una fístula broncoperitoneal
Imagen: “Post-operative computed tomography (CT) scan” por Johns Hopkins Hospital, Department of Surgery, Baltimore, MD, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0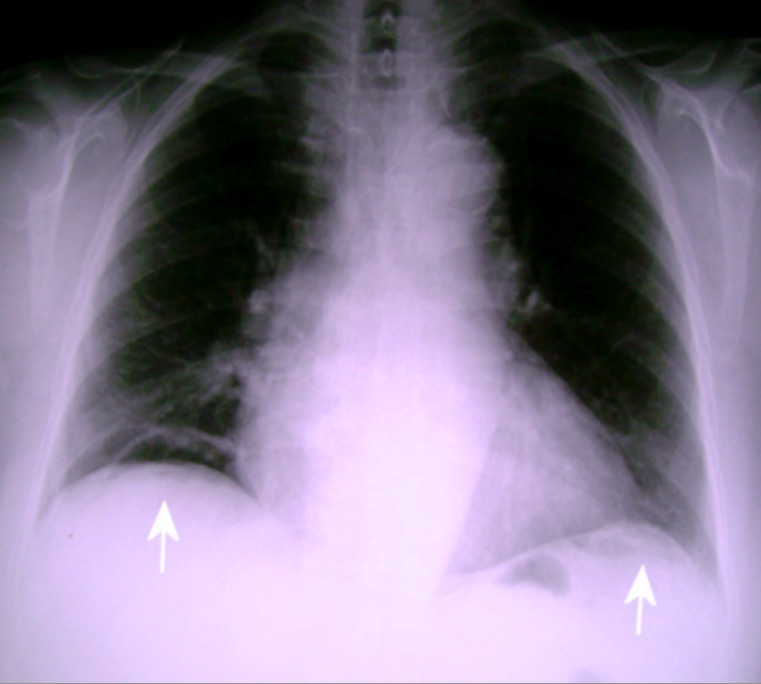
Radiografía de tórax posteroanterior en bipedestación:
Presencia de aire libre subdiafragmático bilateralmente, que se nota más claramente en el lado derecho (flechas blancas).