La osteogénesis imperfecta, o "enfermedad de los huesos frágiles", es un trastorno genético raro del tejido conectivo caracterizado por una grave fragilidad ósea. Aunque la osteogénesis imperfecta se considera una sola enfermedad, incluye más de 20 genotipos y fenotipos clínicos con diferente gravedad de los síntomas. De estos, los tipos I–IV son los más comunes. Debido a la rareza de la osteogénesis imperfecta, esta se considera una "enfermedad huérfana" en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente, a través de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen físico, y se confirma mediante hallazgos radiológicos y análisis de ADN. Aunque no existe una cura definitiva, el tratamiento es de soporte, generalmente con bifosfonatos, y se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reducir el dolor Dolor Inflammation, disminuir la frecuencia de las fracturas, reducir la deformidad ósea y aumentar la deambulación. El pronóstico es variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, dependiendo del tipo de osteogénesis imperfecta.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La osteogénesis imperfecta es un trastorno hereditario del tejido conectivo que se caracteriza por la alteración de la formación de los LOS Neisseria huesos y una grave fragilidad ósea.
| Tipo I | Tipo II | Tipo III | Tipo IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gen mutado | COL1A1, COL1A2 (cadenas de colágeno tipo 1 alfa 1 y 2) | COL1A1, COL1A2 y CRTAP (proteína asociada al AL Amyloidosis cartílago) | COL1A1, COL1A2 | COL1A1, COL1A2 |
| Modalidad de herencia | Autosómica dominante | Autosómica dominante y autosómica recesiva | Autosómica dominante | Autosómica dominante |
| Defecto | Mutaciones por desplazamiento del marco de lectura en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las cadenas alfa 1 y 2 del colágeno tipo 1 que dan lugar a una disminución de las cantidades de colágeno normal | Formación alterada de la estructura de triple hélice del colágeno, lo que lleva a que el colágeno normal sea escaso o nulo | Mutaciones que causan defectos estructurales de las proteínas que conducen a una patología grave | Mutaciones que causan defectos estructurales de las proteínas que conducen a una patología mínima o leve |
| Tipo I | Tipo II | Tipo III | Tipo IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descripción | No deformante con esclerótica azul | Letal desde el punto de vista perinatal | Deformación progresiva | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables con escleróticas normales |
| Gravedad | Leve | Letal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el período perinatal | Severa | De leve a moderada |
| Fracturas | < 100 | > 100 | > 100 | > 100 |
| Deformación ósea | Inusual | Severa | Moderada a severa | De leve a moderada |
| Estatura | Normal a ligeramente reducida | Muy reducida | Reducida | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
| Dentogénesis imperfecta | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | Común | Común | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
| Color de las escleróticas | Azul | Azul oscuro | Azul | Normal a gris |
| Pérdida de la audición | Presente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aproximadamente el 50% | — | Frecuente | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
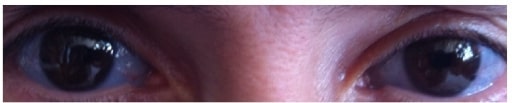
Esclerótica de color azul asociada a la osteogénesis imperfecta
Imagen: “Blue sclera” por the Department of Medical Oncology, Ankara University School of Medicine, 06300 Ankara, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.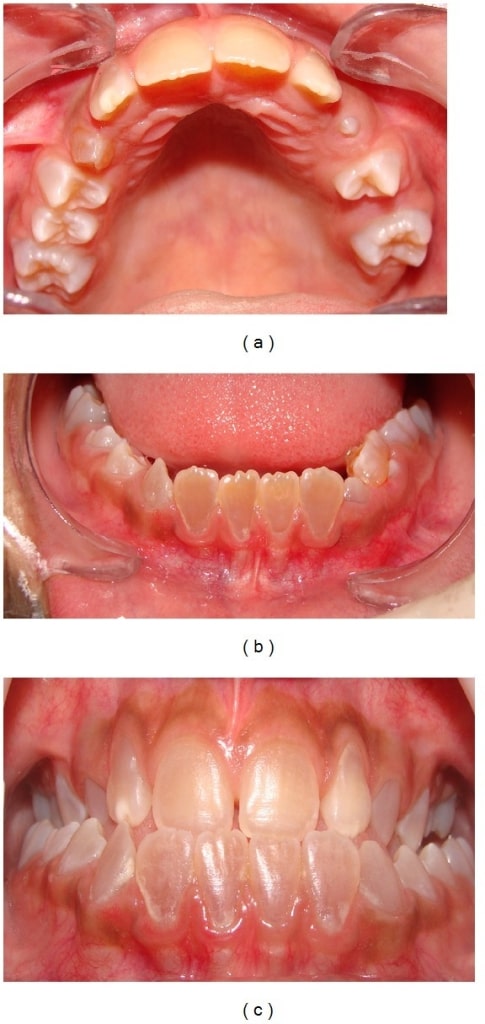
Dentinogénesis imperfecta:
Los dientes anteriores muestran una decoloración marrón (arcada dental superior (a), arcada inferior (b) y oclusión dental (c)).
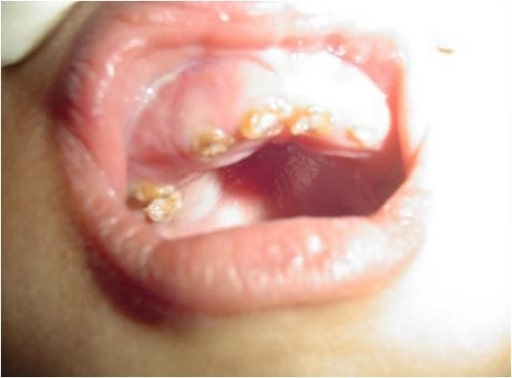
Fotografía intraoral que muestra una decoloración amarillenta y astillamiento de la dentición: un niño de 4 años con osteogénesis imperfecta (tipo IV)
Imagen: “Chipping of the dentition” por the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, AB Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, Nitte University, Mangalore 575018, India. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.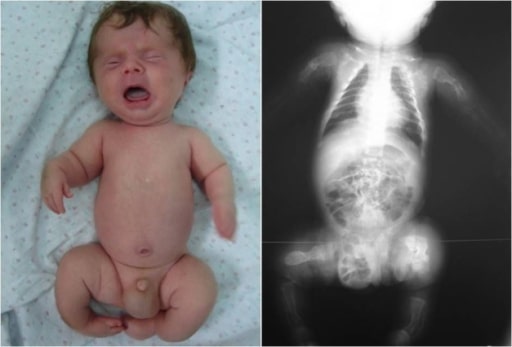
Lactante con osteogénesis imperfecta: obsérvese la deformación de las extremidades, indicio de posibles fracturas durante la inspección.
Imagen: “Congenita A type of osteogenesis imperfecta” por the Maria Sklodowska Curie Clinical Emergency Hospital for Children, Bucharest, Romania. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.| Tipo I | Tipo II | Tipo III | Tipo IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hallazgos radiográficos del cráneo | Huesos intrasuturales | Submineralización; zonas calcificadas | Huesos intrasuturales | Huesos intrasuturales (a veces) |
| Hallazgos radiográficos de la columna vertebral | Vértebras bicóncavas (adultos) | Cuerpos vertebrales ensanchados (platispondilia) | Vértebras bicóncavas; cifoescoliosis | Vértebras bicóncavas |
| Hallazgos radiográficos de las extremidades | Corticales finas | Fémures severamente deformados | Metáfisis acampanadas, arqueadas, corticales delgadas | Corticales finas |
| Otros hallazgos radiográficos | Osteopenia Osteopenia Osteoporosis | Costillas pequeñas y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuentas (patognomónico) | Costillas delgadas, osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis severa | Protrusión del acetábulo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un subgrupo |

Ultrasonido prenatal para diagnosticar la osteogénesis imperfecta:
Este ultrasonido prenatal a las 22 semanas de gestación muestra la curvatura del fémur (las cruces muestran los extremos del fémur).
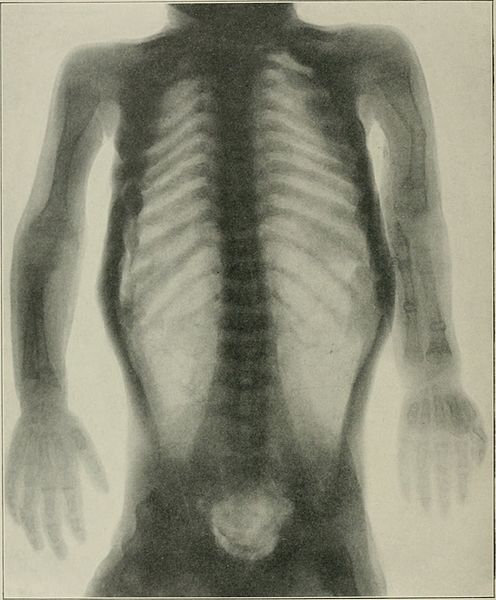
Radiografía que muestra osteogénesis imperfecta:
displasia del periostio, ausencia casi total de hueso cortical y numerosas fracturas
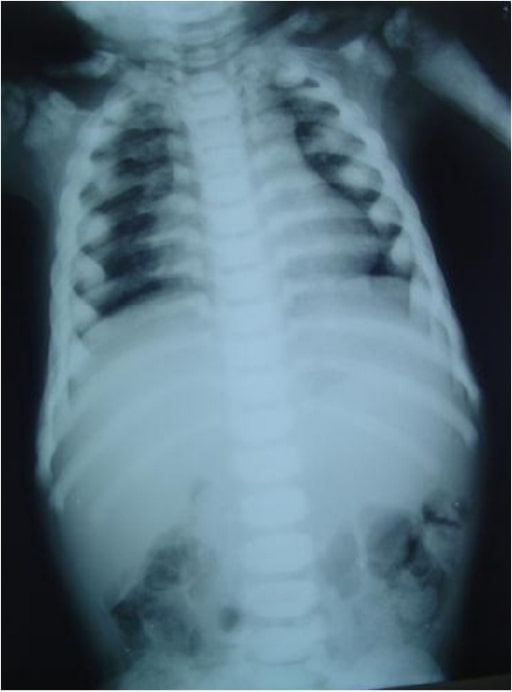
Radiografía de tórax que muestra un tórax largo y estrecho (tórax en forma de barril) con compresión anterior
Imagen: “Barrel-shaped chest” por the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, AB Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, Nitte University, Mangalore 575018, India. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.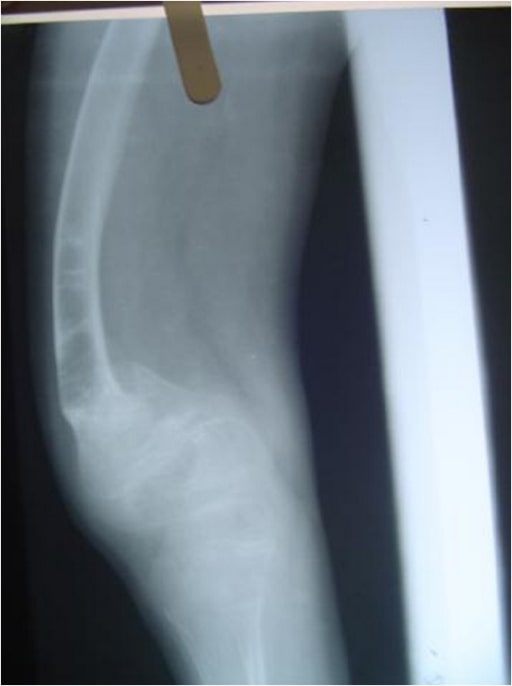
Radiografía de los miembros inferiores que muestra el arqueo del fémur, con ensanchamiento de las metáfisis:
un niño de 4 años con osteogénesis imperfecta (tipo IV)
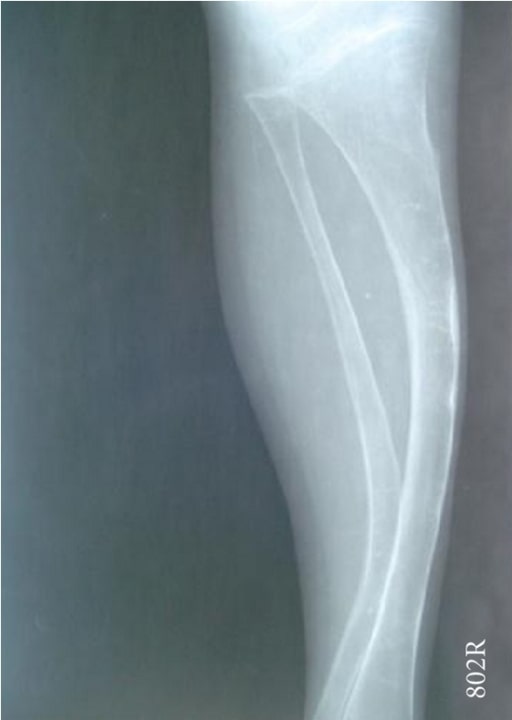
Radiografía que muestra una tibia y un peroné arqueados (espinillas de sable):
un niño de 4 años con osteogénesis imperfecta (tipo IV)
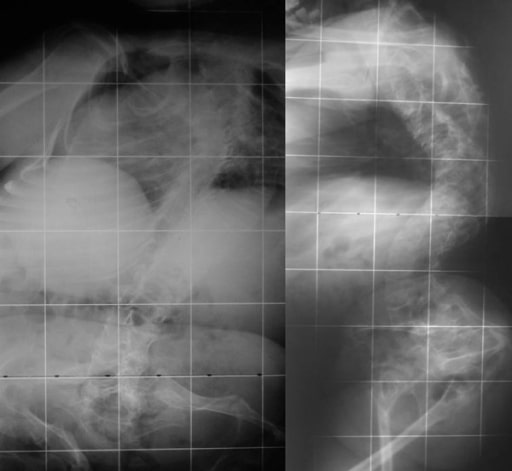
Deformidades bicóncavas en las vértebras torácicas y lumbares inferiores en un paciente de 15 años con osteogénesis imperfecta (vértebras de “bacalao”)
Imagen: “Osteogenesis imperfecta” por the 1st Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Athens, “Attikon” Hospital, Rimini 1 Haidari 12462, Athens, Greece. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.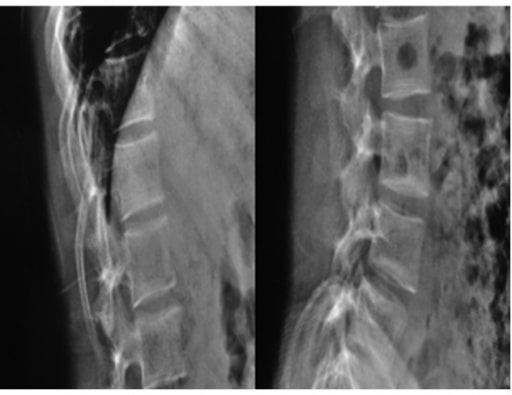
Radiografías de una mujer de 19 años con osteogénesis imperfecta: se observan huesos frágiles, tronco corto, cifoescoliosis severa y platispondilia.
Imagen: “Biconcavity deformities” por the Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012, P.R. China. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.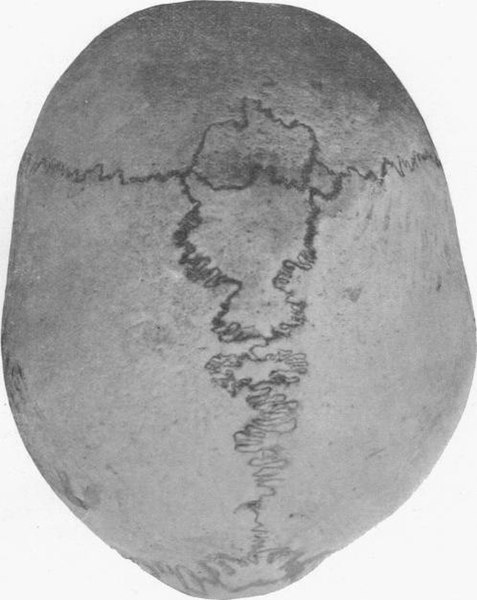
Cráneo humano con huesos wormianos en un hombre de 21 años
Imagen: “Wormian bones” por E. Barclay-Smith. Licencia: Dominio Público.No existe una cura definitiva para la osteogénesis imperfecta.