La creación de gametos eucariotas implica una fase de replicación del ADN seguida de 2 etapas de división celular: meiosis I Meiosis I Following DNA replication, meiosis I creates 2 daughter cells containing half the genetic information of the mother cell (1n) but the same number of chromosomes (2c) by segregating sister chromatids into the same daughter cell Meiosis y meiosis II Meiosis II Meiosis II is a cellular division event wherein the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is halved from that of the mother cell. Meiosis II: similar to meiosis I but not preceded by interphase (DNA replication) Meiosis. La meiosis I Meiosis I Following DNA replication, meiosis I creates 2 daughter cells containing half the genetic information of the mother cell (1n) but the same number of chromosomes (2c) by segregating sister chromatids into the same daughter cell Meiosis separa los LOS Neisseria cromosomas homólogos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células separadas (1n, 2c), mientras que la meiosis II Meiosis II Meiosis II is a cellular division event wherein the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is halved from that of the mother cell. Meiosis II: similar to meiosis I but not preceded by interphase (DNA replication) Meiosis separa las cromátidas hermanas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gametos (1n, 1c). Las combinaciones únicas de gametos a través de la reproducción sexual son un importante impulsor de la aptitud evolutiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum organismos complejos.
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
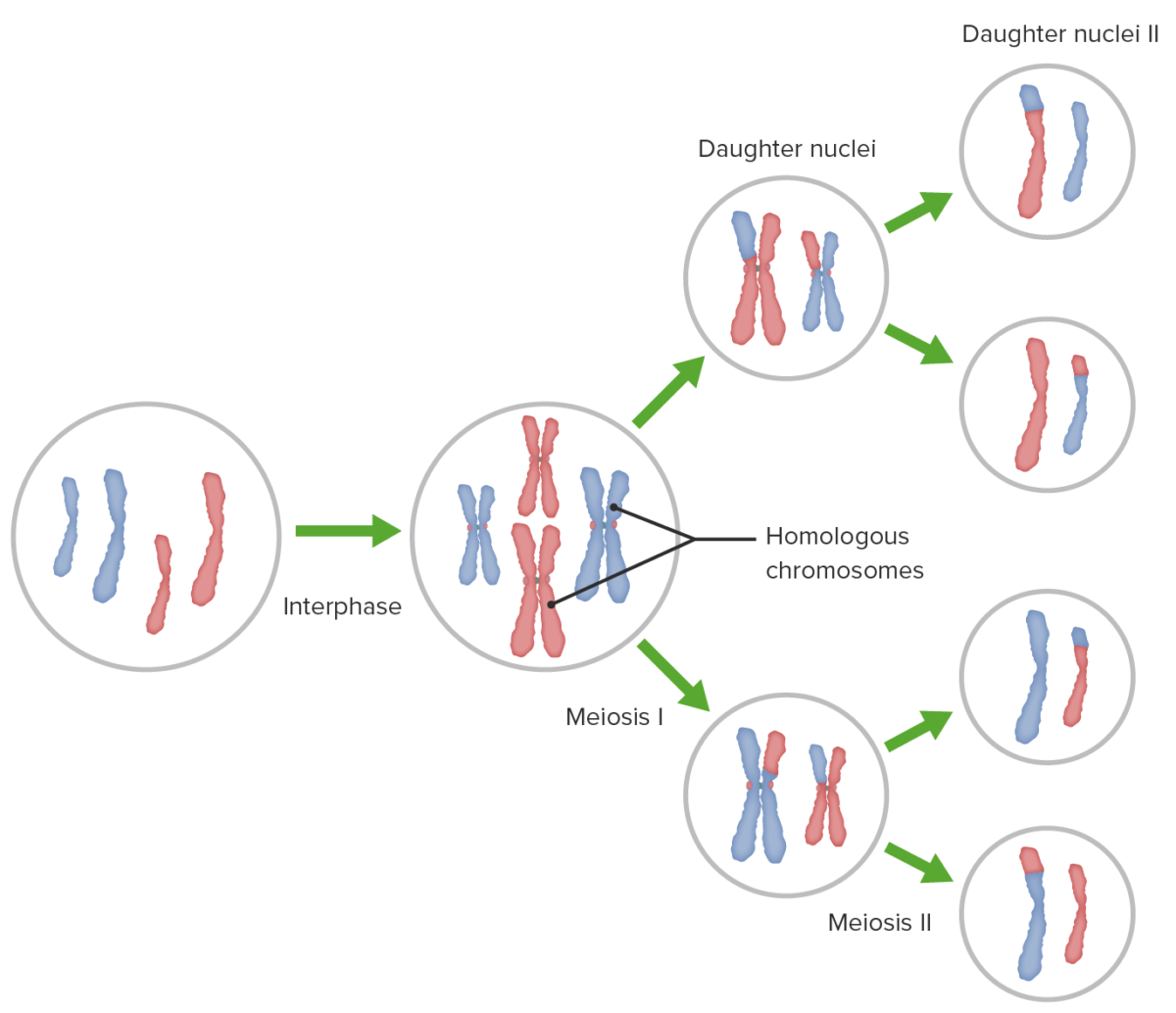
Descripción general de la meiosis I y II, entrecruzamiento (recombinación homóloga) y distribución independiente
Imagen por Lecturio.Después de la replicación del ADN, la meiosis I Meiosis I Following DNA replication, meiosis I creates 2 daughter cells containing half the genetic information of the mother cell (1n) but the same number of chromosomes (2c) by segregating sister chromatids into the same daughter cell Meiosis crea 2 células hijas que contienen la mitad de la información genética de la célula madre (1n) pero la misma cantidad de cromosomas (2c) mediante la segregación de cromátidas hermanas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la misma célula hija.
Reaparición de la membrana nuclear y del nucléolo: la telofase
Imagen: “Reappearance of the nuclear membrane and nucleolus: the telophase” por Roy van Heesbeen. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa meiosis II Meiosis II Meiosis II is a cellular division event wherein the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells is halved from that of the mother cell. Meiosis II: similar to meiosis I but not preceded by interphase (DNA replication) Meiosis es un evento de división celular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que el número de cromosomas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células hijas se reduce a la mitad del de la célula madre.
El cariotipo humano normalmente contiene 23 pares de cromosomas.
La meiosis Meiosis The creation of eukaryotic gametes involves a DNA replication phase followed by 2 cellular division stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes into separate cells (1n, 2c), while meiosis II separates sister chromatids into gametes (1n, 1c). Meiosis es importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la producción de células haploides (gametos).
Espermatogénesis
Ovogénesis
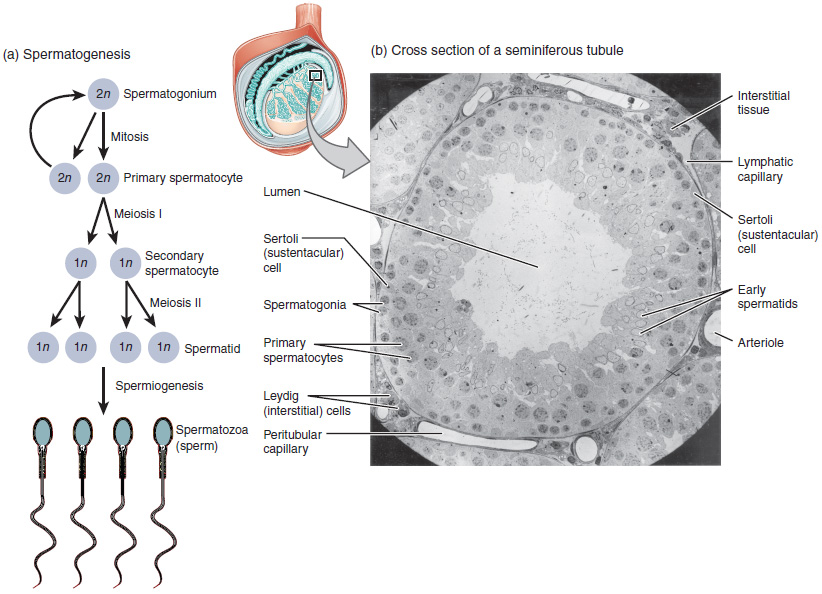
El proceso de espermatogénesis a medida que las células progresan de espermatocitos primarios a espermatocitos secundarios a espermátides a espermatozoides.
Imagen: “Illustration from Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0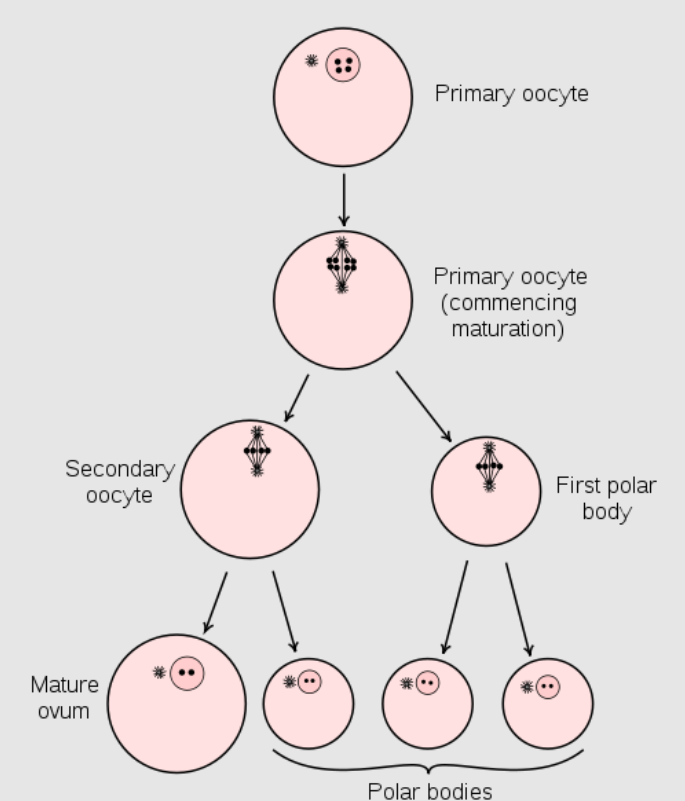
Diagrama que muestra la reducción del número de cromosomas en el proceso de maduración del óvulo. (En los mamíferos, el primer cuerpo polar normalmente se desintegra antes de dividirse, por lo que solo se producen dos cuerpos polares).
Imagen: “Maturation of the ovum” por Henry Vandyke Carter et al. Licencia: Dominio Público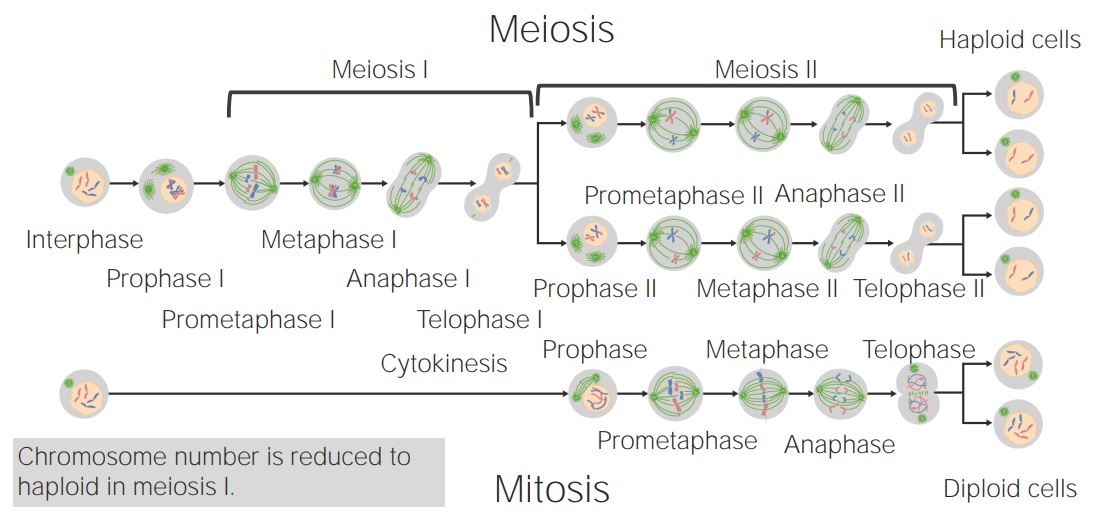
Comparando mitosis y meiosis
Imagen por Lecturio.