La hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias femoral es un tipo poco común de hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias inguinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que el contenido intraabdominal se hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias por debajo del ligamento inguinal y a través del anillo femoral hacia el canal femoral. Más frecuentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños, las hernias femorales suelen presentarse con una inflamación que sobresale en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el triángulo femoral (inferior al AL Amyloidosis ligamento inguinal y medial a la vena femoral). Aunque son infrecuentes, las hernias femorales se asocian con frecuencia a complicaciones secundarias al AL Amyloidosis tamaño reducido del canal, que conducen al AL Amyloidosis encarcelamiento y/o a la estrangulación de la hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El anillo femoral es la apertura proximal o abdominal/pélvica del canal femoral.
Límites:
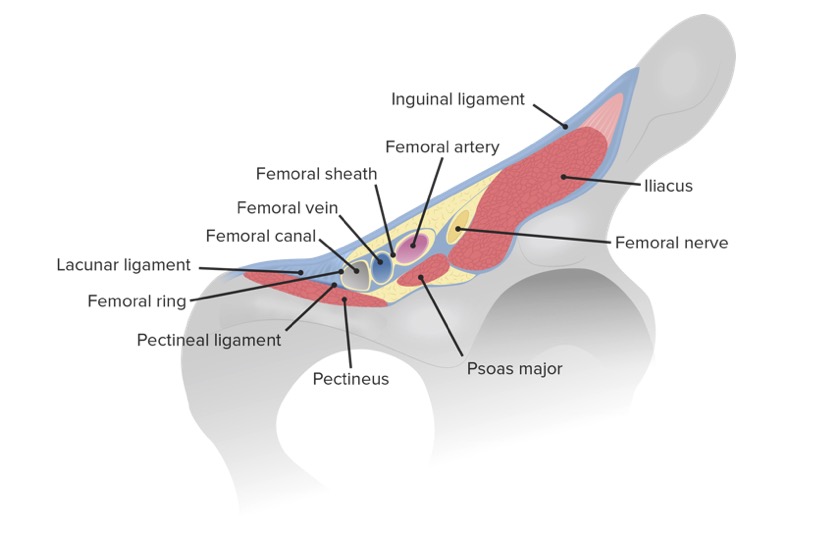
Límites del anillo y del canal femoral en relación con los vasos y el nervio femoral
Imagen por Lecturio.El canal femoral es un espacio cilíndrico que constituye el compartimento medial encerrado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vaina femoral.
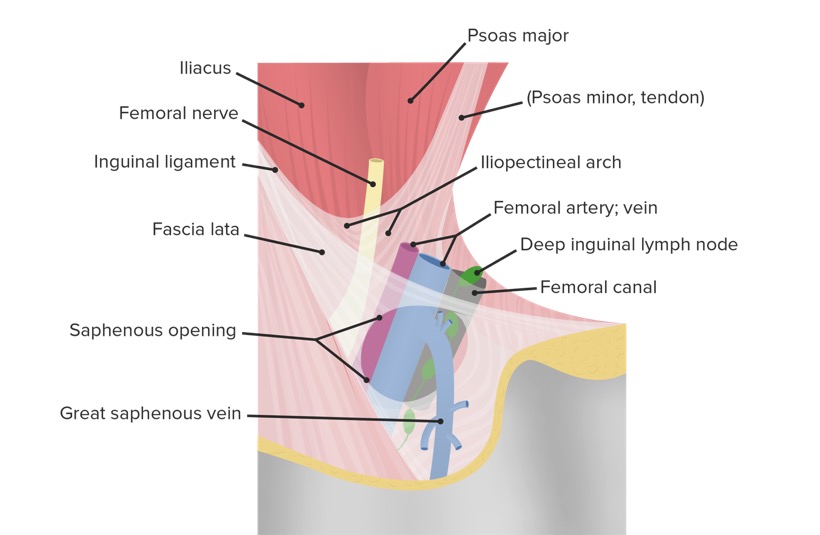
Imagen detallada del triángulo femoral que muestra la ubicación del canal femoral en relación con las estructuras vecinas de la cara interna del muslo
Imagen por Lecturio.El triángulo femoral está situado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara medial de la parte anterior del muslo.
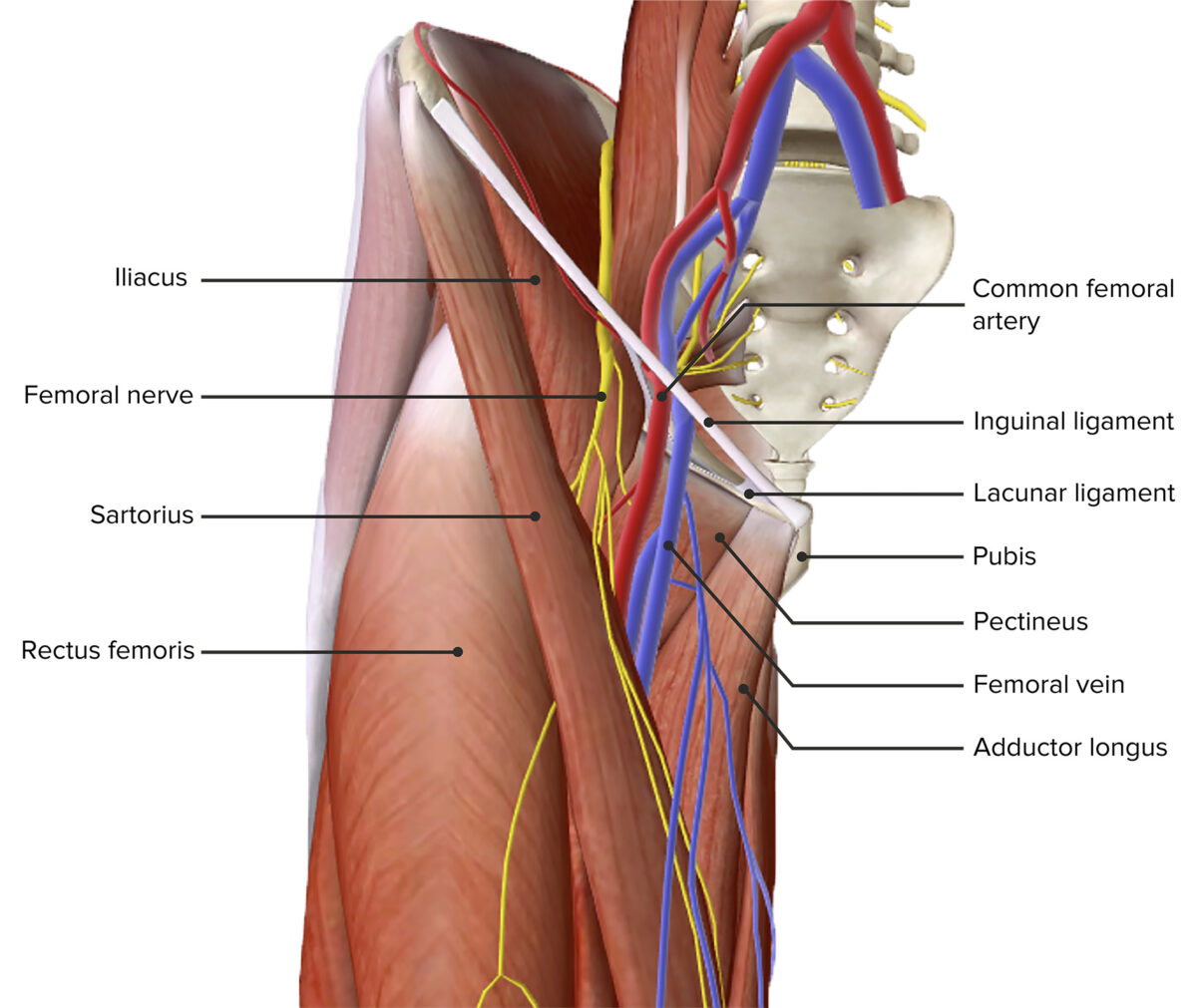
Vista anterior del muslo, mostrando el triángulo femoral
Imagen por Lecturio.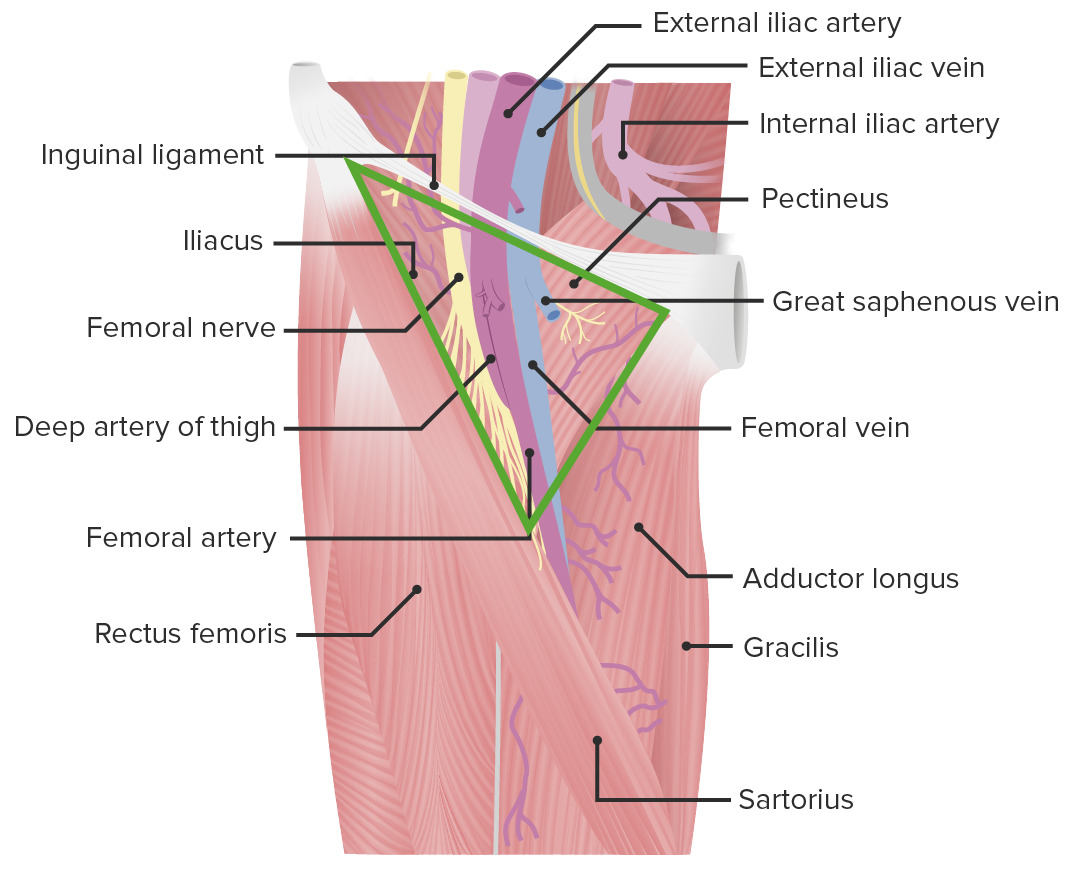
Vista anterior del muslo, mostrando el triángulo femoral con sus bordes y contenido
Imagen por Lecturio.La hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias femoral es la protrusión del contenido intraabdominal por debajo del ligamento inguinal, a través del anillo femoral y hacia el canal femoral, produciendo un “bulto” o inflamación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el triángulo femoral.
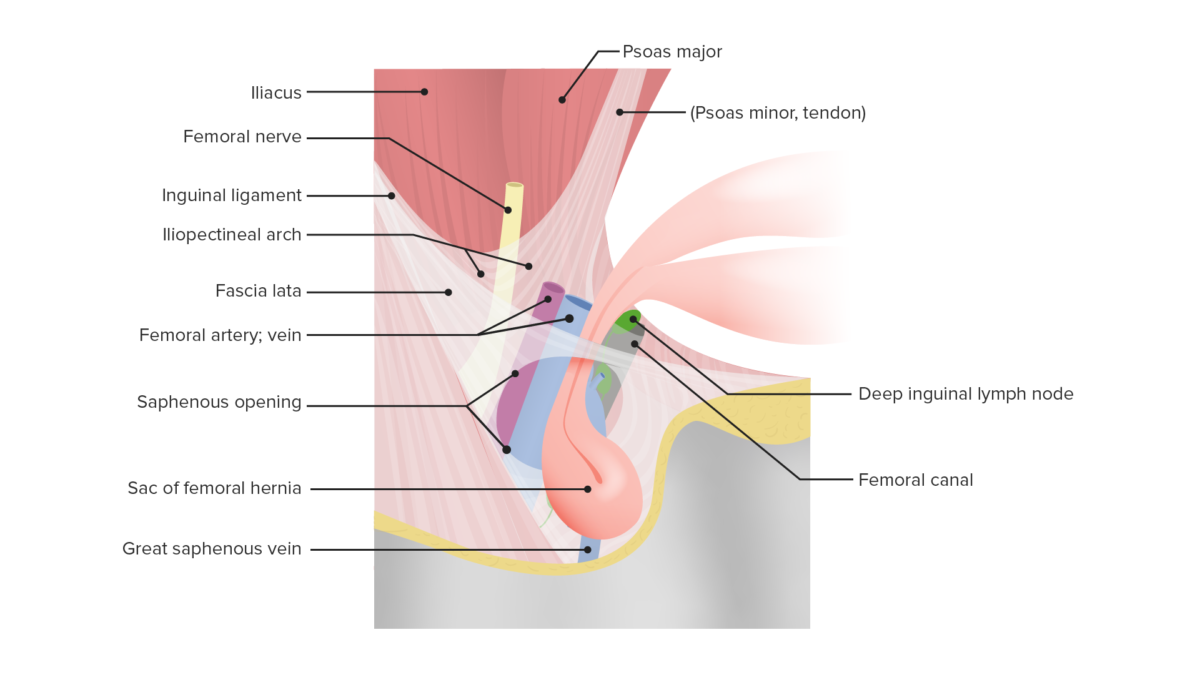
Acercamiento del triángulo femoral que muestra la localización de una hernia femoral
Imagen por Lecturio.Para recordar los LOS Neisseria bordes del triángulo femoral-SAIL ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Para recordar el contenido del triángulo femoral (de lateral a medial)-NAVEL ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
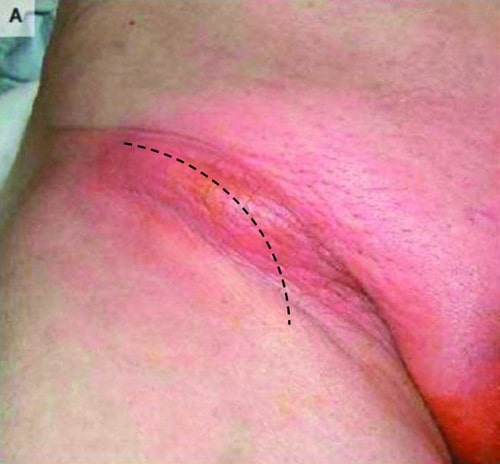
Vista frontal preoperatoria de un paciente con una hernia femoral que demuestra una protuberancia roja y redonda en la zona de la ingle. La línea punteada muestra cómo se realizó la incisión inguinal curva.
Imagen: “De Garengeot’s hernia in a 60-year-old woman: a case report” por Konofaos P, Spartalis E, Smirnis A, Kontzoglou K, Kouraklis G. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Según la localización y el contenido de la protrusión, se han descrito varios subtipos de hernias femorales:
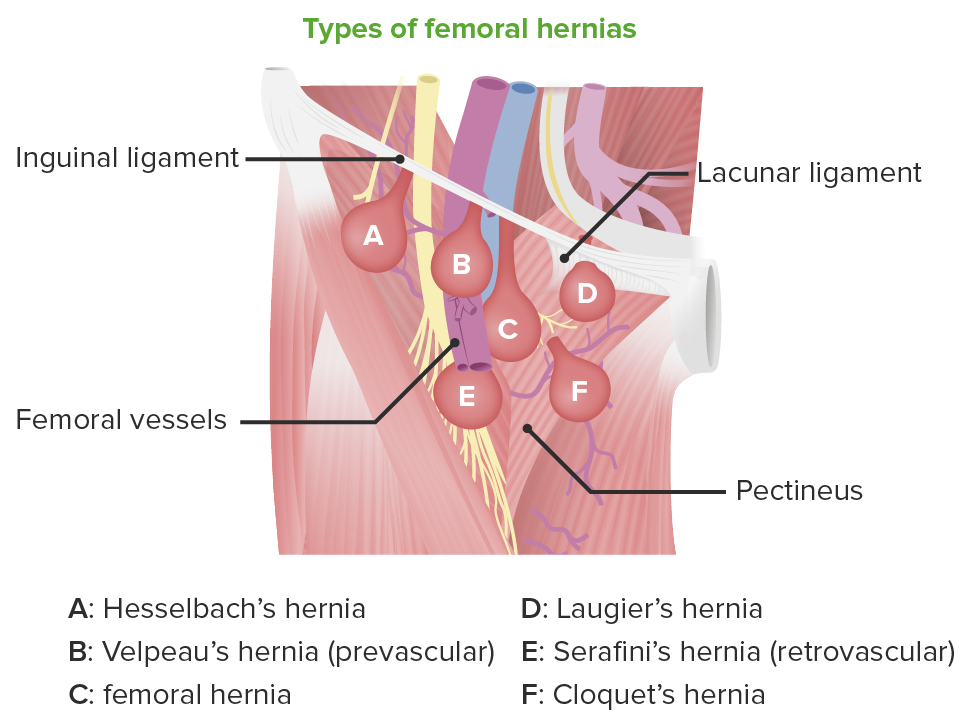
Tipos de hernias femorales
Imagen por Lecturio.
Diagrama esquemático que muestra la diferencia de localización entre las hernias inguinales directas, las inguinales indirectas y las femorales
Imagen por Lecturio.
Ultrasonido de una hernia femoral encarcelada que muestra el saco herniario edematoso, por encima de los vasos femorales
Imagen: “Incarcerated femoral hernia containing ipsilateral falopian tube” por Atmatzidis S, Chatzimavroudis G, Dragoumis D, Atmatzidis K. Licencia: CC BY 3.0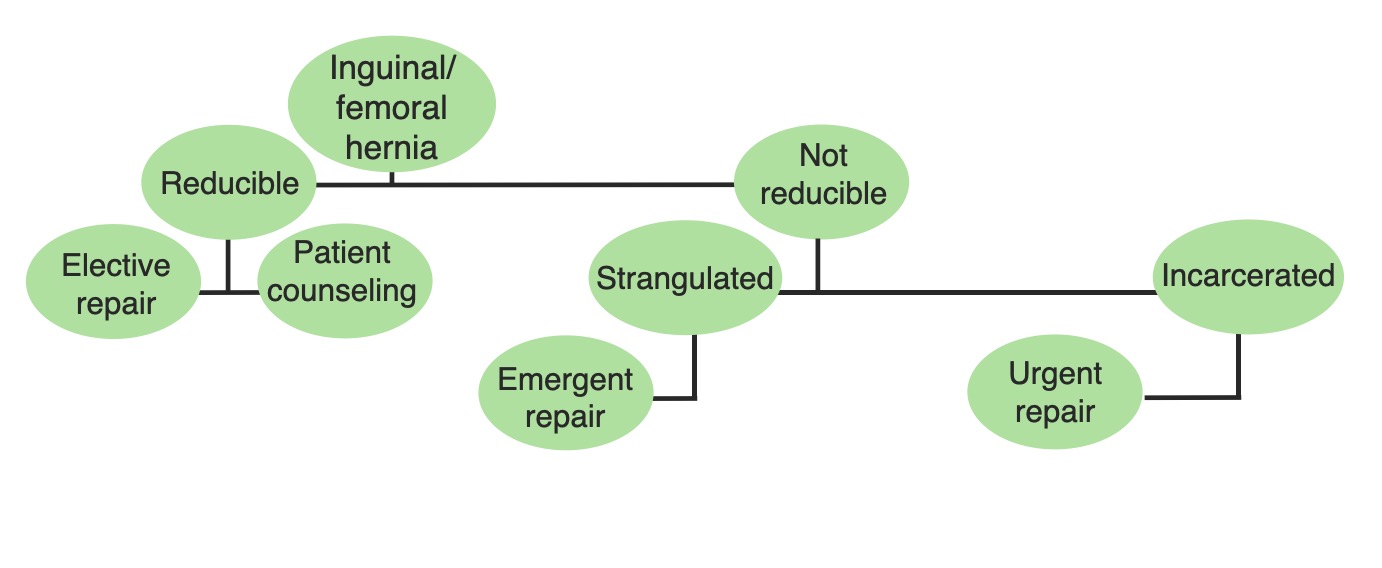
Diagrama esquemático que lista las opciones de tratamiento de las hernias femorales, en función de su estado de reducibilidad.
Imagen por Lecturio.Acceso vascular femoral: la arteria y vena femoral son fácilmente accesibles dentro del triángulo femoral para los LOS Neisseria procedimientos invasivos.
Las siguientes afecciones se incluyen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos diferenciales de las hernias femorales: