La cinética enzimática es el estudio de las velocidades de reacción catalizadas por enzimas y de los LOS Neisseria factores que afectan a las velocidades de reacción enzimática. Estos parámetros suelen incluir la temperatura, el pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance y la concentración de sustrato. La relación de estos parámetros con la velocidad de reacción puede modelarse matemáticamente, lo que permite conocer las condiciones ideales para una determinada reacción enzimática y los LOS Neisseria posibles mecanismos de control fisiológico.
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
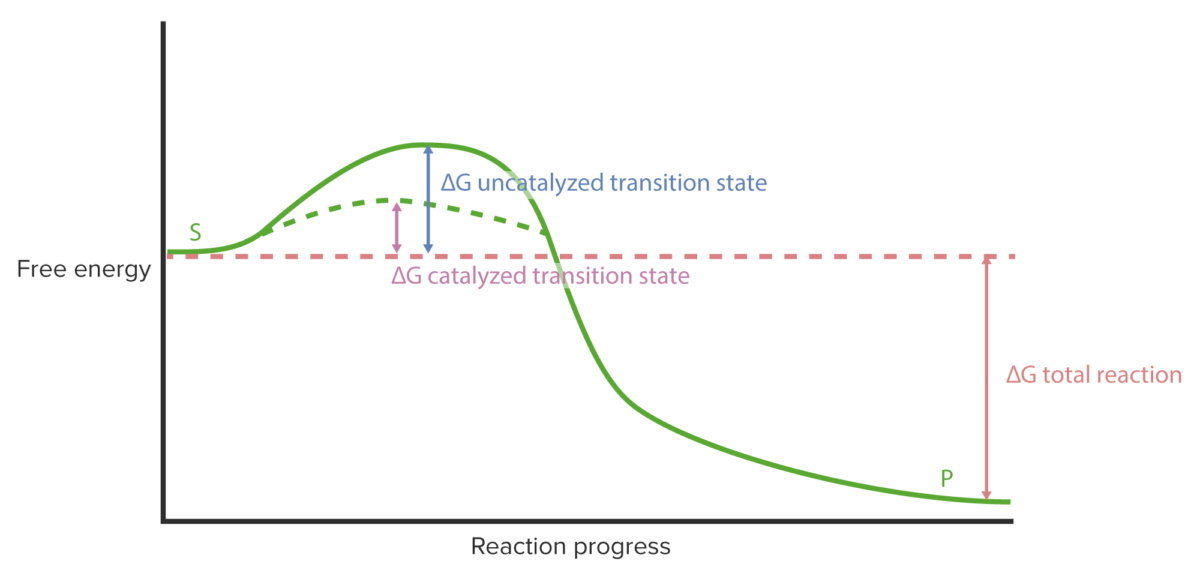
Cinética enzimática: curva de progreso de la reacción
Imagen por Lecturio.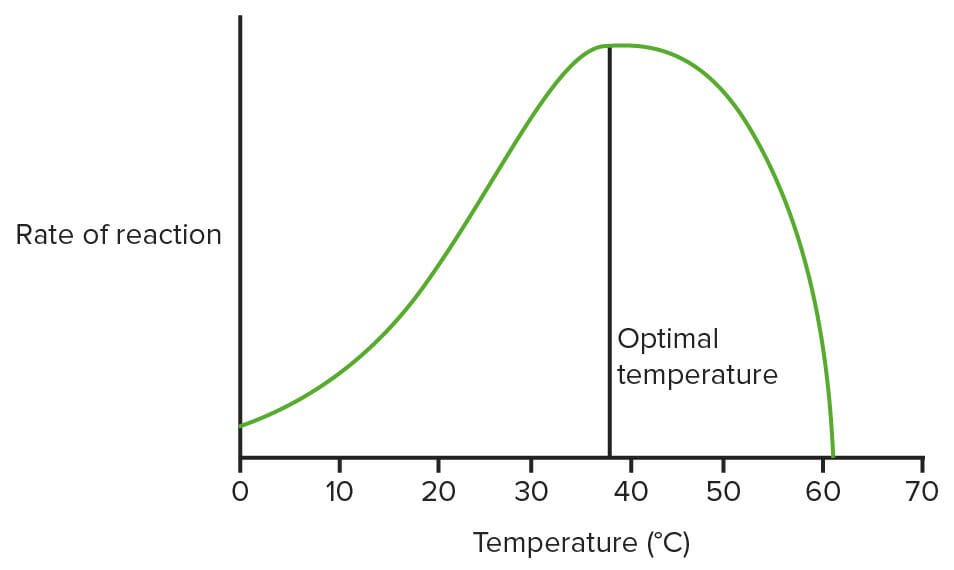
Gráfico que muestra el efecto de la temperatura sobre las enzimas:
Este no está utilizando datos reales, solo un diagrama para mostrar cuál es el patrón general. (Temperatura óptima = 37,5°C aquí)
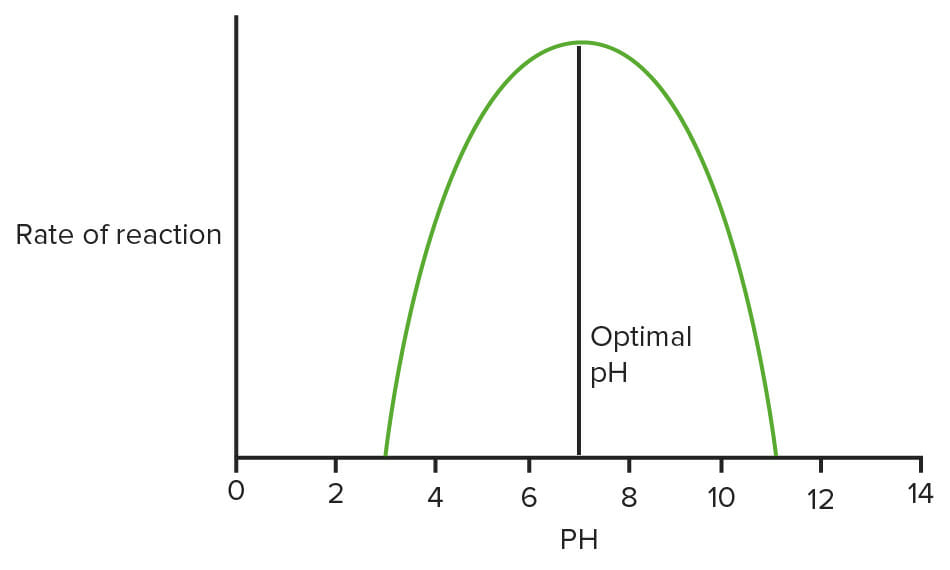
Gráfico que muestra el efecto del pH sobre las enzimas
Imagen: “Effect of temperature on enzymes” por domdomegg. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.Condiciones de estado estable
Los LOS Neisseria primeros cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las concentraciones de sustrato, enzima, complejo enzima-sustrato y el producto ocurren drásticamente y son difíciles de medir. El estado estacionario ocurre cuando los LOS Neisseria cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la enzima y complejo enzima-sustrato son relativamente pequeños.
Velocidad de reacción inicial (Vo)
La velocidad inicial de la reacción se usa para evitar la medición de la reacción inversa una vez que se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia obtenido suficiente producto.
Gráfico de Michaelis-Menten
Trazar la velocidad de reacción inicial (V0) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje y opuesto a la concentración de sustrato en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje x en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un gráfico da como resultado una curva hiperbólica, que se acerca a la velocidad máxima Vmax a altas concentraciones de sustrato debido a la saturación de la enzima con sustrato
Constante de Michaelis-Menten (KM)
KM es la concentración de sustrato a la que se alcanza la mitad de la velocidad máxima (½ Vmáx ) (KM se mide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje x mientras que ½ Vmáx se mide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje y).
Diagrama de Lineweaver-Burke
1/V0 se traza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje y, y 1/[S] se traza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el eje x, lo que da como resultado un gráfico lineal de los LOS Neisseria mismos datos utilizados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cinética de Michaelis-Menten.
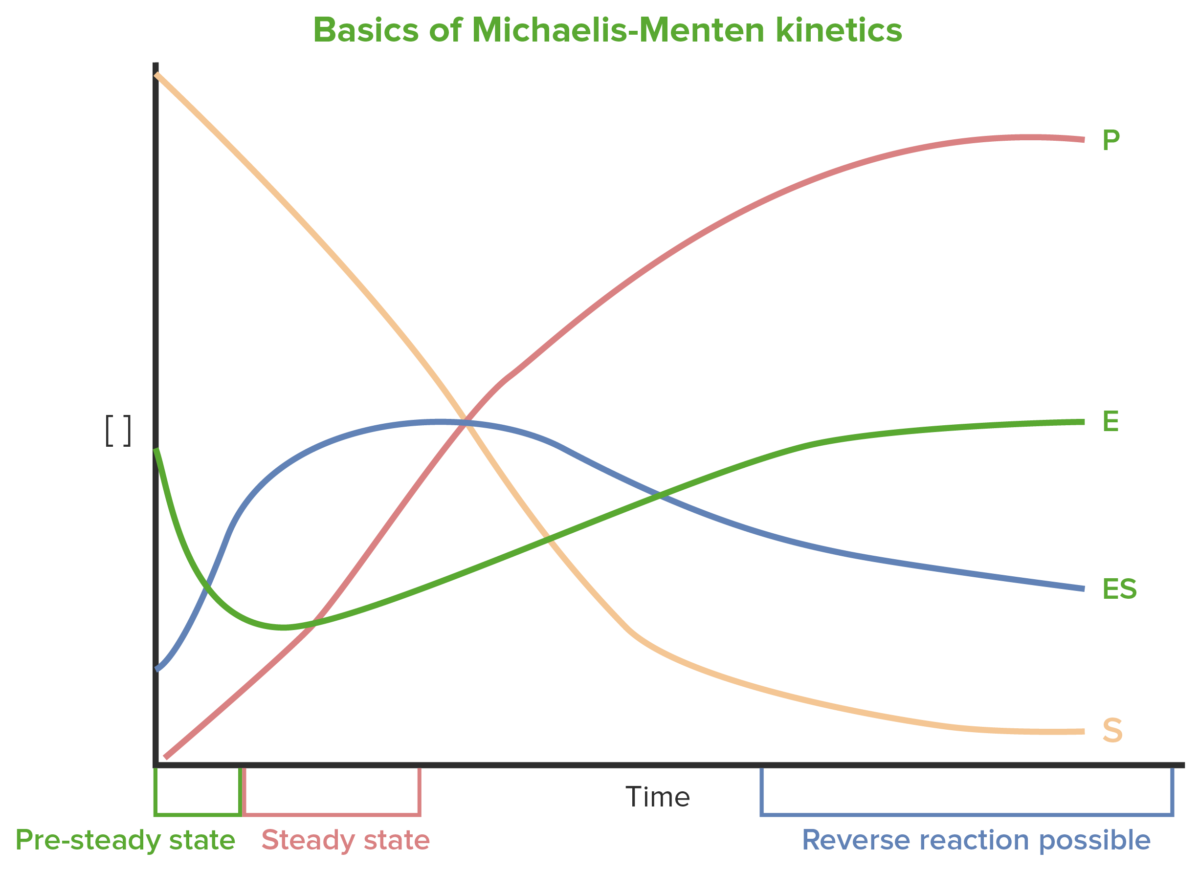
Básicos de la cinética de Michaelis-Menten
Imagen por Lecturio.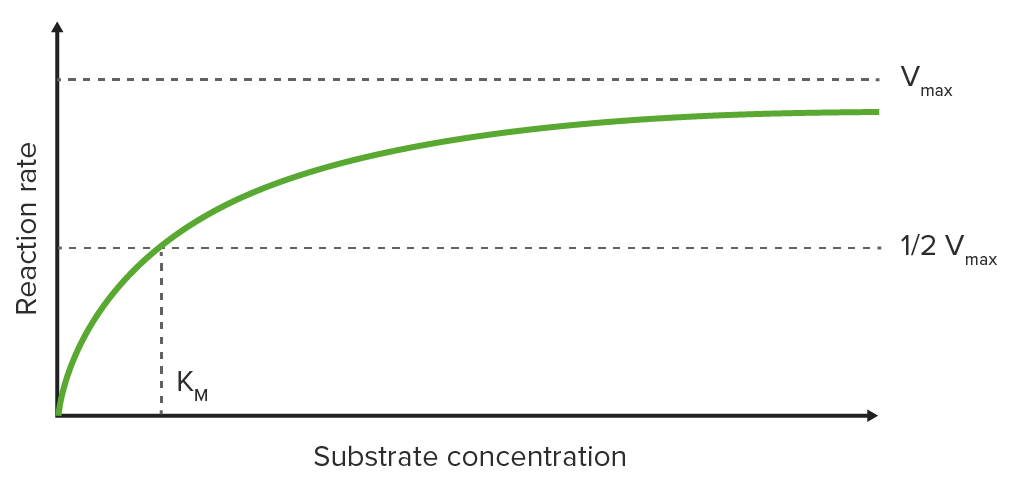
Curva de saturación para una reacción enzimática que muestra la relación entre la concentración de sustrato y la velocidad de reacción
Imagen: “Michaelis Menten curve 2” por Thomas Shafee. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.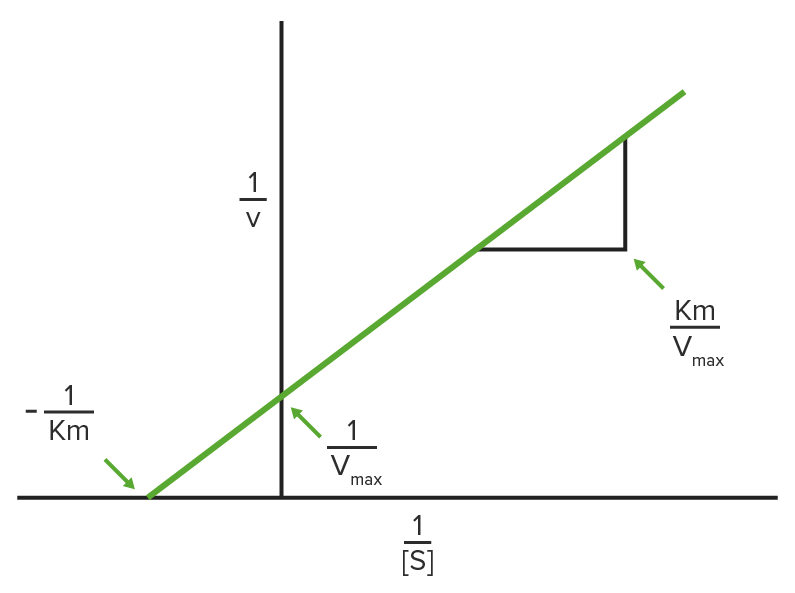
Básicos de la cinética de Michaelis-Menten
Imagen por Lecturio.