El examen pulmonar es la parte de la exploración física que implica el examen de los LOS Neisseria pulmones y las vías aéreas por parte de un trabajador sanitario para evaluar los LOS Neisseria signos patológicos. El examen incluye inspección, auscultación, percusión y palpación. Un examen pulmonar cuidadoso proporciona hallazgos importantes que, junto con los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, pueden guiar al AL Amyloidosis médico hacia un diagnóstico presuntivo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Posicionamiento:
Entorno:
Pasos iniciales:
La 1ra parte del examen pulmonar comienza con una inspección del paciente, anotando los LOS Neisseria hallazgos positivos y negativos pertinentes.
Aspecto general/nivel de distrés del paciente:
Nivel de conciencia:
Frecuencia respiratoria:
| Grupo etario | Edad | Rango de frecuencia respiratoria normal |
|---|---|---|
| Lactante menor | 0–12 meses | 30–60/min |
| Lactante mayor | 1–3 años | 24–40/min |
| Preescolar | 4–5 años | 22–34/min |
| Escolar | 6–12 años | 18–30/min |
| Adolescentes y adultos | 13 años o más | 12–16/min |
Trabajo respiratorio:
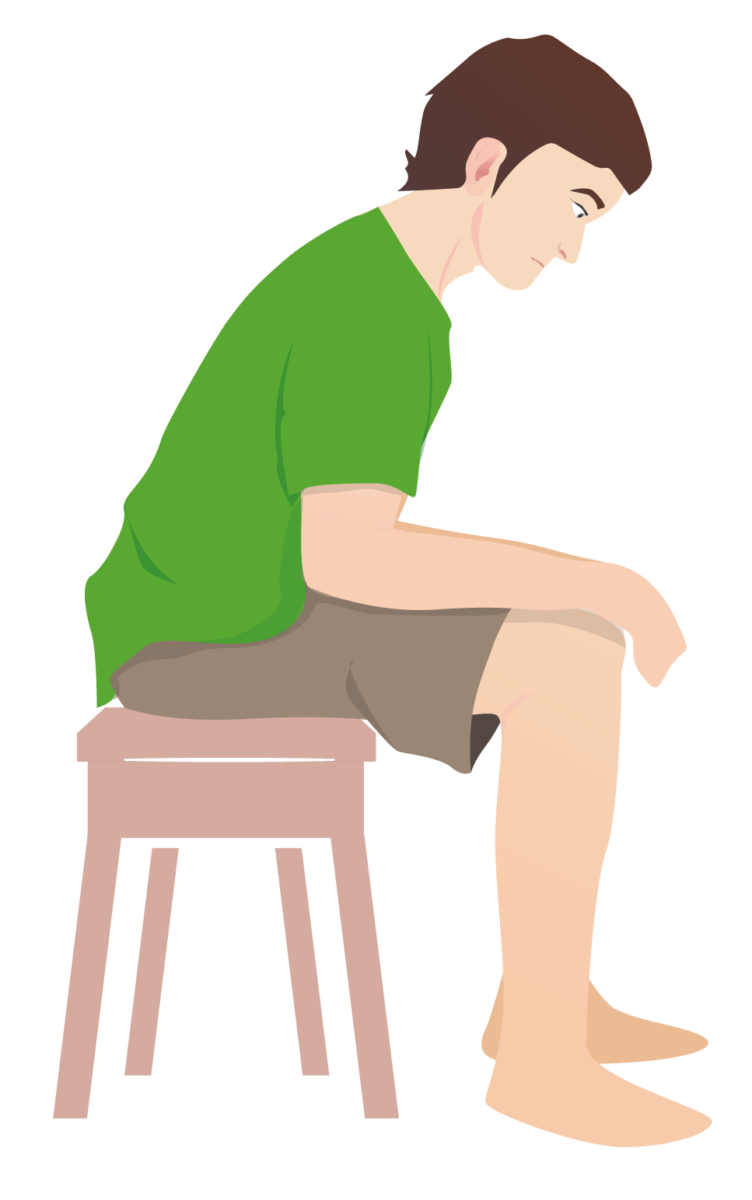

Los pacientes con dificultad respiratoria suelen adoptar de forma natural la posición de trípode:
Los pacientes se inclinan hacia delante mientras están sentados y apoyan las manos en las rodillas. La posición permite la máxima expansión de los pulmones y las vías aéreas para contrarrestar la sensación de asfixia que siente el paciente.
Inspección del tórax:
Examine las extremidades en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum busca de signos de enfermedad respiratoria:
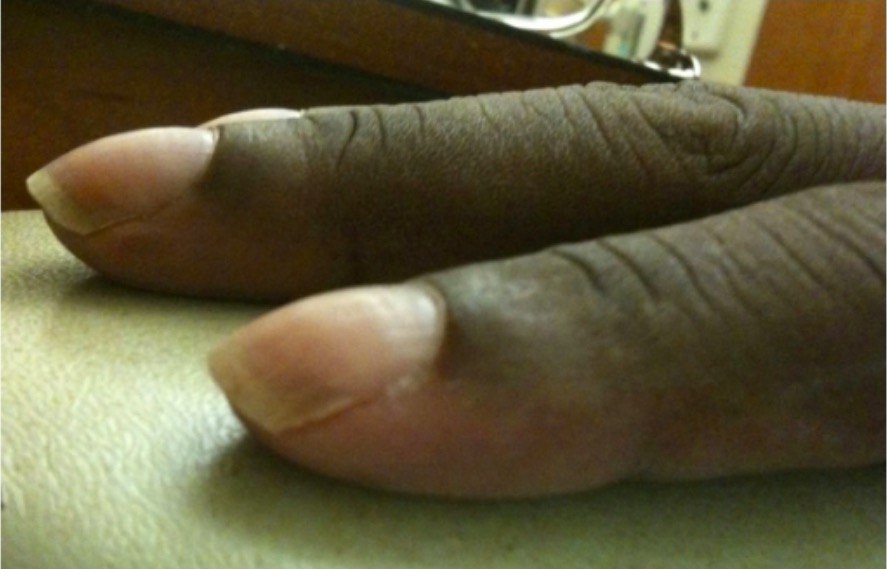
Dedos en palillos de tambor:
Los dedos en palillo de tambor son lechos ungueales anormales y redondeados que suelen estar asociados a afecciones que provocan hipoxemia crónica, como la fibrosis quística o la enfermedad pulmonar intersticial.
Examine el cuello:
Algunos patrones respiratorios ayudan a afinar el diagnóstico diferencial y a dirigir los LOS Neisseria cuidados del paciente.
| Patrón respiratorio | Signos del examen físico | Patologías asociadas |
|---|---|---|
| Taquipnea | Frecuencia respiratoria > 20/min en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos |
|
| Bradipnea | Frecuencia respiratoria < 12/min |
|
| Apnea | Sin respiración |
|
| Fase espiratoria prolongada | Fase espiratoria > ⅔ de la duración de la respiración (inspiración normal ⅓ de la respiración, espiración ⅔ de la respiración) |
|
| Respiración de Cheyne-Stokes |
|
|
| Respiración de Kussmaul | Respiración rápida similar a suspiros | Acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis metabólica (e.g., DKA DKA Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) are serious, acute complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis due to an absolute insulin deficiency. Hyperglycemic Crises) |
| Agónico | Patrón respiratorio irregular | Parada cardiorespiratoria inminente |
La visualización de la pared torácica puede ayudar a determinar la etiología de la patología.
| Hallazgo de la pared torácica | Causas clínicas importantes |
|---|---|
| Caquexia (delgadez extrema o emaciación) |
|
| Obesidad |
|
| Cicatrices quirúrgicas |
|
| Tórax hiperexpandido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum barril |
|
| Anomalías de la columna vertebral |
|
| Anomalías del esternón |
|
| Masas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pared torácica |
|
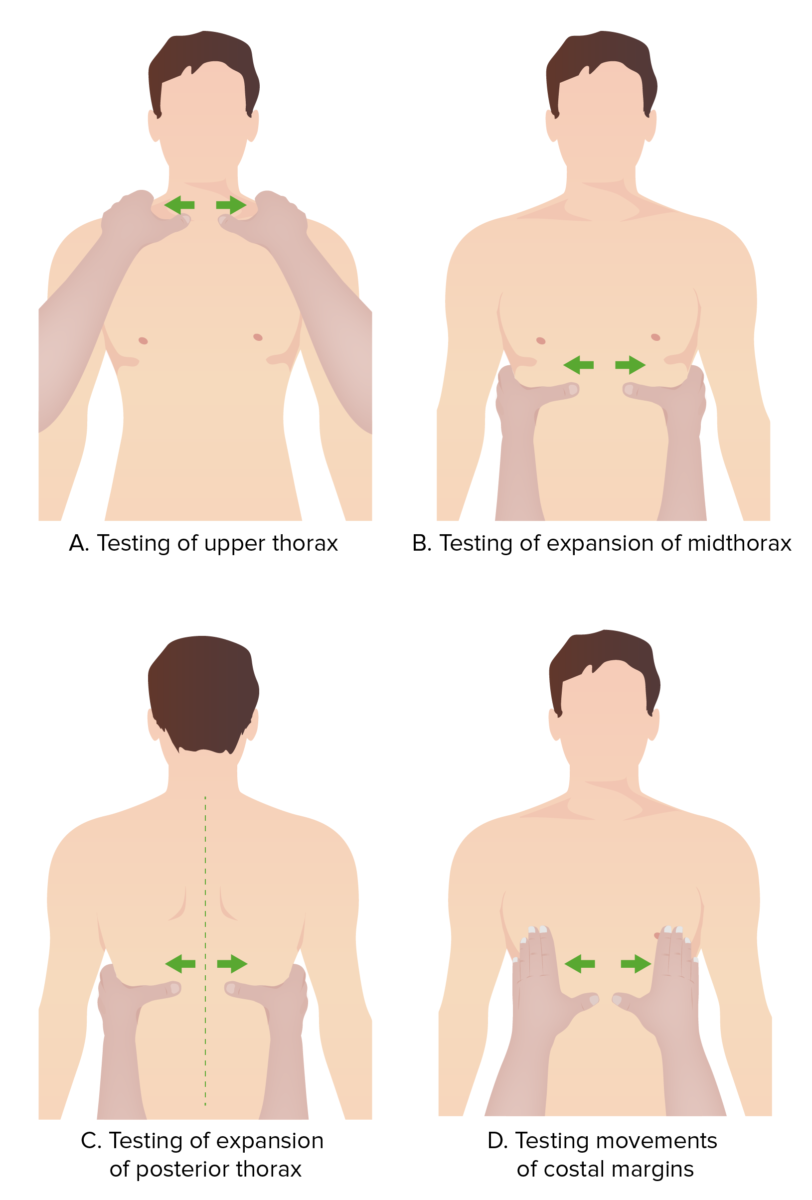
Evaluación del movimiento del tórax:
Durante el examen pulmonar, el médico puede utilizar sus manos como referencia para evaluar diferentes porciones del tórax que se mueven simétricamente durante el ciclo respiratorio.
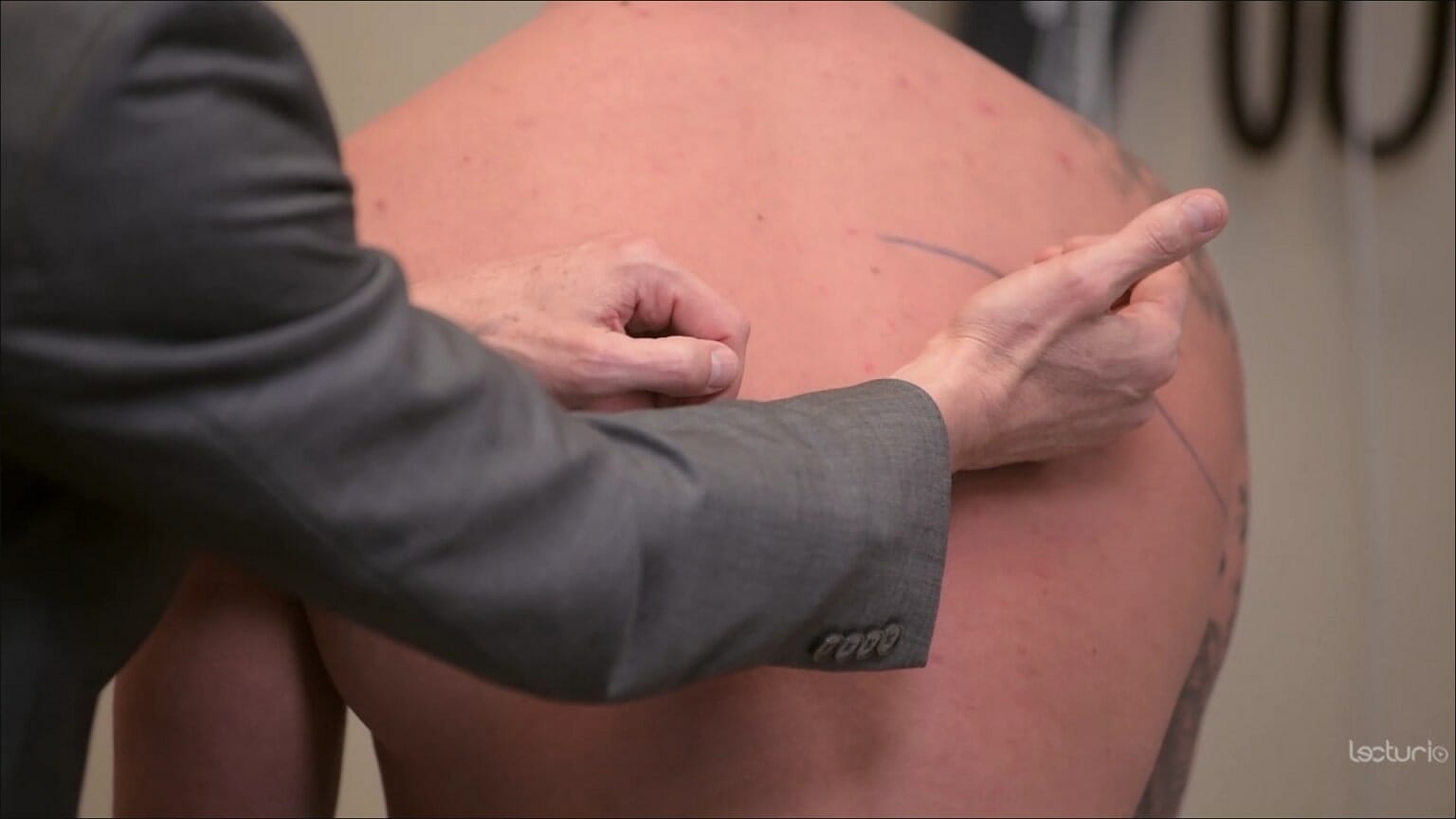
Frémito táctil:
El clínico coloca la superficie cubital de sus manos en ambos lados de la espalda para comparar la transmisión de vibraciones mientras el individuo habla.
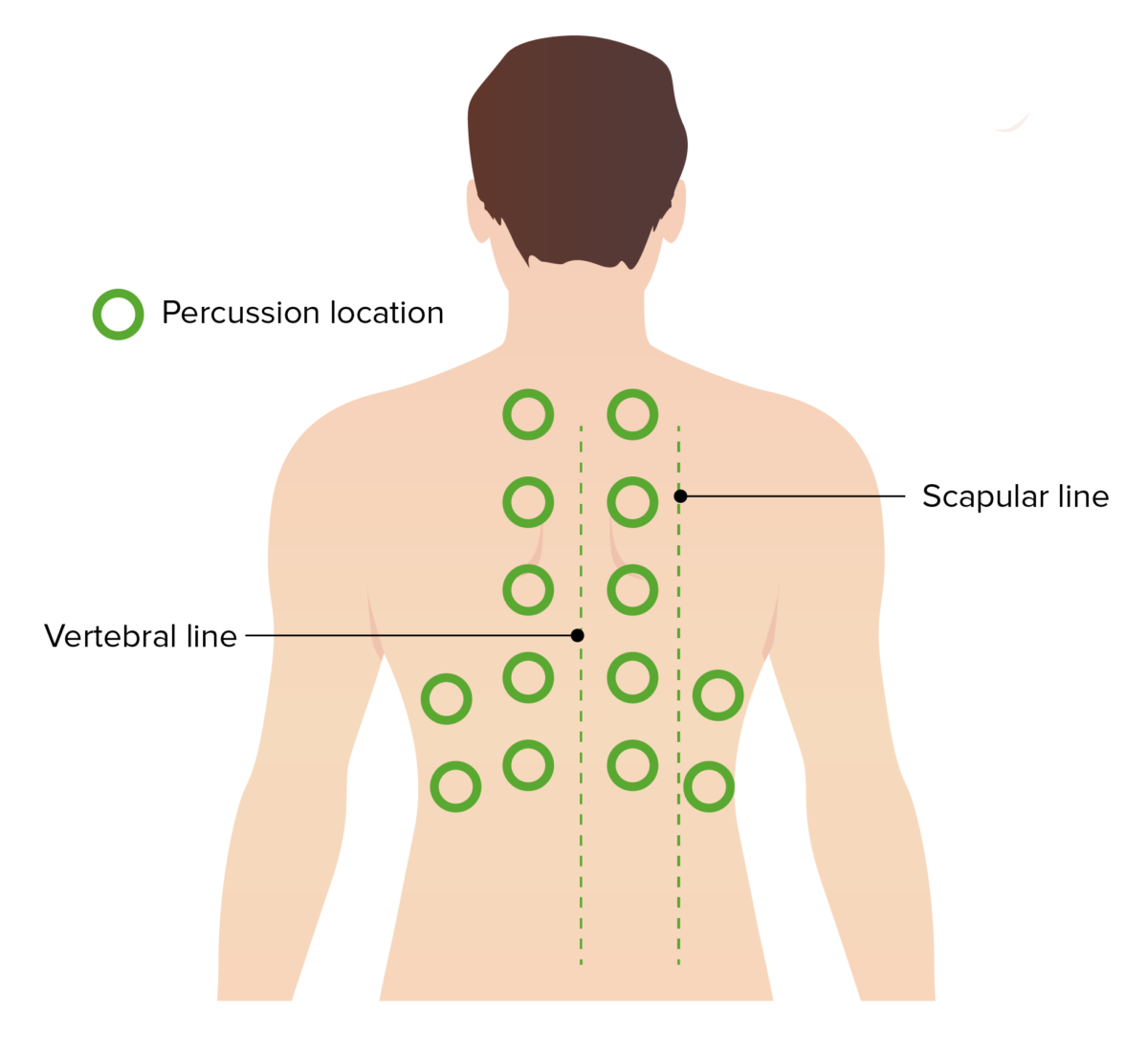
Ubicación de la percusión:
La percusión es un componente clave del examen pulmonar. Una percusión sistemática y simétrica de la espalda del paciente puede ayudar a identificar zonas de matidez compatibles con una infección, un derrame o una atelectasia.
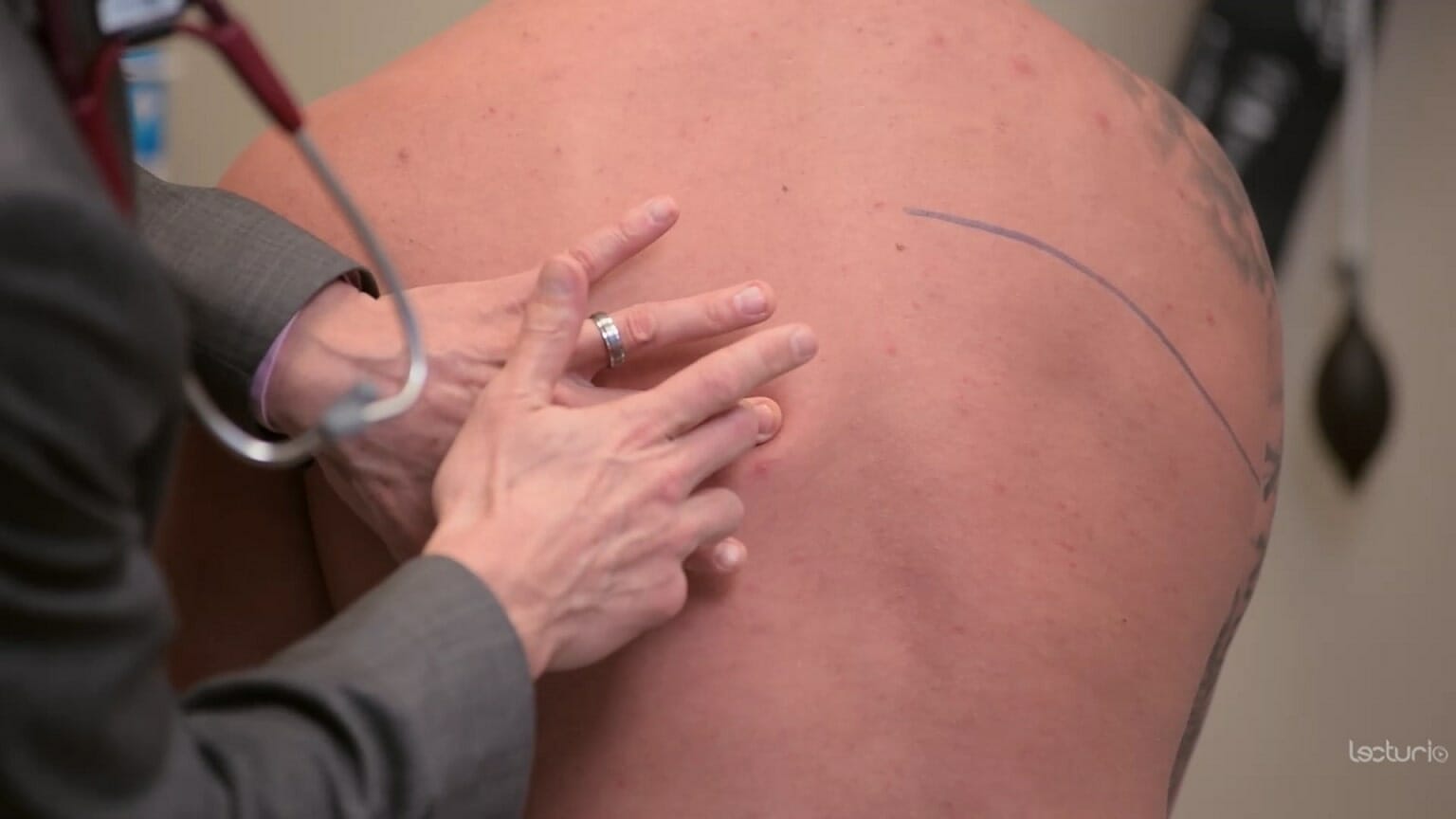
Técnica de percusión:
El dedo medio del clínico se coloca en la zona de interés. La otra mano golpea el dedo medio en la articulación interfalángica distal.
La auscultación se realiza con el diafragma del estetoscopio sobre la piel sin ropa.
| Sonido | Descripción | Localización normal |
|---|---|---|
| Respiración traqueal | Fuerte y de tono agudo | Escuchada sobre el cuello |
| Respiración bronquial | Escuchada sobre las vías aéreas grandes (sobre el esternón) | |
| Respiración broncovesicular | Escuchada sobre los LOS Neisseria espacios intercostales 1 y 2 | |
| Respiración vesicular | Escuchada sobre los LOS Neisseria dos campos pulmonares |
| Sonido | Descripción | Afecciones asociadas |
|---|---|---|
| Crepitantes |
|
|
| Sibilancias o roncus |
|
|
| Estridor inspiratorio | Sonido de respiración musical y de tono agudo debido al AL Amyloidosis flujo de aire turbulento durante la inspiración | Obstrucción por encima de la glotis:
|
| Estridor espiratorio | Sonido de respiración musical y de tono agudo debido al AL Amyloidosis flujo de aire turbulento durante la espiración | Obstrucción por debajo de la glotis:
|
| Estridor bifásico | Sonido respiratorio musical y de tono agudo procedente de un flujo de aire turbulento durante todo el ciclo respiratorio | Obstrucción
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum la glotis:
|
| Frote pleural |
|
Pleuritis Pleuritis Pleuritis, also known as pleurisy, is an inflammation of the visceral and parietal layers of the pleural membranes of the lungs. The condition can be primary or secondary and results in sudden, sharp, and intense chest pain on inhalation and exhalation. Pleuritis |
| Sonidos respiratorios amortiguados o ausentes |
|
|
| Enfermedad | Inspección | Palpación | Percusión | Auscultación |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crisis asmática | Aumento del frémito |
|
Sibilancias espiratorias | |
| Neumotórax |
|
|
Hiperresonancia | Sonidos respiratorios débiles/ausentes |
| Derrame pleural |
|
|
Sordo | Sonido respiratorio débil |
| Atelectasias |
|
|
Sordo | Sonido respiratorio débil |
| Consolidación (neumonía) |
|
↑ Frémito táctil | Sordo |
|
Las siguientes son afecciones comunes encontradas utilizando el examen pulmonar de 4 partes.