La enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico es un espectro de patologías hepáticas que surgen debido a la acumulación de triglicéridos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo incluyen diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus, resistencia a la insulina, obesidad e hipertensión, entre otros. La enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico varía desde el hígado graso o la esteatosis hepática, pero puede conducir a la esteatohepatitis no alcohólica, que presenta depósitos de grasa e inflamación. La lesión hepática progresiva y la fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans se convierten de manera irreversible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cirrosis y, posiblemente, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cáncer hepático primario. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen estar asintomáticos, pero pueden presentar hepatomegalia y molestias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho. Aunque la biopsia hepática es el estándar de oro de diagnóstico, el diagnóstico también se puede establecer mediante los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, imagenología y pruebas de laboratorio. El pilar del tratamiento son las modificaciones del estilo de vida (pérdida de peso y ejercicio) con control de las comorbilidades asociadas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El hígado graso se subdivide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tipo alcohólico o no alcohólico.
Enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico:
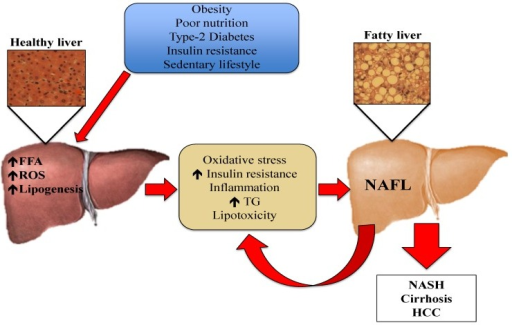
Patogenia de la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico: factores de riesgo como la obesidad, la mala nutrición, la diabetes tipo 2, la resistencia a la insulina y el estilo de vida sedentario provocan la salida de ácidos grasos libres del tejido adiposo al hígado. El aumento de ácidos grasos libres en el tejido hepático estimula la síntesis y acumulación de triglicéridos. Este exceso de lípidos induce una respuesta inmune, provocando la producción de citoquinas, especies reactivas de oxígeno y empeorando la resistencia a la insulina. El estrés oxidativo provoca peroxidación de lípidos y daño tisular, lo que amplifica la respuesta inflamatoria y conduce a la progresión de la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico
HCC: carcinoma hepatocelularSi la progresión no se revierte, la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico conduce a esteatohepatitis no alcohólica. Con más daño hepático, la cirrosis y el carcinoma hepático (ambos irreversibles) se pueden convertir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum resultados potenciales:
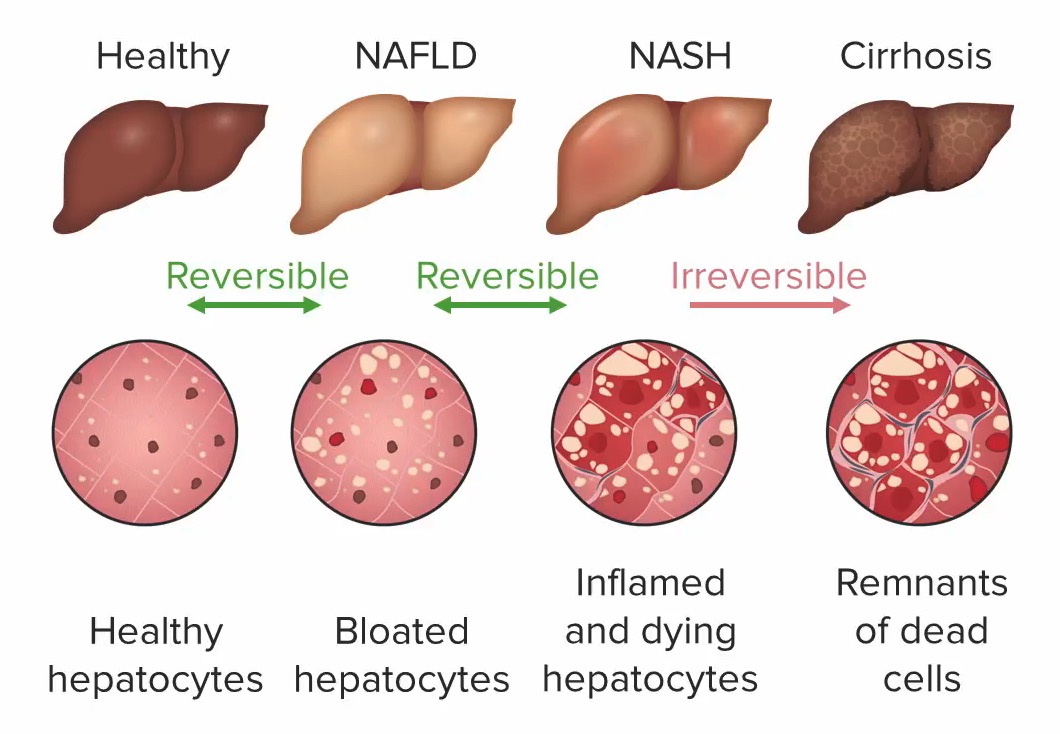
Progresión de la enfermedad hepática por esteatosis:
1: Hepatocitos sanos: sin daño hepático
2: Hepatocitos abultados con esteatosis (distendidos por gotitas de grasa), sin inflamación: enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico/esteatosis (todavía reversible)
3: Hepatocitos inflamados y moribundos, con posible fibrosis: esteatohepatitis no alcohólica (todavía reversible)
4: Células muertas: cirrosis (daño hepático irreversible)
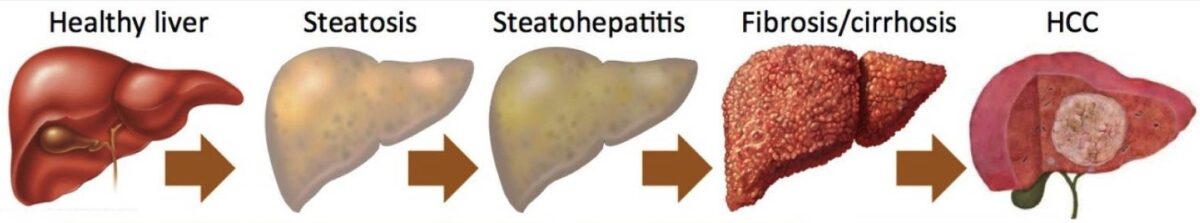
Progresión de la enfermedad hepática: esteatosis a carcinoma hepatocelular
Imagen: “Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease” por Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, 150 S. Huntington Ave., Room 6A-46, Boston, MA 02130, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editado por Lecturio.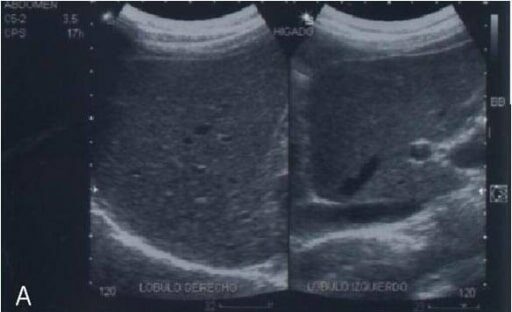
Ultrasonido abdominal de un paciente con enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico que muestra un aumento de la ecotextura del parénquima hepático debido a la infiltración de grasa (“hígado brillante”)
Imagen: “Abdominal ultrasonography of a patient with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease” por Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), Mexico, 04510, Mexico. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editado por Lecturio.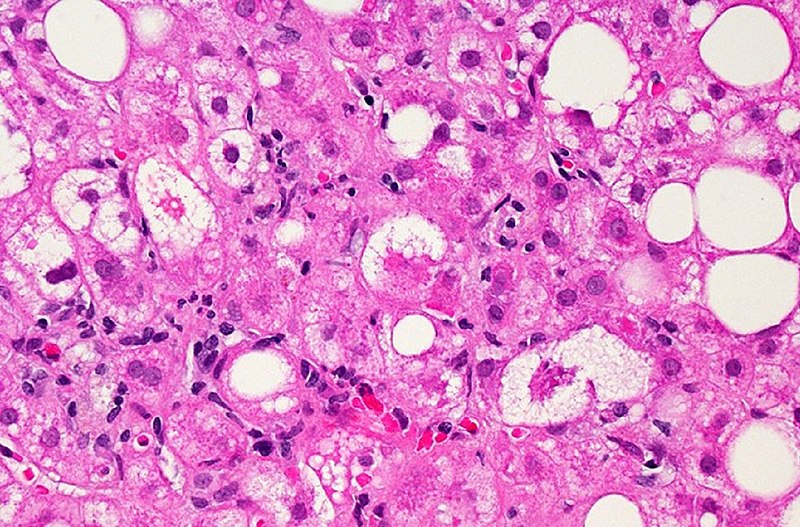
Imagen microscópica del tejido hepático afectado por enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólico: las manchas blancas grandes y pequeñas son gotitas de grasa en exceso que llenan las células hepáticas (hepatocitos).
Imagen: “Liver Tissue with NAFLD” por Dr. David Kleiner, National Cancer Institute/NIH. Licencia: Dominio Público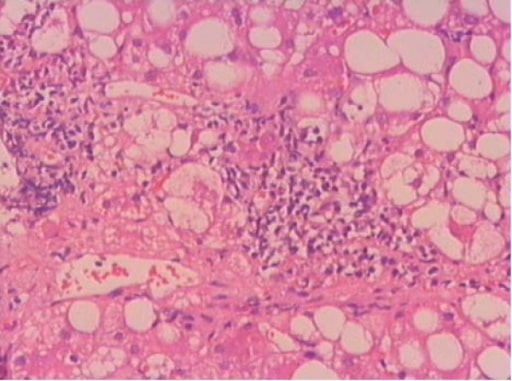
La inflamación portal es un hallazgo diagnóstico en esteatohepatitis no alcohólica. El corte histopatológico se obtuvo de un paciente con esteatohepatitis.
Imagen: “F1” por Gastroenterology Department, Ege University Faculty of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.0