La enfermedad de Wilson (degeneración hepatolenticular) es un trastorno autosómico recesivo causado por varias mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen ATP7B, que regula el transporte de cobre dentro de los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos. La disfunción de este mecanismo de transporte conduce a acumulaciones anormales de cobre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado, el cerebro, los LOS Neisseria ojos y otros órganos, con los LOS Neisseria consiguientes trastornos; hepáticos, neurológicos y psiquiátricos importantes y expresados de forma variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables. La afectación hepática puede manifestarse como hepatitis, insuficiencia hepática o cirrosis, mientras que la afectación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios basales provoca signos extrapiramidales. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes son diagnosticados entre los LOS Neisseria 5 y los LOS Neisseria 35 años (media: 13 años). El diagnóstico se establece si el paciente tiene ceruloplasmina plasmática baja, depósitos de cobre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la córnea (anillos de Kayser-Fleischer) y niveles elevados de cobre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la orina. Sin embargo, a menudo se necesitan otras pruebas, ya que no todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes tendrán todos estos hallazgos. El pronóstico es bueno para pacientes sin enfermedad hepática avanzada y que son tratados con los LOS Neisseria agentes quelantes penicilamina o trientina. La enfermedad de Wilson no tratada es en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum última instancia fatal, y los LOS Neisseria pacientes mueren por cirrosis, insuficiencia hepática aguda o complicaciones secundarias a una enfermedad neurológica progresiva.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad de Wilson generalmente se presenta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y adultos jóvenes. Raramente se manifiesta después de los LOS Neisseria 40 años de edad. Las manifestaciones son principalmente hepáticas, neurológicas y psiquiátricas y pueden incluir:
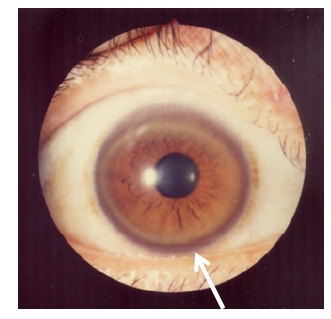
Anillo de Kayser-Fleischer: depósito de cobre en la córnea
Imagen: “Kayser-Fleischer rings” por Bentham Science Publishers, 2012. Licencia: CC-BY-2.5Presentación clínica de la enfermedad de Wilson: ABCD