La enfermedad de Hirschsprung, también conocida como aganglionosis congénita o megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon congénito, es una anomalía congénita del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy causada por la incapacidad de las células ganglionares derivadas de la cresta neural para migrar al AL Amyloidosis colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy distal. La falta de inervación afecta siempre al AL Amyloidosis recto y se extiende de forma proximal y contigua a distancias variables. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se diagnostican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el periodo neonatal, con una tríada clásica de síntomas que incluye retraso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la expulsión del meconio, distensión abdominal y vómitos biliosos. Los LOS Neisseria individuos con grados menos graves de obstrucción funcional pueden no ser diagnosticados hasta más tarde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la niñez, cuando presentan síntomas de estreñimiento crónico refractario, distensión abdominal y retraso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el crecimiento. El diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Hirschsprung se confirma por la ausencia de células ganglionares en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la biopsia rectal tras la realización de pruebas no invasivas como la manometría anorrectal y el uso de enema de contraste. La resección quirúrgica del segmento agangliónico es el tratamiento estándar.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad de Hirschsprung, también conocida como aganglionosis congénita o megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon congénito, es una anomalía congénita del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy causada por la incapacidad de las células ganglionares derivadas de la cresta neural para migrar al AL Amyloidosis colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy distal.
La fisiopatología detrás la enfermedad de Hirschsprung es la ausencia completa de células ganglionares (aganglionosis) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la red nerviosa intrínseca del intestino debido al AL Amyloidosis fracaso de estas células, derivadas de la cresta neural, para migrar completamente a los LOS Neisseria plexos mientéricos de la pared del colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy.
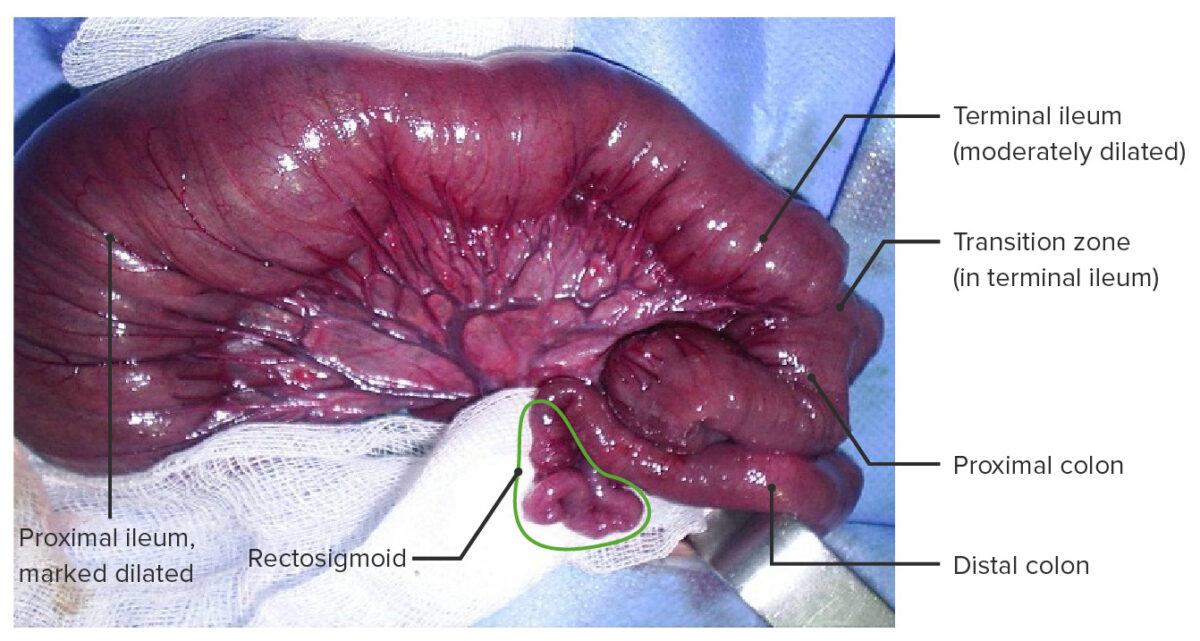
Enfermedad de Hirschsprung con aganglionosis colónica total que incluye un segmento corto del íleon terminal.
Este tipo de aganglionosis se da en el < 5% de los casos.
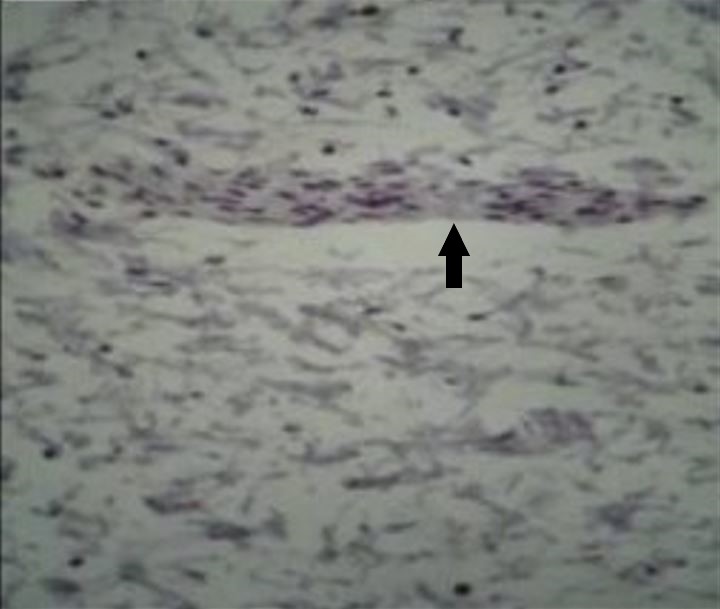
Microfotografía de un segmento de intestino afectado por la enfermedad de Hirschsprung teñido con el marcador inmunohistoquímico calretina, que no muestra la tinción marrón de las células ganglionares dentro de un nervio (flecha) en el plexo mientérico
Imagen: “Total absence of staining after calretinin immunohistochemistry in the aganglionic segment” por Hiradfar M, Sharifi N, Khajedaluee M, Zabolinejad N, Taraz Jamshidi S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, editada por Lecturio.La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria individuos con enfermedad de Hirschsprung son diagnosticados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 1er mes de vida. Los LOS Neisseria individuos con una enfermedad menos grave pueden no presentar síntomas hasta los LOS Neisseria 3 años de edad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aproximadamente el 10% de los LOS Neisseria casos.
Si se sospecha que la enfermedad de Hirschsprung está basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las presentaciones clínicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria períodos neonatal o posnatal, se utilizan las siguientes pruebas diagnósticas:
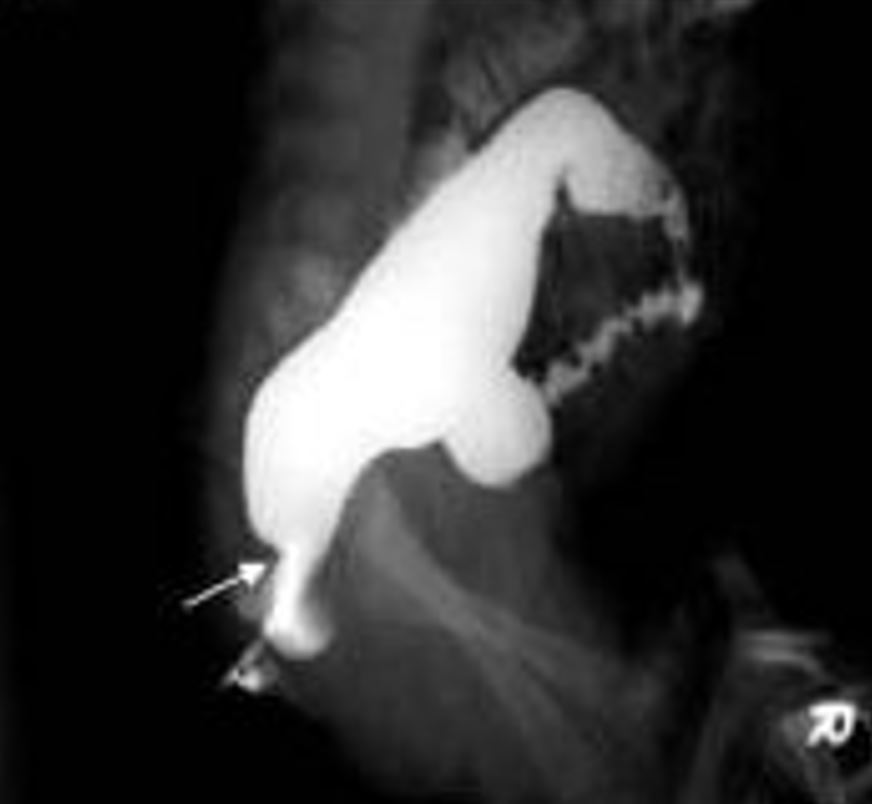
Enfermedad de Hirschsprung vista en un estudio de enema de bario con contraste, con la flecha mostrando la “zona de transición” entre el intestino normal y el agangliónico
Imagen: “Contrast enema showing a CETZ at rectosigmoid, arrow” por Pratap, A., et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, recortado por Lecturio.Las causas de obstrucción intestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el periodo neonatal pueden distinguirse de la enfermedad de Hirschsprung en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum base a sus características clínicas y a la presencia de ganglios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una biopsia rectal.
Causas de obstrucción intestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lactantes y niños mayores: