La deficiencia de aromatasa es una afección genética muy rara con herencia autosómica recesiva. La deficiencia de aromatasa se caracteriza por una privación congénita de estrógenos con un aumento de los LOS Neisseria niveles de testosterona debido a la disminución de los LOS Neisseria niveles de la enzima aromatasa. Las mujeres afectadas presentan un desarrollo anormal de los LOS Neisseria genitales externos, virilización, amenorrea primaria y estatura elevada. Los LOS Neisseria varones suelen desarrollar síntomas más tarde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida, incluyendo hiperinsulinemia y trastornos del metabolismo de los LOS Neisseria lípidos. Los LOS Neisseria individuos afectados por la deficiencia de aromatasa tienen un mayor riesgo de desarrollar osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una terapia de sustitución hormonal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Acné por virilización durante la semana 12–30 de embarazo
Imagen: “Retoqueacne”por Jesus Angel Rey. Licencia: Dominio Público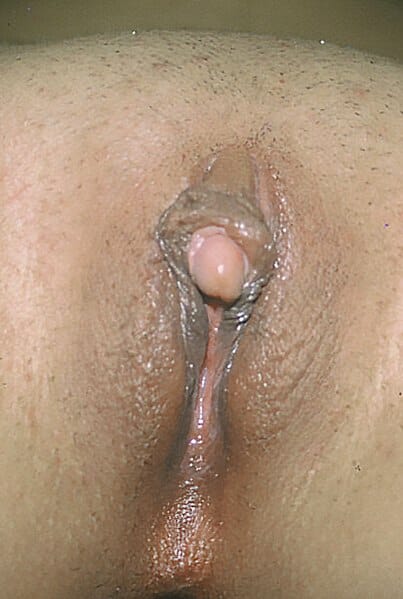
Clitoromegalia, otro signo que se produce debido a la virilización
Imagen: “Clitoromegaly” por Copcu, E, Aktas, A, Sivrioglu, N, Copcu, O, Oztan, Y. Licencia: CC BY 2.0
Radiografía de un hombre de 27 años con deficiencia de aromatasa
La radiografía simple de hueso de la muñeca y la mano izquierdas demuestra que las epífisis metacarpianas y de las falanges están abiertas. La edad ósea estimada es de 15 años.