El ciclo del glioxilato es una vía anabólica que se considera una variación del ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico. El ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum plantas, bacterias y hongos y el acetil-CoA se convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum succinato. Se pensaba que el ciclo del glioxilato no se producía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum animales debido a la ausencia de las enzimas isocitrato liasa y malato sintasa; sin embargo, esta hipótesis está siendo aún explorada. El ciclo del glioxilato ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria glioxisomas, que son peroxisomas especializados. No existen reacciones de descarboxilación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ciclo del glioxilato. El ciclo del glioxilato permite que las células utilicen 2 unidades de carbono de acetato y las conviertan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 4 unidades de carbono y succinato, para la producción de energía y la biosíntesis. Además, cada vuelta del ciclo produce una molécula de flavín adenín dinucleótido hidruro 2 (FADH2, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y nicotinamida adenina dinucleótido hidruro (NADH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés).
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
Las plantas, hongos y bacterias requieren de carbohidratos para la energía y la síntesis de la pared celular (e.g., celulosa, quitina y glicanos). El ciclo del glioxilato permite a los LOS Neisseria organismos producir carbohidratos utilizando acetil-CoA a partir de la β-oxidación de ácidos grasos.
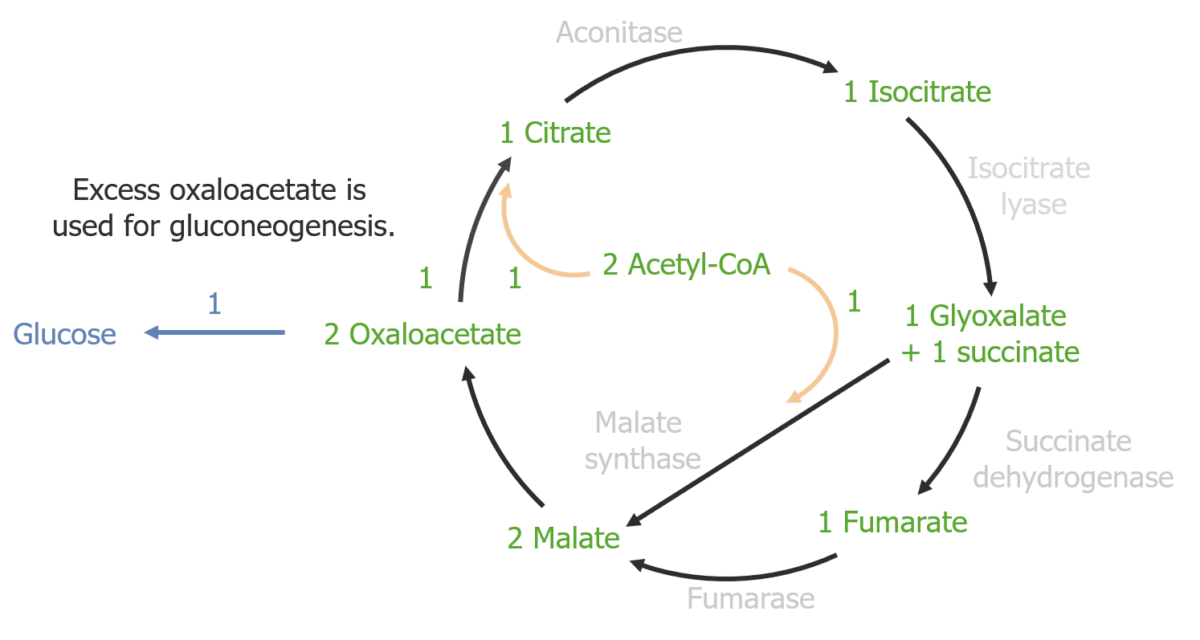
Figura que representa el ciclo del glioxilato
Imagen por Lecturio.Las 2 enzimas clave involucradas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ciclo del glioxilato producen 2 moléculas de malato, que a su vez producen 2 moléculas de oxalacetato. La molécula de oxalacetato sobrante se utiliza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gluconeogénesis para la producción de glucosa. Las 2 enzimas clave son:
El ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico es el principal medio para generar energía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo.
| Ciclo de glioxilato | Ciclo del ácido tricarboxílico | |
|---|---|---|
| Sitio | Glioxisomas de plantas, hongos y posiblemente vertebrados | Mitocondrias animales |
| Número de carbonos | Entrada de 4 carbonos | Entrada de 2 carbonos |
| Moléculas de CO2 liberadas | Ninguna | 2 |
| Número de reacciones oxidativas | 2 | 4 |
| Energía producida por ciclo |
|
|
| Síntesis neta de glucosa | Síntesis neta de glucosa debido a la formación de 1 molécula extra de oxalacetato | Sin síntesis neta de glucosa |
Se han identificado genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure del ciclo del glioxilato en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2 organismos capaces de sobrevivir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria macrófagos: la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology M. tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis y el hongo C. albicans. Las enzimas necesarias para que progrese el ciclo del glioxilato no están presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria seres humanos y, por lo tanto, son objetivos ideales para los LOS Neisseria nuevos antibióticos.