Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B, también conocidos como células B, son componentes importantes del sistema inmunitario adaptativo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea, las células madre hematopoyéticas pasan por una serie de pasos para convertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum linfocitos B maduros vírgenes. Las células migran a los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides secundarios para su activación y posterior maduración. El proceso implica la estimulación con antígenos, con o sin la ayuda de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T. La activación independiente de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T genera una respuesta inmunitaria de corta duración (a través de las células plasmáticas), y esto se observa con antígenos como los LOS Neisseria lipopolisacáridos bacterianos. La activación dependiente de linfocitos T, por otro lado, produce tanto células plasmáticas como linfocitos B de memoria. Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B activados luego proliferan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria centros germinales, pero no todas se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum linfocitos B efectores. A través de la hipermutación somática, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B se someten a mecanismos adicionales para aumentar la afinidad del anticuerpo por el antígeno. Solo aquellos con receptores de linfocito B de alta afinidad avanzan posteriormente hacia la diferenciación terminal. Luego, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B pasan por un cambio de clase (de IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions a otra clase de Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia) bajo la influencia de las citoquinas. Después del cambio de clase, los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células plasmáticas (que producen anticuerpos) o linfocitos B de memoria (que establecen una respuesta inmunitaria secundaria robusta).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B (derivados de la bursa), o células B, son un tipo de linfocito que surge del progenitor linfoide común.
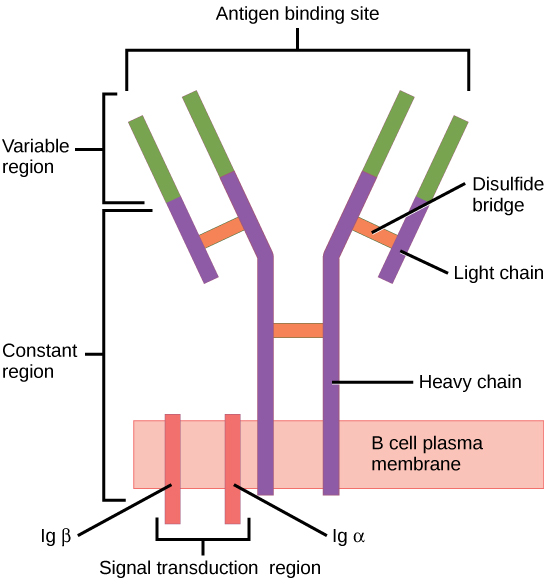
El receptor de linfocitos B consiste en la molécula de Ig y la molécula de señalización:
La Ig contiene 2 cadenas pesadas idénticas y 2 cadenas ligeras idénticas unidas por un puente disulfuro. La Ig unida a la membrana está anclada a la superficie celular.
Para alcanzar la funcionalidad, el linfocito B pasa por estadios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea y los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides secundarios:
| Estadio de maduración | Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia | Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos B | Eventos asociados |
|---|---|---|---|
| Independiente de antígeno | |||
| Célula pre-pro-B | ADN de línea germinal | Ninguno | Sin expresión de cadenas pesadas o ligeras |
| Célula pro-B | IgH con recombinación D-J | Ninguno | Comienza a expresar CD19, CD34 y sistema del antígeno leucocitario humano (HLA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)-DR (antígeno de histocompatibilidad de clase II) |
| Célula pre-B | IgH con recombinación V-D-J | Se forma el pre-receptor de linfocito B:
|
Aparecen otros marcadores (CD79, CD10, CD20, CD40 CD40 Members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily with specificity for CD40 ligand. They are found on mature B-lymphocytes, some epithelial cells; and lymphoid dendritic cells. Evidence suggests that CD40-dependent activation of B-cells is important for generation of memory B-cells within the germinal centers. Mutations in the CD40 antigen gene result in hyper-igm immunodeficiency syndrome, type 3. Signaling of the receptor occurs through its association with tnf receptor-associated factors. Hyper-IgM Syndrome y la desoxinucleotidil transferasa terminal entre ellos). |
| Linfocito B inmaduro |
|
Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocito B maduro (molécula de IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) | La expresión de HLA-DR, CD19, CD20 y CD40 CD40 Members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily with specificity for CD40 ligand. They are found on mature B-lymphocytes, some epithelial cells; and lymphoid dendritic cells. Evidence suggests that CD40-dependent activation of B-cells is important for generation of memory B-cells within the germinal centers. Mutations in the CD40 antigen gene result in hyper-igm immunodeficiency syndrome, type 3. Signaling of the receptor occurs through its association with tnf receptor-associated factors. Hyper-IgM Syndrome continúa, pero no la de los LOS Neisseria otros marcadores (e.g., CD10, CD34 y desoxinucleotidil transferasa terminal). |
| Linfocito B maduro (virgen) |
|
Con receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocitos B maduro ( IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) → salida de médula ósea | Todos expresan CD19 y CD20. |
| Dependiente de antígeno | |||
| Linfocito B maduro ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tejidos linfoides secundarios) | Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de linfocito B maduro (expresa IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions e IgD IgD An immunoglobulin which accounts for less than 1% of plasma immunoglobulin. It is found on the membrane of many circulating B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions al AL Amyloidosis estar dentro de los LOS Neisseria tejidos linfoides secundarios) | Las células pueden descansar o puede ocurrir la activación de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B: los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B interactúan con el antígeno exógeno y/o los LOS Neisseria linfocitos T colaboradores. | |
| Linfocito B activado | Cambio de clase | Una vez activado, puede cambiar a IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions o permanecer como IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | |
| Linfocito B de memoria |
|
||
| Célula plasmática |
|
||
Estadios de diferenciación del linfocito B:
En estadios independientes del antígeno, la producción de linfocitos B comienza con la célula madre hematopoyética, que se convierte en un progenitor linfoide común y luego en una célula pre-pro-B o célula progenitora B. Los siguientes pasos incluyen la recombinación de genes para ensamblar la molécula de Ig. Las cadenas pesadas de Ig comienzan con la recombinación de los segmentos de diversidad y acoplamiento para formar la célula pro-B. En el siguiente paso (células pre-B), se completa la recombinación de la cadena pesada de Ig (región variable, segmento de diversidad, región de acoplamiento) y se forma el receptor de célula pre-B. Se produce la recombinación de la cadena ligera (kappa (κ) o lambda (λ)), lo que da como resultado la expresión de una molécula de anticuerpo IgM completa por parte de un linfocito B inmaduro. Sigue la formación del linfocito B maduro (virgen) con IgM e IgD.
Los estadios dependientes de antígeno ocurren en tejidos linfoides secundarios. Una vez que el linfocito B maduro produce IgM e IgD, puede tener lugar un cambio de clase para producir IgE, IgG e IgA. Los linfocitos B se activan y se convierten en células plasmáticas o linfocitos B de memoria.
El linfocito B migra desde la médula ósea a los LOS Neisseria órganos linfoides secundarios. Este proceso toma una serie de medidas para producir un linfocito B diferenciado funcional: activación por un antígeno, proliferación, maduración por afinidad, cambio de clase y diferenciación ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum células plasmáticas o linfocitos B de memoria).
Sección histológica del ganglio linfático que muestra la corteza, la paracorteza y la médula
Imagen por Geoffrey Meyer, editada por Lecturio.
Estructura y regiones funcionales de un ganglio linfático: comprenden una cápsula fibrosa rica en colágeno y un seno subcapsular subyacente.
Las células se segregan en (1) la corteza (que consta de linfocitos B, linfocitos T colaboradores foliculares y células dendríticas foliculares dispuestos en folículos primarios, en los que los linfocitos B examinan los antígenos presentados en la red estromal de células dendríticas foliculares); y (2) la paracorteza (aloja los linfocitos T, las células dendríticas y células reticulares fibroblásticas que forman redes de células estromales y fibras reticulares).
La médula interna está compuesta de tejidos linfáticos (cordones medulares) separados por senos medulares que consisten en linfa.
La activación de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B por presentación de antígeno puede tener diferentes caminos:
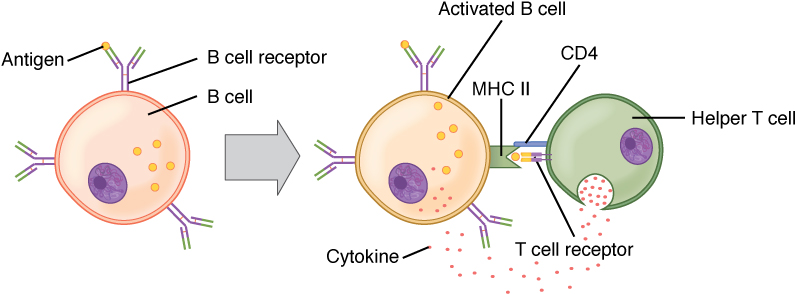
Activación de linfocitos B (dependiente de linfocitos T):
El antígeno circulante interactúa con el receptor de linfocito B. El antígeno se somete a endocitosis y se degrada y los componentes peptídicos forman un complejo con moléculas del CMH II de la superficie celular. Los linfocitos T colaboradores foliculares (Tfh) (linfocitos T colaboradores CD4+ especializados) reconocen y se unen al complejo antígeno-CMH II. Los Tfh liberan citocinas, lo que lleva a la activación y proliferación de linfocitos B. Los linfocitos B activados ingresan a los centros germinales, donde continúan el proceso, lo que lleva a la diferenciación.
Procesos de activación y maduración de los linfocitos B que tienen lugar en el centro germinal:
Al activarse, el linfocito B se mueve desde la zona del manto y entra al centro germinal. Ocurre la proliferación de linfocitos B (expansión clonal) y la afinidad del anticuerpo por el antígeno aumenta a través del proceso de hipermutación somática. Los ciclos repetidos de proliferación e hipermutación afinan el receptor de linfocito B. Sin embargo, no todos los linfocitos B continúan diferenciándose, especialmente si la afinidad es débil. La apoptosis ocurre si la unión antígeno-anticuerpo no se optimiza. Aquellos con fuerte afinidad sobreviven (selección), con la ayuda de señales de supervivencia de células dendríticas foliculares y linfocitos T. Estos linfocitos B seleccionados pasan al cambio de clase y la diferenciación en células plasmáticas o linfocitos B de memoria.
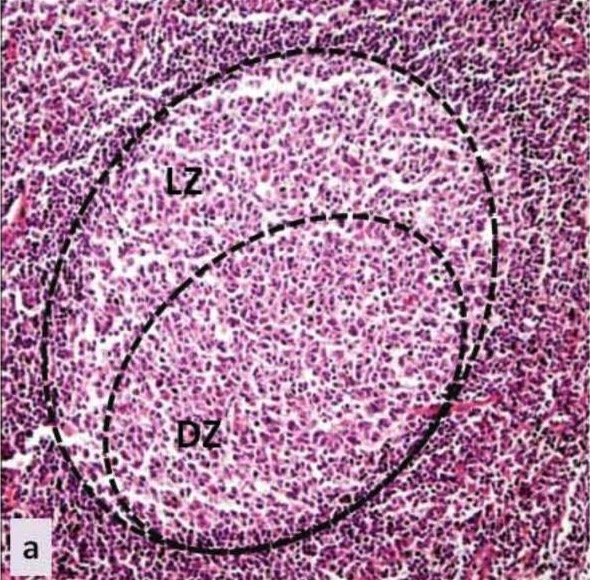
Centro germinal: histología del centro germinal de un tejido linfoide secundario
LZ: zona clara (en inglés)
DZ: zona oscura (en inglés)
Resumen del desarrollo de los linfocitos B hasta la diferenciación (desde la médula ósea hasta el órgano linfoide secundario):
Desarrollo de linfocitos B:
En la médula ósea, los linfocitos B se convierten en linfocitos B inmaduros, un proceso en el que se ensambla el receptor de linfocitos B. Luego, el linfocito B migra a los órganos linfoides secundarios, donde se produce la activación.
Activación de linfocitos B:
El antígeno se une al linfocito B con el receptor de “mejor compatibilidad”. Una vía de activación es independiente de los linfocitos T, por lo que el linfocito B activado se activa para diferenciarse en una célula plasmática de vida corta (que produce anticuerpos) sin la ayuda del linfocito T. En la activación dependiente de linfocitos T, el linfocito T reconoce el antígeno CMH II y desencadena la proliferación del linfocito B en el centro germinal del tejido linfoide.
Proliferación y maduración:
El proceso va seguido de una hipermutación somática (una mutación programada para ajustar aún más la afinidad del anticuerpo por el antígeno). Los ciclos repetidos de proliferación e hipermutación refinan el receptor de linfocito B. Solo aquellos con la mejor afinidad serán seleccionados y sobrevivirán; aquellos con baja afinidad sufrirán apoptosis. Los linfocitos B supervivientes luego pasan por una recombinación de cambio de clase, en la que se cambia la composición de la cadena pesada (IgM a otros isotipos) con la ayuda de citoquinas.
Diferenciación:
Estos linfocitos B luego se diferencian en células plasmáticas y linfocitos B de memoria, dejando el centro germinal.
Desde la producción inicial de linfocitos B, muchos procesos permiten a los LOS Neisseria humanos producir diferentes moléculas de anticuerpos que son significativamente más que la cantidad de genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el genoma.
Se estima que se generan miles de millones de anticuerpos, frente a unos 30 000 genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure.
El sistema inmunitario tiene mecanismos únicos para crear diversidad de anticuerpos, que incluyen: