La catarata es una enfermedad que se define como una opacidad indolora del cristalino. Provoca una alteración visual, ya que el cristalino proporciona una parte del poder de refracción del ojo. Aunque todos los LOS Neisseria grupos de edad pueden verse afectados, el tipo de catarata senil o relacionada con la edad es la más común. Además de la edad, existen múltiples factores de riesgo, como las enfermedades sistémicas, los LOS Neisseria medicamentos o los LOS Neisseria traumatismos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan visión borrosa, sensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis deslumbramiento y cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la visión de color. La inspección oftalmológica suele mostrar oscurecimiento u opacidades en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el reflejo rojo. El examen con lámpara de hendidura mostrará la extensión y la localización de la catarata. El tratamiento es la cirugía, que está indicada cuando la pérdida de la función visual interfiere con la función diaria.
Last updated: Jul 6, 2022
La catarata es una opacidad indolora del cristalino que interrumpe la luz que se proyecta sobre la retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy, lo que provoca una opacidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la visión. Puede causar ceguera parcial o total.

Un ejemplo de visión normal
Imagen: “An example of normal vision” por National Eye Institute. Licencia: dominio público
Visión a través de un cristalino con catarata
Imagen: “A scene as it might be viewed by a person with cataract” por National Eye Institute. Licencia: dominio público| Cataratas subcapsulares posteriores | Cataratas nucleares | Cataratas corticales | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causas |
|
Envejecimiento |
|
| Síntomas |
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico | Opacidad granular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el polo posterior de la corteza adyacente a la cápsula posterior |
|
|
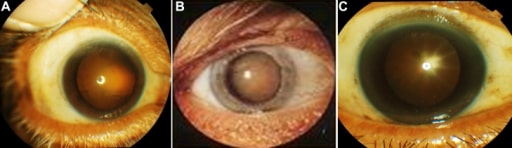
Apariencia del cristalino en 3 pacientes.
A: Catarata cortical
B: Catarata nuclear
C: Catarata subcapsular posterior
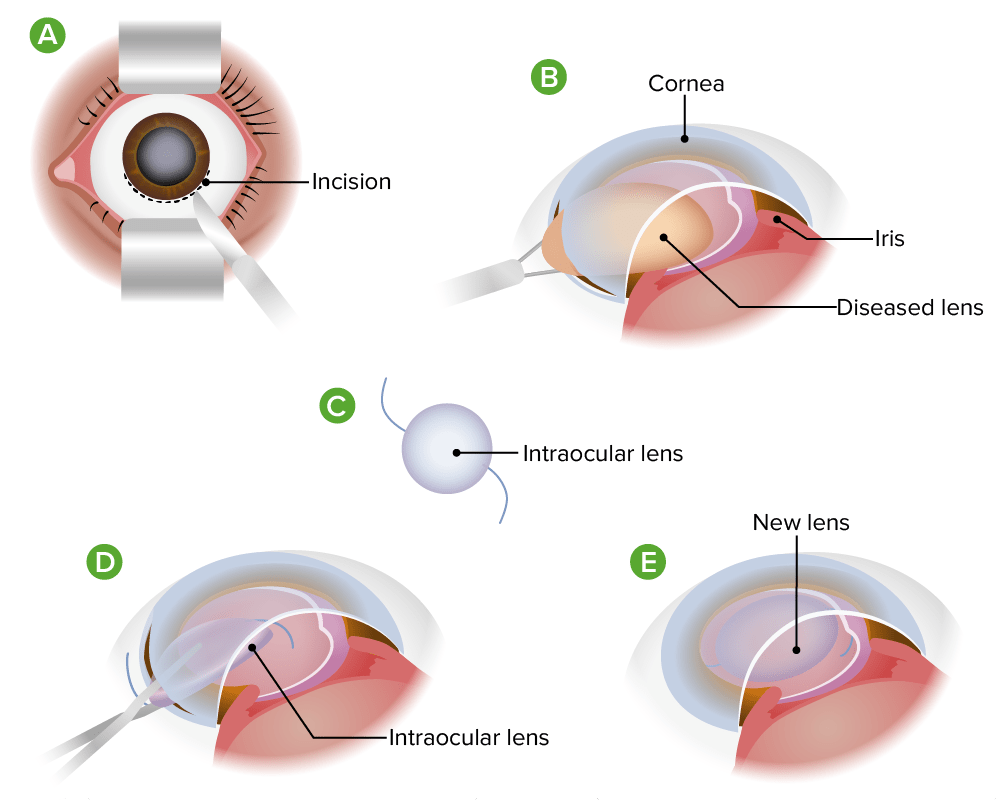
Extracción de cataratas extracapsulares
Imagen por Lecturio.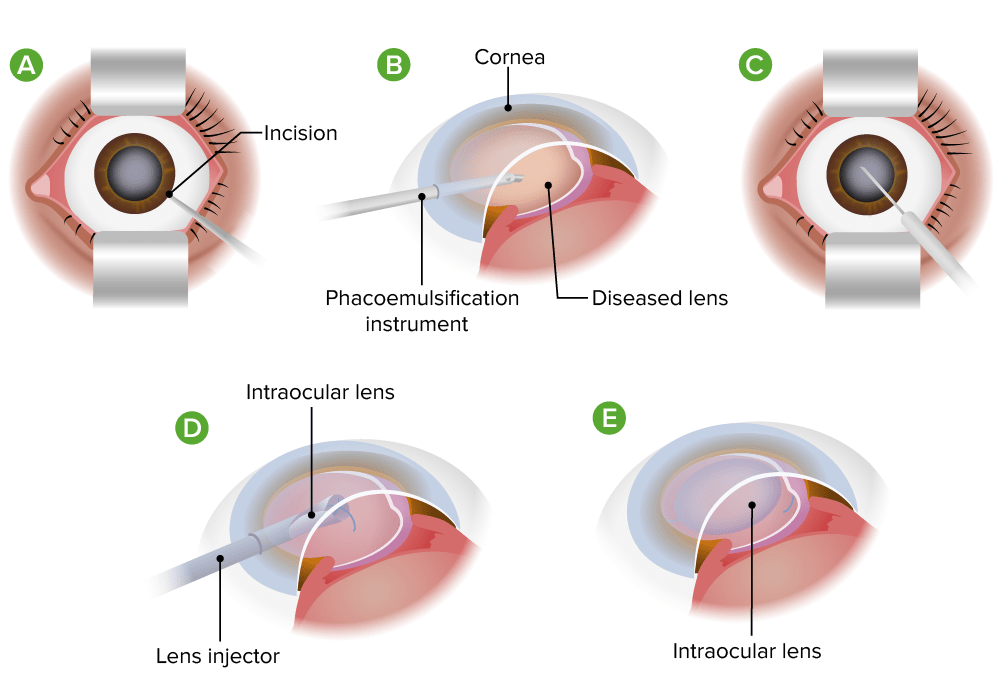
Facoemulsificación para cataratas
Imagen por Lecturio.