La bronquiolitis aguda es principalmente una afección respiratoria pediátrica causada por la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria bronquiolos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a una infección vírica. Esta afección es una causa común de hospitalización en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños de Estados Unidos, y la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos están causados por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology sincitial respiratorio ( RSV RSV Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is an enveloped, single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae and the genus Orthopneumovirus. Two subtypes (A and B) are present in outbreaks, but type A causes more severe disease. Respiratory syncytial virus causes infections of the lungs and respiratory tract. Respiratory Syncytial Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar síntomas respiratorios superiores, como tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome y congestión, posteriormente desarrollan signos respiratorios inferiores como disnea, sibilancias, crepitantes e hipoxia, durante un máximo de 10 días. El diagnóstico es clínico y el tratamiento se dirige a mejorar la oxigenación y la hidratación. Como el curso de la enfermedad es autolimitado, la bronquiolitis aguda tiene buen pronóstico con un tratamiento adecuado.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La bronquiolitis aguda es un conjunto de síntomas respiratorios (aumento del trabajo respiratorio, sibilancias y crepitantes) causada por una inflamación aguda de las vías respiratorias de menor calibre (bronquios y bronquiolos pequeños), normalmente secundaria a infecciones víricas.
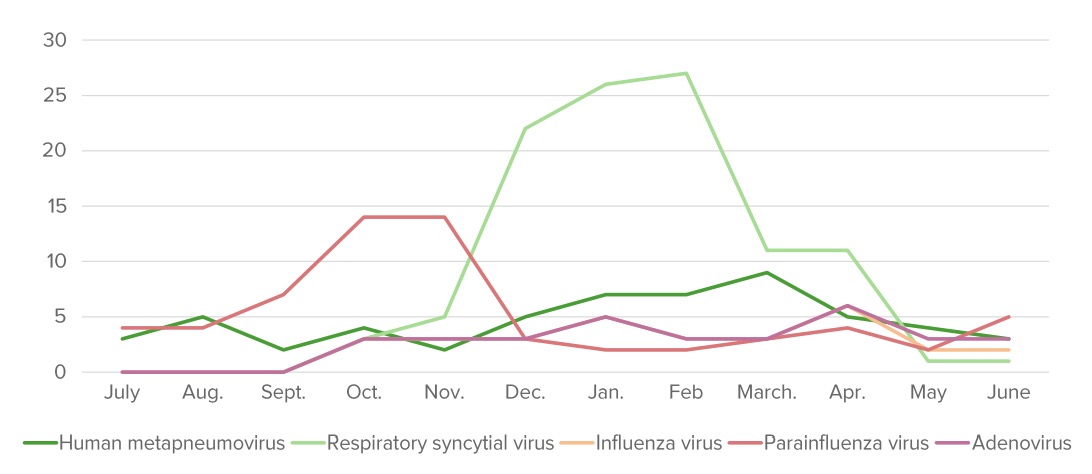
La distribución anual (%) de los patógenos que causan bronquiolitis. La “temporada de bronquiolitis” comienza alrededor de octubre y termina alrededor de mayo en el hemisferio norte.
Imagen por Lecturio.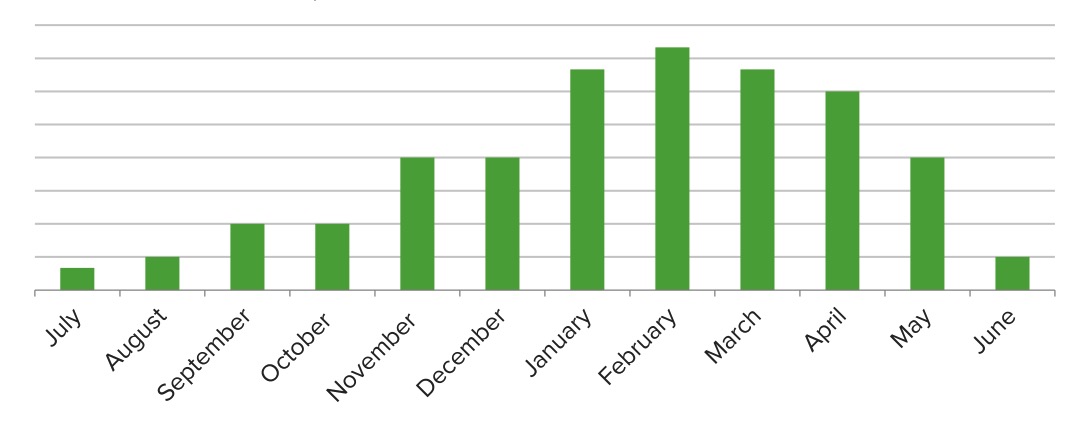
Variaciones estacionales en el número de casos que pueden atribuirse al virus sincitial respiratorio (RSV): En su punto máximo, el RSV es responsable de aproximadamente ⅓ de las bronquiolitis.
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria cambios patológicos se observan a las 24 horas del contacto con un patógeno:
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un espectro basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gravedad de la enfermedad:
El tratamiento depende de la gravedad: