Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos son análogos del pirofosfato, estos agentes son principalmente conocidos por su uso para tratar la osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis al AL Amyloidosis prevenir la pérdida ósea. Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos terminan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sufijo “-dronato” o “ácido -drónico” (e.g., alendronato, risedronato, pamidronato) y se unen a los LOS Neisseria cristales de hidroxiapatita en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hueso, inhibiendo la resorción ósea inducida por osteoclastos. Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos están indicados para la osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis posmenopáusica, la osteopenia Osteopenia Osteoporosis/ osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis inducida por glucocorticoides y la enfermedad ósea de Paget. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios incluyen hipocalcemia, hipofosfatemia, necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage avascular Avascular Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers del fémur y osteonecrosis de la mandíbula. Las contraindicaciones incluyen reacciones de hipersensibilidad y trastornos esofágicos. Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos pueden interactuar con los LOS Neisseria aminoglucósidos, la aspirina y los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la bomba de protones.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
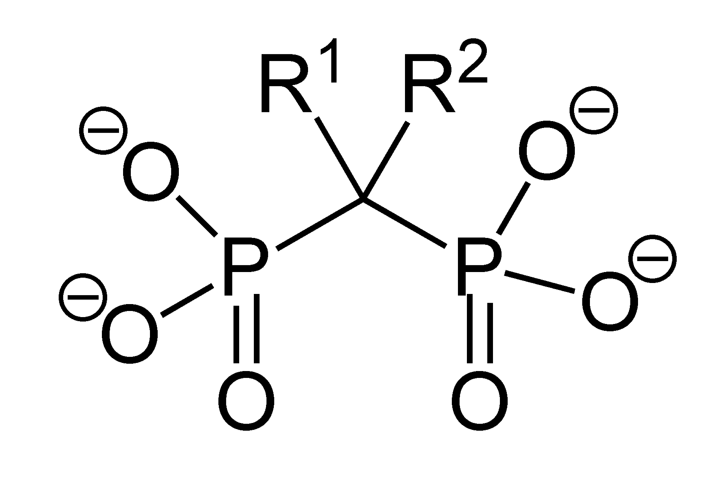
Estructura de los bifosfonatos:
La estructura básica de los bifosfonatos se centra en un enlace común fósforo-carbono-fósforo, pero con variaciones en los grupos R.
Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos se clasifican por su estructura. Los LOS Neisseria compuestos de los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos son nitrogenados o no nitrogenados. Los LOS Neisseria subtipos nitrogenados contienen nitrógeno en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cadena larga (R2).
Los LOS Neisseria bifosfonatos tratan una serie de afecciones asociadas con los LOS Neisseria huesos:
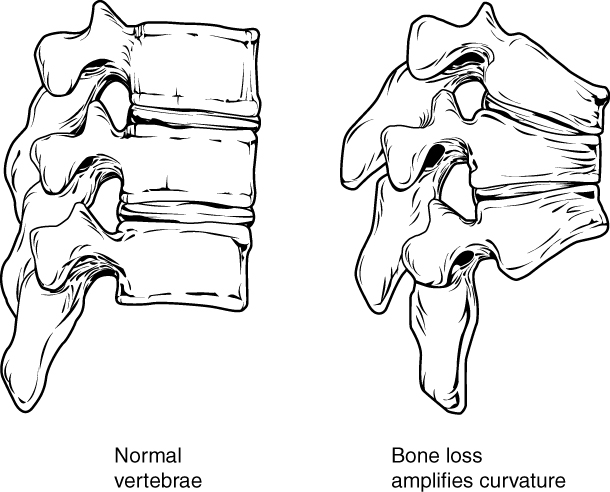
Diagrama de los cambios patológicos observados en una columna vertebral con osteoporosis:
La pérdida gradual de la densidad ósea provoca el colapso de las vértebras, dando como resultado una cifosis.
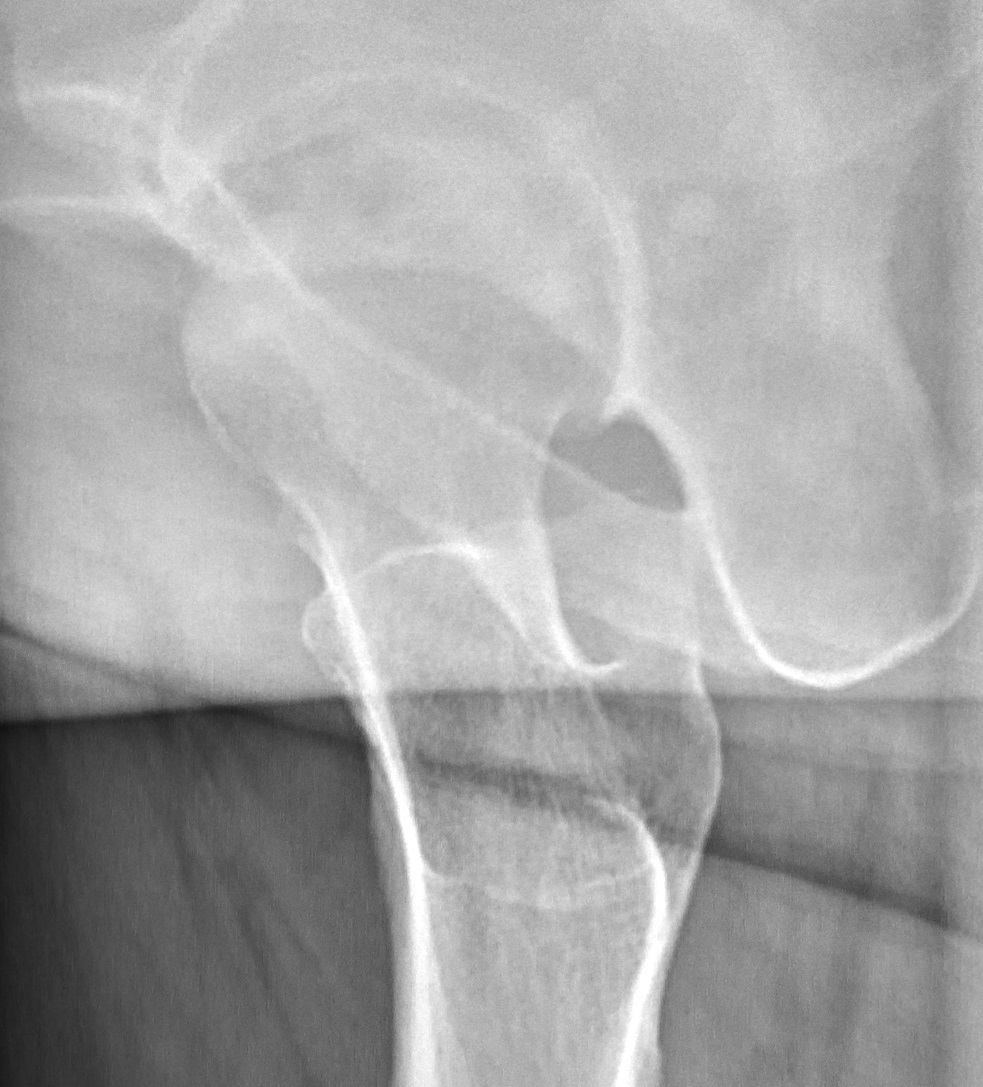
Radiografía de necrosis avascular que muestra osteopenia, esclerosis y calcificación de los bordes:
El signo clásico de enfermedad avanzada es una forma de media luna causada por la acumulación de hueso subcondral y el colapso de la superficie articular.
| Medicamento | Clasificación | Vida media de eliminación | Indicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alendronato | Nitrogenado | > 10 años |
|
| Risedronato | 480–561 horas (terminal) | ||
| Pamidronato | Aproximadamente 28 horas | Además de lo anterior:
|
|
| Ácido zoledrónico | 146 horas (terminal) | ||
| Etidronato | No nitrogenado | 1–6 horas |
|
| Clodronato | 13 horas (terminal) |
|
|
| Tiludronato | 40–60 horas |