Los LOS Neisseria antivirales para la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus incluyen los LOS Neisseria análogos de nucleósidos/nucleótidos, también conocidos como inhibidores nucleósidos/nucleótidos de la transcriptasa inversa. Debido a su estructura química similar a los LOS Neisseria nucleósidos y nucleótidos, los LOS Neisseria inhibidores nucleósidos/nucleótidos de la transcriptasa inversa, pueden integrarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ADN viral durante el proceso de replicación. Este proceso inhibe la función de la ADN polimerasa dependiente del ARN viral, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la terminación de la cadena. Todos estos medicamentos se administran por vía oral y se excretan por los LOS Neisseria riñones. Las indicaciones incluyen infección crónica por hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus y algunas (como la lamivudina) también se utilizan para el VIH. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios incluyen síntomas gastrointestinales, evidencia de toxicidad mitocondrial (como acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis láctica) e infección de rebote al AL Amyloidosis suspender el tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria antivirales para la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus tienen estructuras similares a las de los LOS Neisseria nucleótidos y nucleósidos, por lo que se clasifican como análogos de nucleósidos/nucleótidos (también conocidos como inhibidores nucleósidos/nucleótidos de la transcriptasa inversa).
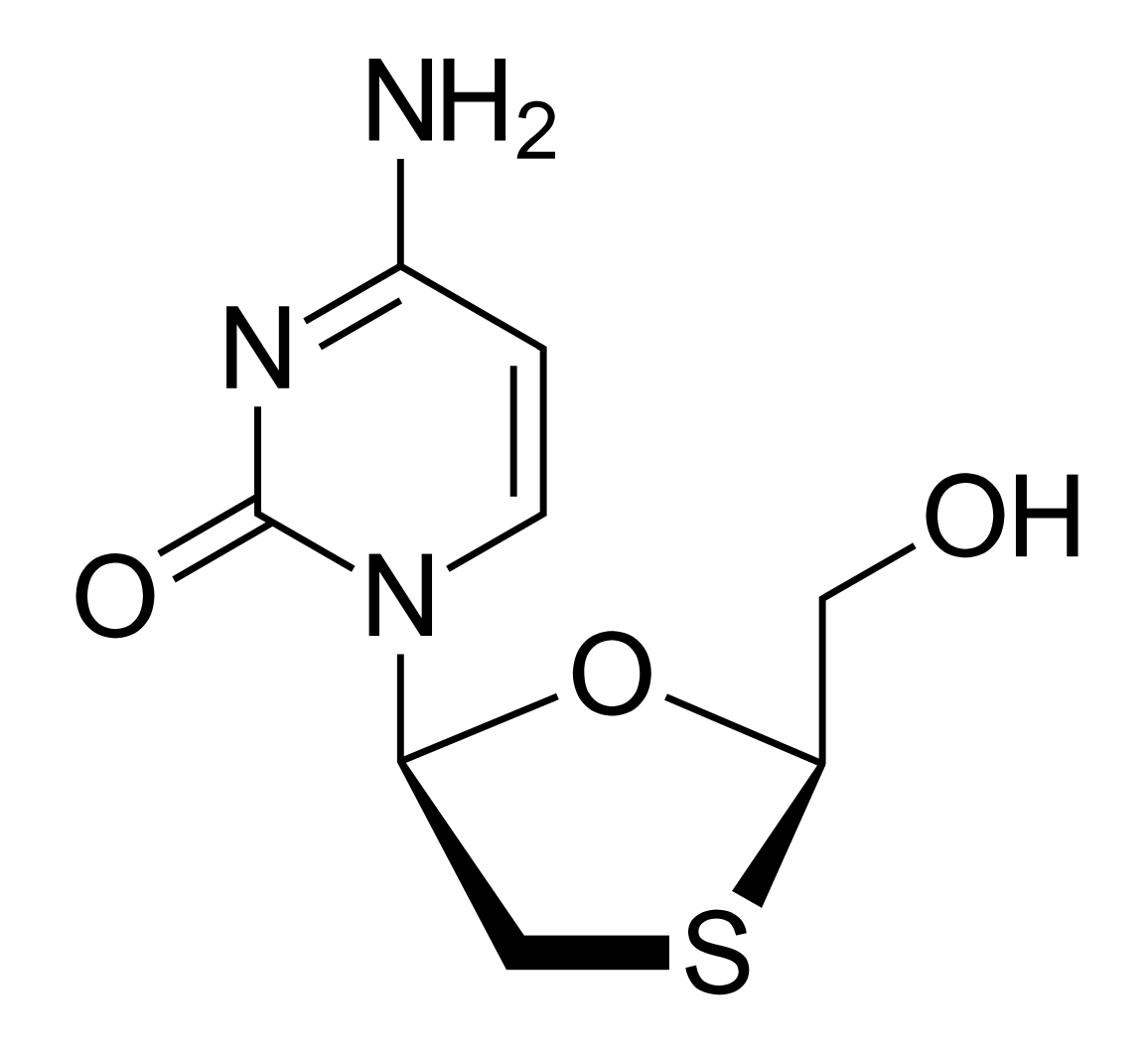
Estructura química de lamivudina
Imagen: “2D structure of lamivudine. Created with ChemDoodle and Adobe Illustrator” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio Público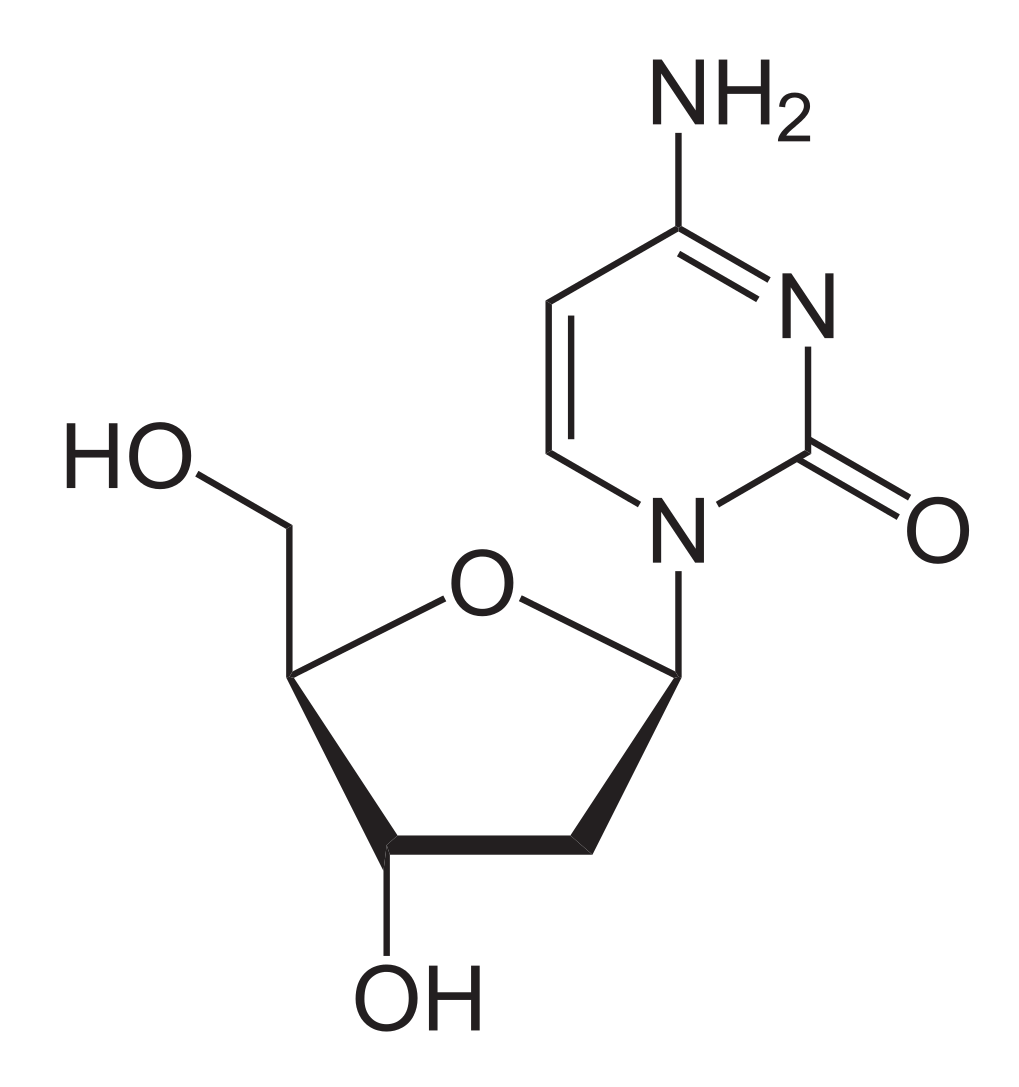
Estructura química de la desoxicitidina:
Obsérvese la similitud que tiene lamivudina con este nucleósido.
Todos estos medicamentos se excretan por los LOS Neisseria riñones.
Indicaciones de tratamiento:
Diferencias entre medicamentos: