A molécula de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure é o repositório da informação genética hereditária. Nos humanos, o DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure está contido em 23 pares de cromossomos dentro do núcleo. A molécula fornece o modelo básico para a replicação da informação genética, transcrição de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure e biossíntese de proteínas para promover a função e a sobrevivência celular.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
O DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure material hereditário é um polímero de nucleotídeo de fita dupla:
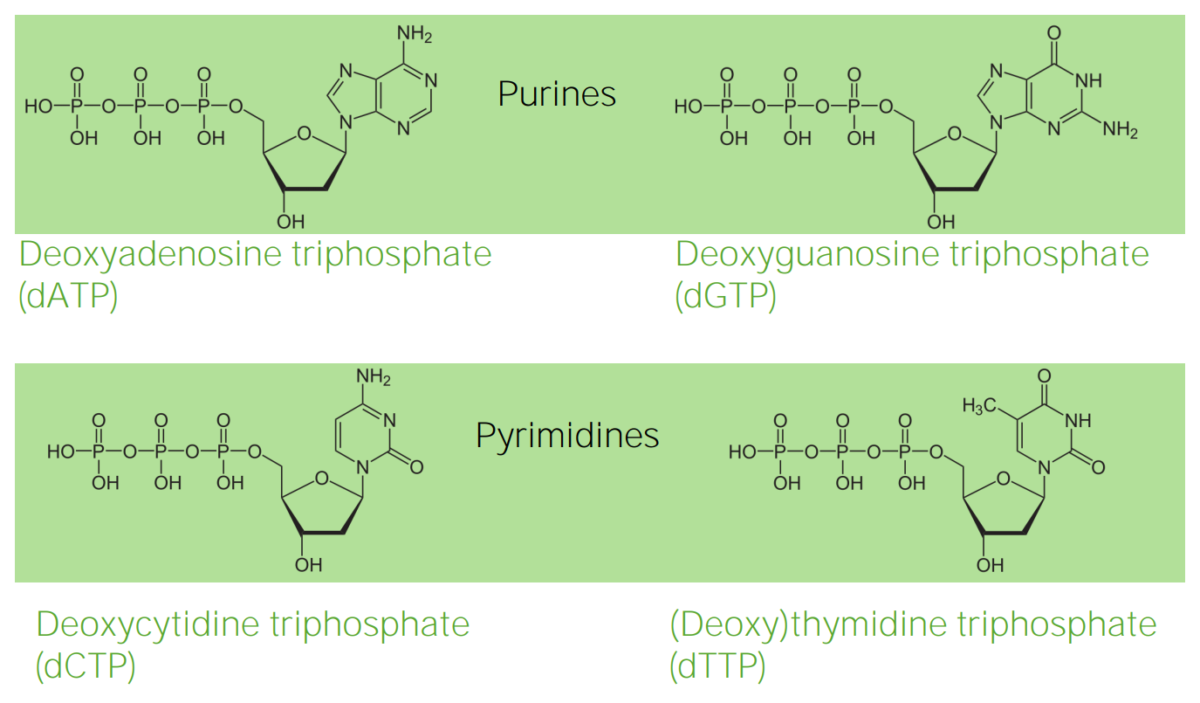
Estrutura dos desoxirribonucleotídeos
Imagem por Lecturio.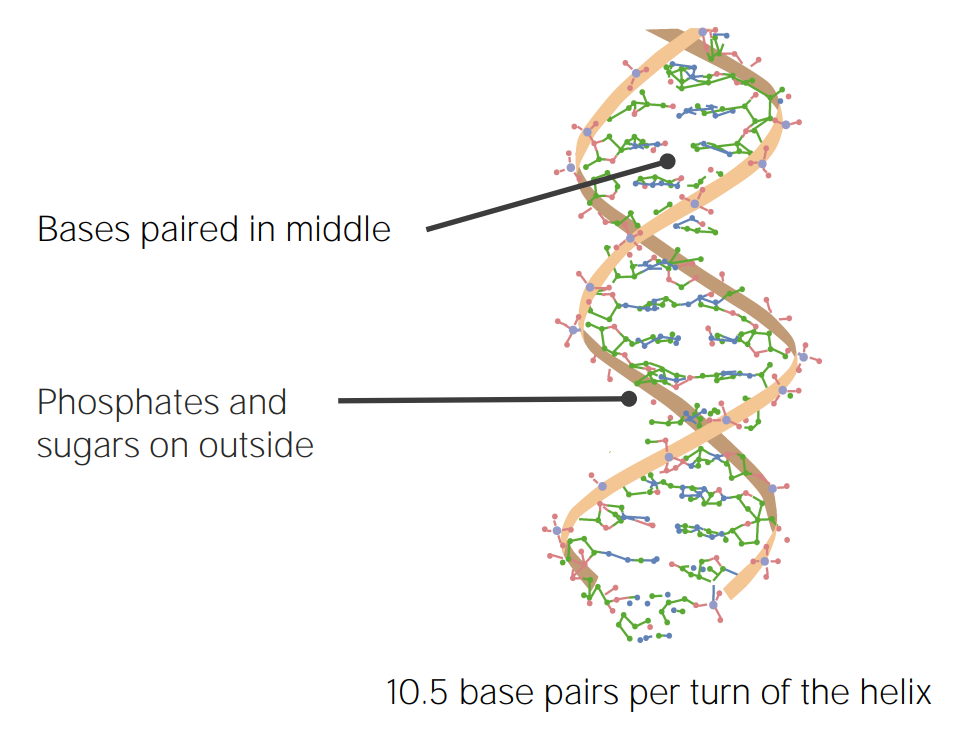
Estrutura do DNA como descrito por Watson e Crick
Imagem por Lecturio.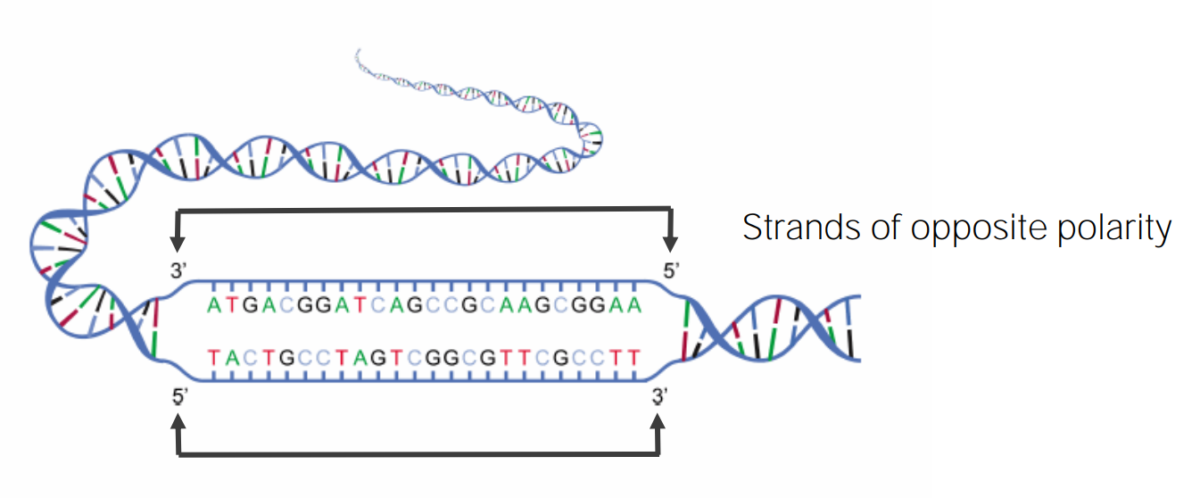
Diagrama da dupla hélice de DNA mostrando a natureza antiparalela (polar) de cada fita complementar
Imagem por Lecturio.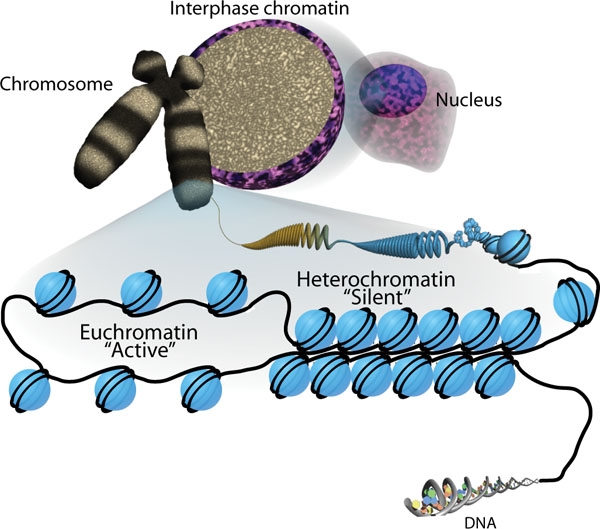
Embalagem do DNA e os 2 estados da cromatina:
Eucromatina (ativa) onde o DNA está sendo replicado ou transcrito; e heterocromatina (silenciosa), onde o DNA não está sendo replicado ou transcrito.