Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter é uma bactéria gram-negativa que causa infeção gástrica. É a espécie de Helicobacter Helicobacter Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium that causes gastric infection. It is the most well known and clinically significant species of Helicobacter. Transmission is believed to occur by ingestion of contaminated food or water; therefore, a higher prevalence of infection is seen in areas with poor sanitation. Helicobacter mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome conhecida e clinicamente significativa. Consta-se que a transmissão ocorra pela ingestão de alimentos ou água contaminados; assim, é observada uma maior prevalência da infeção em áreas com condições precárias de saneamento. Algumas características bacterianas contribuem para a patogenicidade de H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter: produção de urease Urease An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of urea and water to carbon dioxide and ammonia. Nocardia/Nocardiosis (permitindo a sobrevivência num ambiente ácido), motilidade (permitindo o movimento no epitélio gástrico) e várias toxinas (que criam dano local e inflamação). A infeção crónica por H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter pode levar a úlcera péptica ou mesmo a neoplasia gástrica nos casos graves.
Last updated: Apr 2, 2025
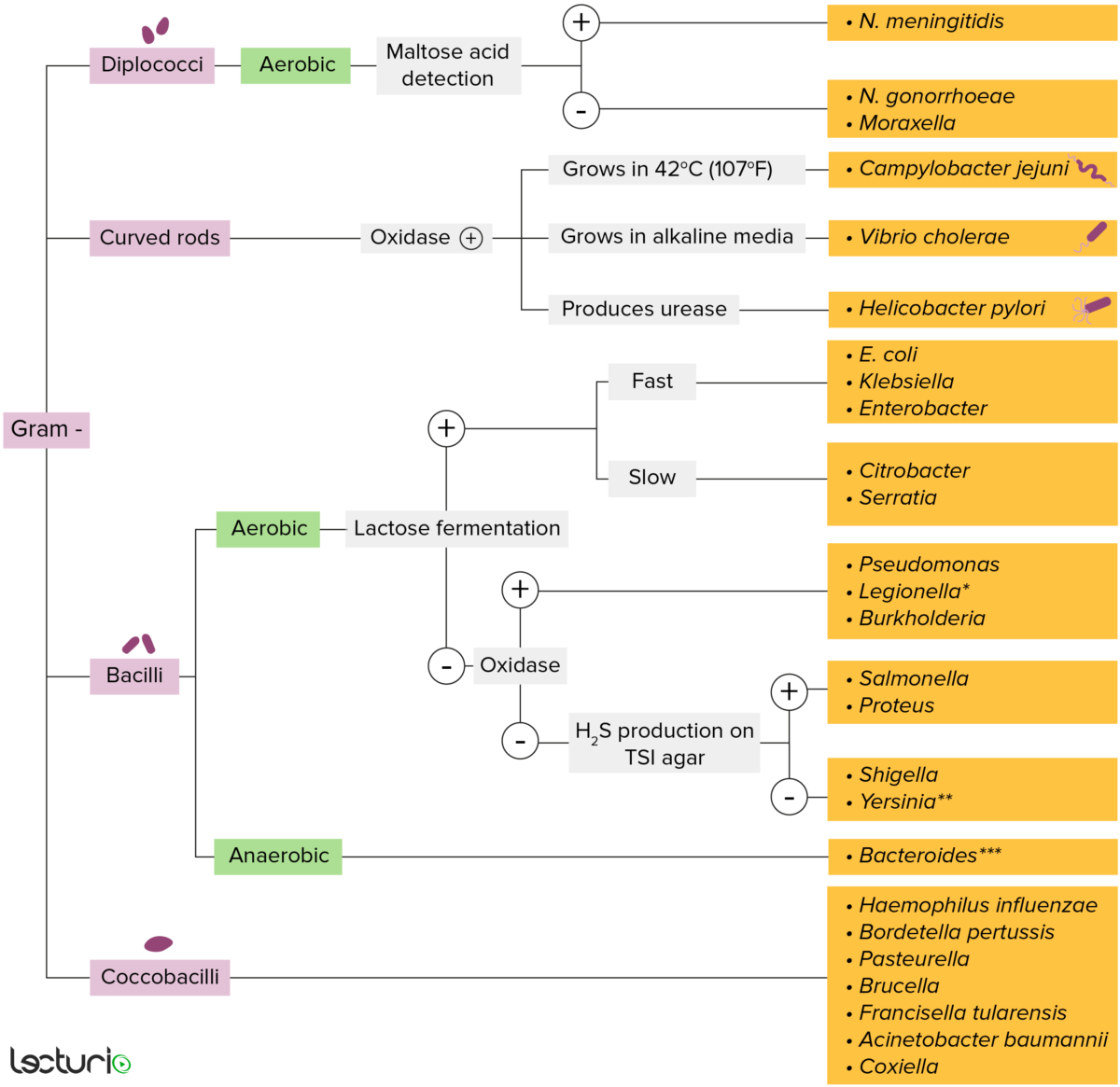
Bactérias gram-negativas:
A maioria das bactérias pode ser classificada de acordo com um procedimento de laboratório chamado coloração de Gram.
As paredes celulares bacterianas com uma camada fina de peptidoglicanos não retêm a coloração cristal violeta utilizada na técnica coloração de Gram. No entanto, as bactérias gram-negativas retêm a coloração de contraste de safranina e aparecem com cor vermelho-rosado. Estas bactérias podem ainda ser classificadas de acordo com a sua morfologia (diplococos, bastonetes curvos, bacilos e cocobacilos) e capacidade de crescerem na presença de oxigénio (aeróbios versus anaeróbios). As bactérias Gram-negativas podem ser identificadas com precisão através de culturas em meios específicos (Agar Tríplice Açúcar Ferro (TSI)), com a identificação das enzimas (urease, oxidase) e determinação da capacidade de fermentar a lactose.
* Cora pouco com coloração de Gram
** Bastonete pleomórfico/cocobacilos
*** Requer meios de transporte especiais
Particularidades:
O género Helicobacter Helicobacter Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacterium that causes gastric infection. It is the most well known and clinically significant species of Helicobacter. Transmission is believed to occur by ingestion of contaminated food or water; therefore, a higher prevalence of infection is seen in areas with poor sanitation. Helicobacter apresenta cerca de 35 espécies, sendo H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter o mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome conhecido.
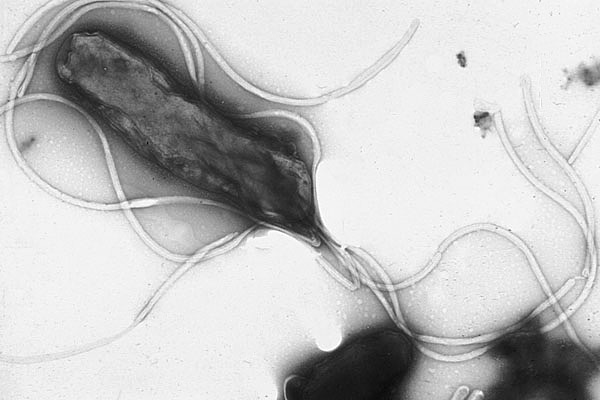
Micrografia eletrónica de Helicobacter pylori com múltiplos flagelos (contraste negativo do corante)
Imagem: “Electron micrograph of helicobacter pylori” por Yutaka Tsutsumi, MD Licença: Domínio Público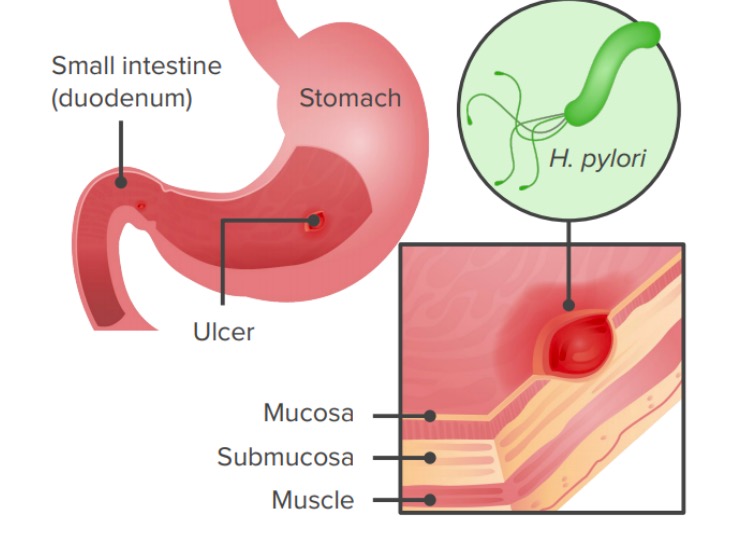
A infeção por Helicobacter pylori através da ingestão de um agente patogénico resulta em úlcera gástrica ou gastrite.
Imagem por Lecturio.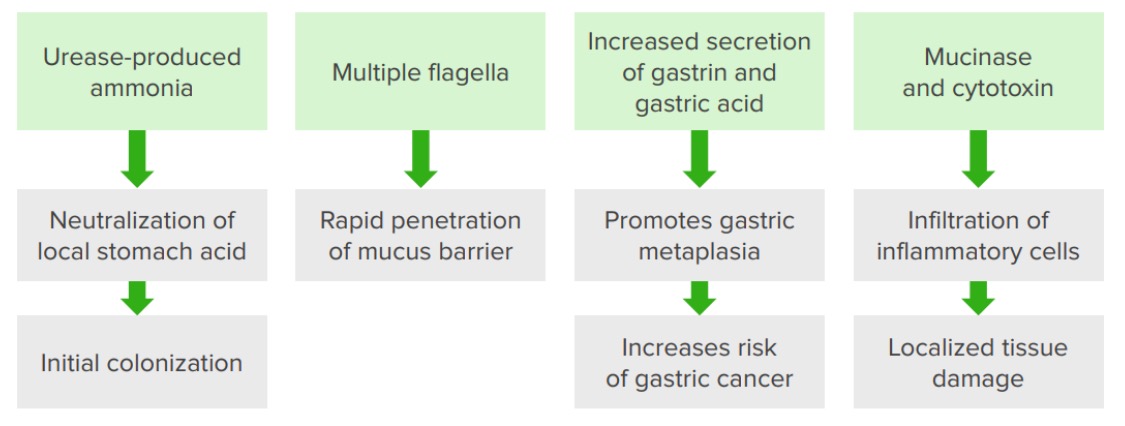
Características patogénicas de Helicobacter pylori
Imagem por Lecturio.Na infecção por H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter :