A doença renal poliquística (PKD) é uma doença genética hereditária que leva ao desenvolvimento de vários quistos, preenchidos por líquido, nos rins. Os 2 tipos principais de PKD são a doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva ( ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)), frequentemente diagnosticada no período pré-natal ou logo após o nascimento, e a doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)), diagnosticada na idade adulta. A doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva é principalmente caracterizada por dilatações quísticas dos ductos coletores renais e dilatação do ducto biliar intra-hepático com fibrose hepática. O diagnóstico é feito através do exame objetivo e ecografia. O tratamento requer uma abordagem multidisciplinar para retardar a progressão da doença renal através do controlo da hipertensão, proteinúria e sintomas. O prognóstico da ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) depende da idade de apresentação, juntamente com o grau de envolvimento hepático e renal. Os doentes que progridem para doença renal em estadio terminal (ESRD) irão precisar de terapia renal de substituição.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A doença renal poliquística (PKD) afeta cerca de 500.000 pessoas nos Estados Unidos. A doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva ( ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)) (anteriormente conhecida como PKD infantil), é um dos 2 principais tipos de PKD.
As manifestações variam com a idade e afetam:
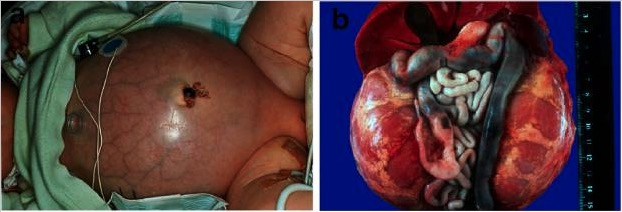
Doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva (ARPKD):
a) Bebé com abdómen distendido devido a rins volumosos, o que leva a problemas respiratórios e morte precoce
b) Situs abdominal de um doente ARPKD com morte perinatal com rins simetricamente aumentados na sua configuração reniforme
Nos primeiros 3 anos, os sobreviventes do período neonatal experimentam uma melhoria temporária da função renal, seguida de um declínio.
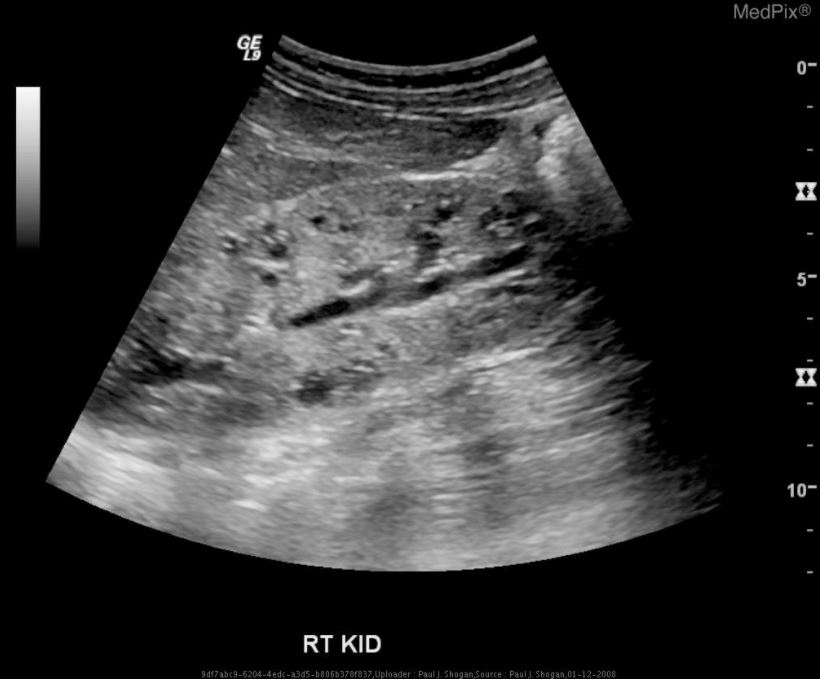
Ecografia do rim direito que mostra doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva (ARPKD):
ecogenicidade difusamente aumentada, perda de diferenciação corticomedular e múltiplos microquistos no parênquima renal
Tratamento pré-natal (se detetado precocemente):
Tratamento neonatal:
Infância e tratamento infantil:
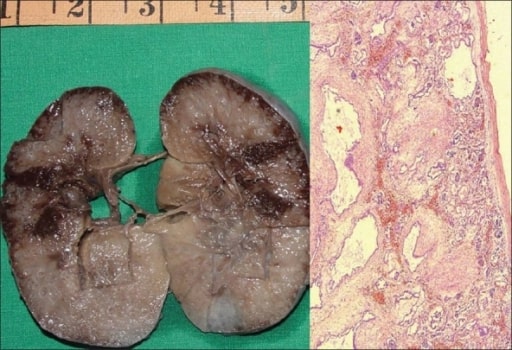
Doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva (ARPKD) num feto:
À esquerda, observa-se uma amostra do rim direito medindo 10 × 7 × 4 cm. A superfície de corte é esponjosa com baixa diferenciação corticomedular. Existem vários quistos minúsculos, alguns em ângulo reto com a superfície cortical.
À direita, uma fotomicrografia mostra vários quistos revestidos por uma única camada de células epiteliais cuboidais baixas com mesênquima peritubular espesso. Os glomérulos são normais (H&E, 40x).
Os 2 tipos principais de PKD são a doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)) e a ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD).
| ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Hereditariedade | Autossómica dominante | Autossómica recessiva |
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure envolvidos | PKD1, PKD2 PKD1, PKD2 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | PKHD1 PKHD1 Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) |
| Proteínas associadas | Policistina-1, policistina-2 | Fibrocistina |
| Idade de apresentação | Idade adulta | Pré-natal, neonatal, bebé |
| Características clínicas |
|
|
| Morfologia macroscópica e patológica |
|
|
| Achados da ecografia |
Quistos múltiplos (com base na idade):
|
|