A doença renal poliquística (PKD) é uma doença genética hereditária que leva ao desenvolvimento de vários quistos, preenchidos por líquido, nos rins. Os 2 tipos principais de PKD são a doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)), diagnosticada na idade adulta, e a doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva ( ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)), diagnosticada no período pré-natal ou logo após o nascimento. Os doentes com ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) frequentemente apresentam hipertensão, hematúria e dor no flanco. As manifestações extra-renais incluem aneurisma intracerebral, quistos hepáticos e pancreáticos, e anomalias valvulares cardíacas. O diagnóstico é feito pela história clínica, exame objetivo e ecografia. O tratamento requer uma abordagem multidisciplinar e muitos doentes necessitam de terapia renal de substituição. O objetivo final é retardar a progressão da doença renal, controlar a hipertensão, a proteinúria e os sintomas. O prognóstico de ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) depende de uma variedade de fatores. O aneurisma cerebral é uma complicação associada a um prognóstico particularmente desfavorável.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A doença renal poliquística (PKD) afeta cerca de 500.000 pessoas nos Estados Unidos. Um dos 2 tipos principais de PKD é a doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante ( ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)).
A idade de aparecimento dos sintomas é variável, mas geralmente ocorre na idade adulta. Doentes com mutação PKD1 apresentam sintomas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome cedo do que doentes com PKD2.
O diagnóstico é feito com a combinação de história familiar positiva e a presença de múltiplos quistos renais bilaterais.
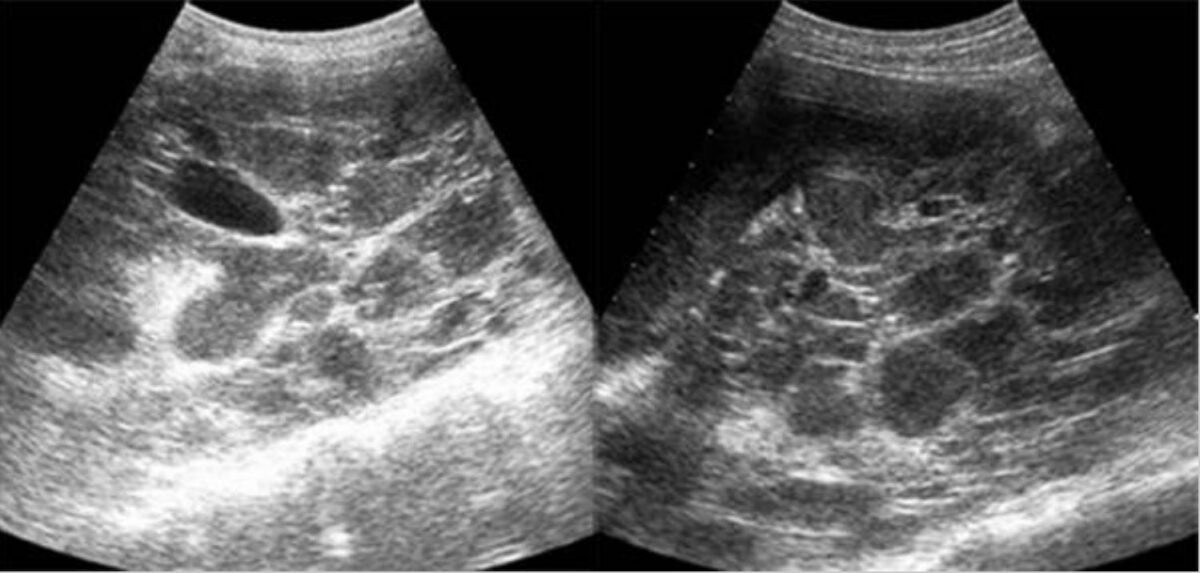
Ecografia na doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante (ADPKD):
ecografia sagital de ambos os rins mostra lesões quísticas que ocupam espaço, com detritos ecogénicos internos marcados e septos espessos, que representam numerosos quistos infetados
Objetivos:
Medidas de tratamento:
Para doença renal em estadio terminal (ESRD):
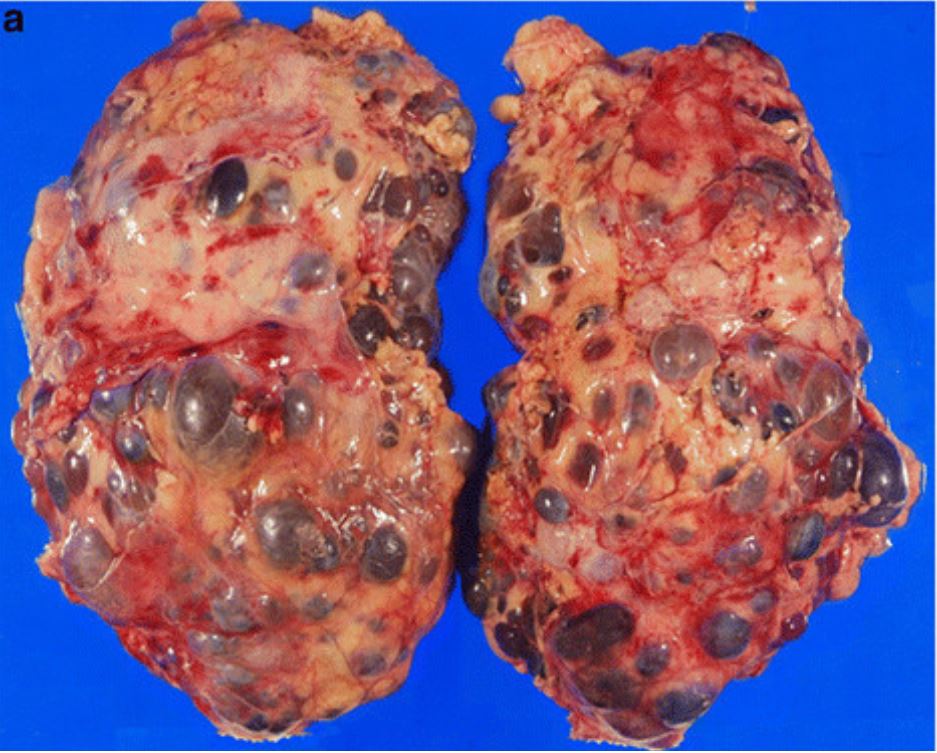
Patologia macroscópica de nefrectomia realizada em paciente com doença renal poliquística autossómica dominante (ADPKD)
Imagem: “Incidental renal cell carcinoma presenting in a renal transplant recipient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease” por Misumi T, Ide K, Onoe T, Banshodani M, Tazawa H, Teraoka Y, Hotta R, Yamashita M, Tashiro H, Ohdan H. Licença: CC BY 2.0, editado por Lecturio.Os 2 principais tipos de doença renal poliquística são ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) e doença renal poliquística autossómica recessiva ( ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)).
| ADPKD ADPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. The 2 main types of PKD are autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), which is often diagnosed in adulthood, and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), which is often diagnosed antenatally or shortly after birth. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | ARPKD ARPKD Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited genetic disorder leading to the development of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is primarily characterized by cystic dilatations of the renal collecting ducts and intrahepatic bile duct dilatation with hepatic fibrosis. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Hereditariedade | Autossómica dominante | Autossómica recessiva |
| Genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure envolvidos | PKD1, PKD2 PKD1, PKD2 Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | PKHD1 PKHD1 Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD) |
| Proteínas associadas | Policistina-1, policistina-2 | Fibrocistina |
| Idade de apresentação | Idade adulta | Pré-natal, neonatal, bebé |
| Características clínicas |
|
|
| Morfologia macroscópica e patológica |
|
|
| Achados da ecografia |
Quistos múltiplos (com base na idade):
|
|