O córtex cerebral é o maior e mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome desenvolvido componente do cérebro humano e do sistema nervoso central (SNC). Ocupando a parte superior da cavidade craniana, o córtex cerebral possui 4 lobos e divide-se em 2 hemisférios unidos centralmente pelo corpo caloso. O córtex é organizado em giros que são separados por sulcos. O córtex cerebral fornece o substrato neuronal para a experiência consciente dos estímulos sensitivos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
O córtex cerebral é a camada mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome superficial do cérebro:
O cérebro é maior porção do encéfalo. O cérebro é composto por matéria cinzenta (córtex cerebral) e estruturas subjacentes de matéria branca:
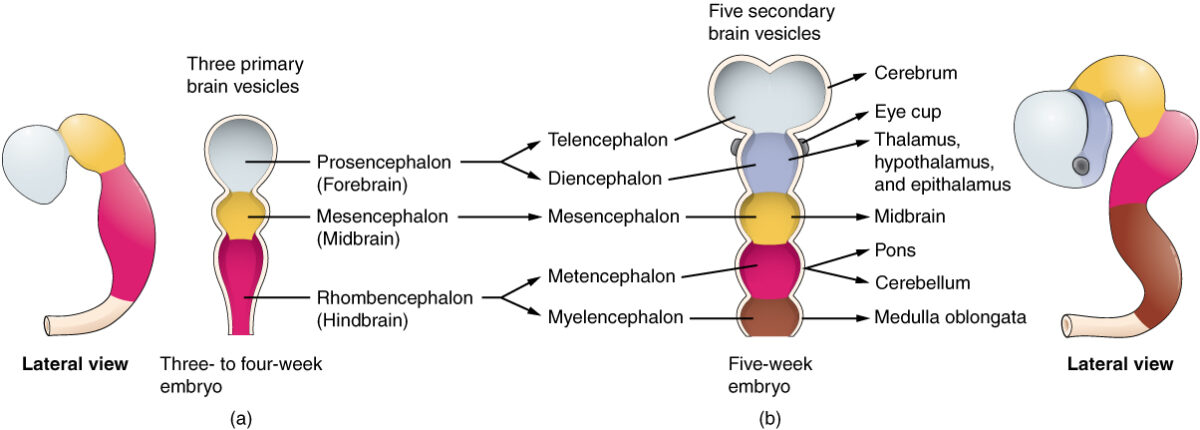
O desenvolvimento embrionário do cérebro: observar a linhagem a partir do tubo neural → prosencéfalo → telencéfalo → cérebro
Imagem: “Brain Vesicle” por Phil Schatz. Licença: CC BY 4.0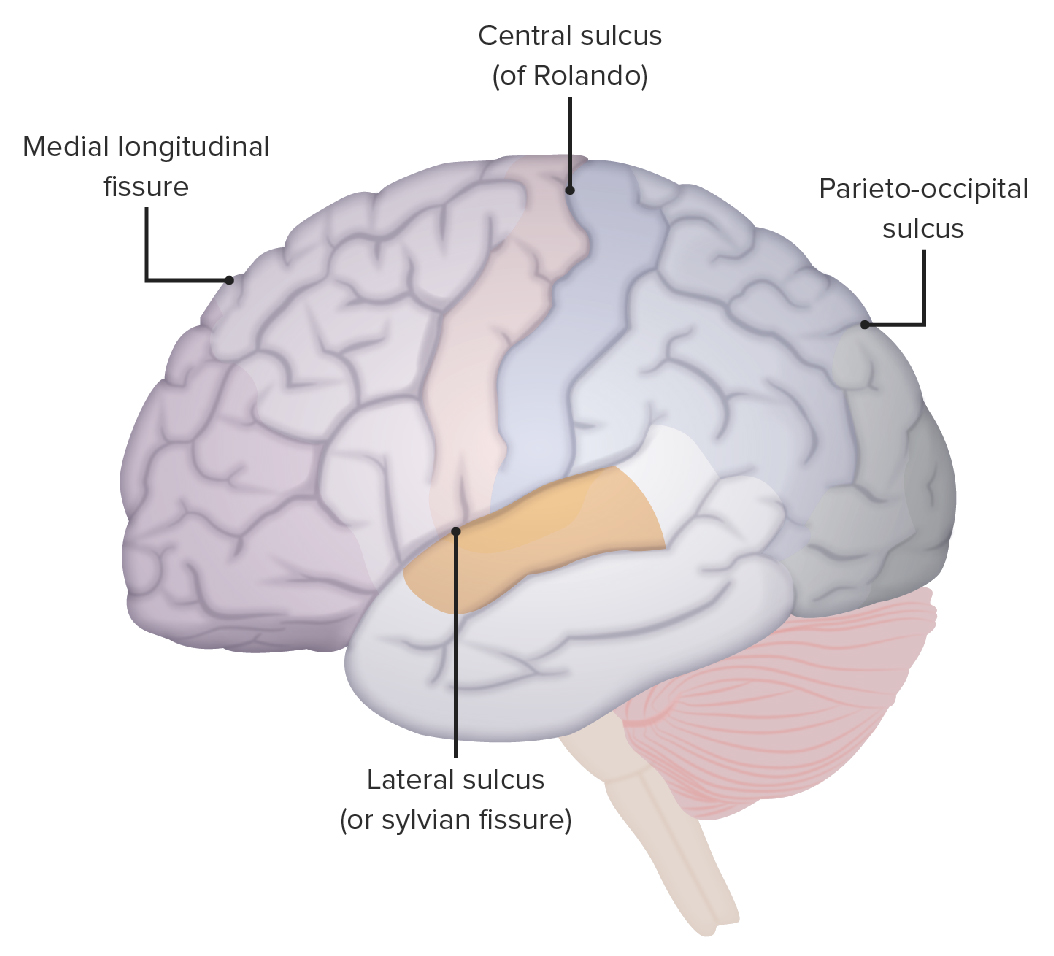
As localizações do sulco lateral, sulco central e sulco parieto-occipital
Imagem por Lecturio.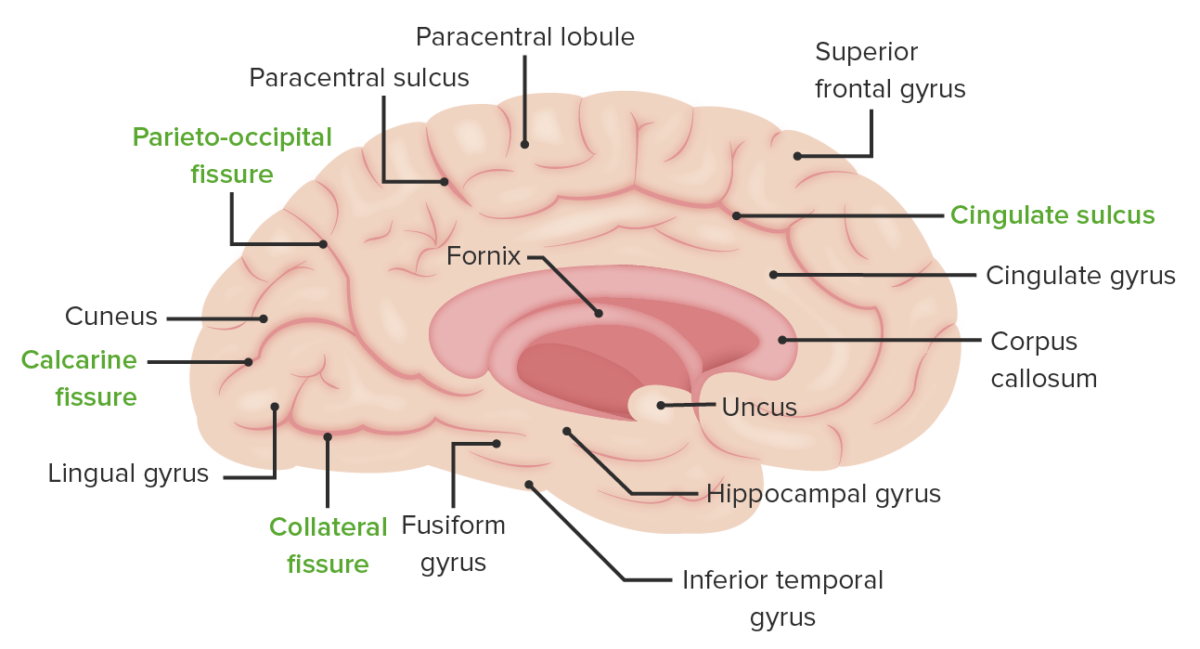
A superfície medial do hemisfério cerebral esquerdo: Observar a localização do sulco colateral que separa o giro lingual do giro fusiforme, a fissura calcarina que separa o giro cúneo do giro lingual e o sulco parieto-occipital que separa o lobo parietal do occipital.
Imagem por Lecturio.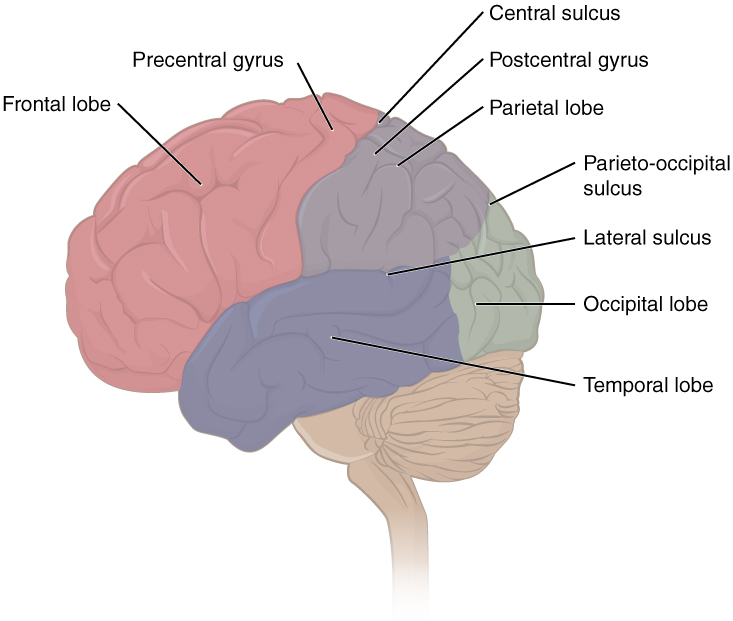
A imagem demonstra a localização de algumas estruturas-chave, incluindo cada um dos 4 lobos, os giros pré-central e pós-central e os sulcos central, lateral e parieto-occipital.
Imagem: “Lobes of Cerebral Cortex” por OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology. Licença: CC BY 4.0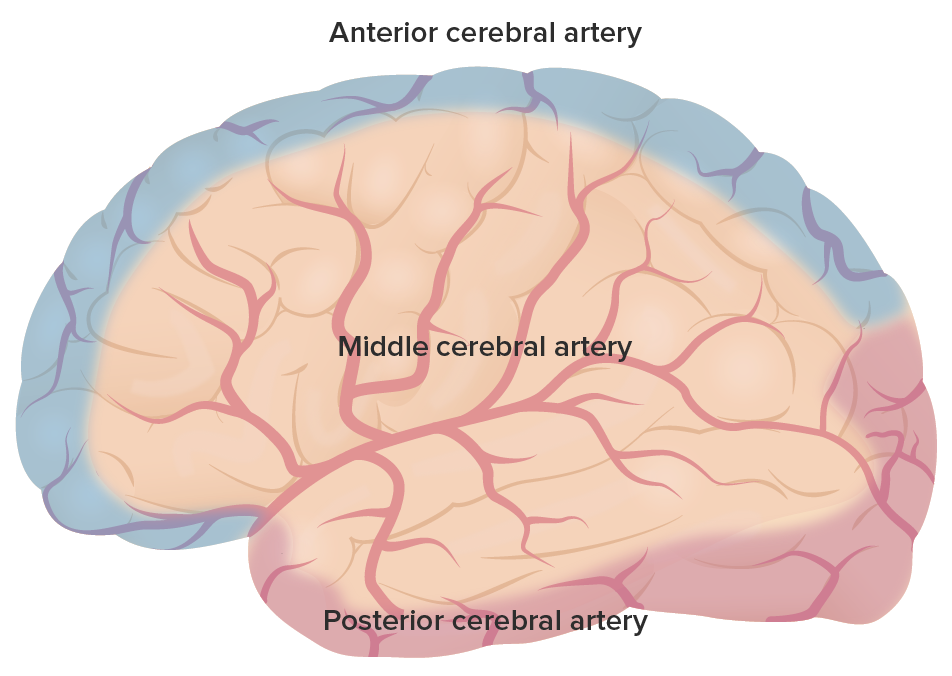
O suprimento arterial primário em todo o cérebro: Observar as regiões cobertas pela artéria cerebral anterior a roxo, a artéria cerebral média (ACM) a vermelho e a artéria cerebral posterior (ACP) a rosa.
Imagem por Lecturio.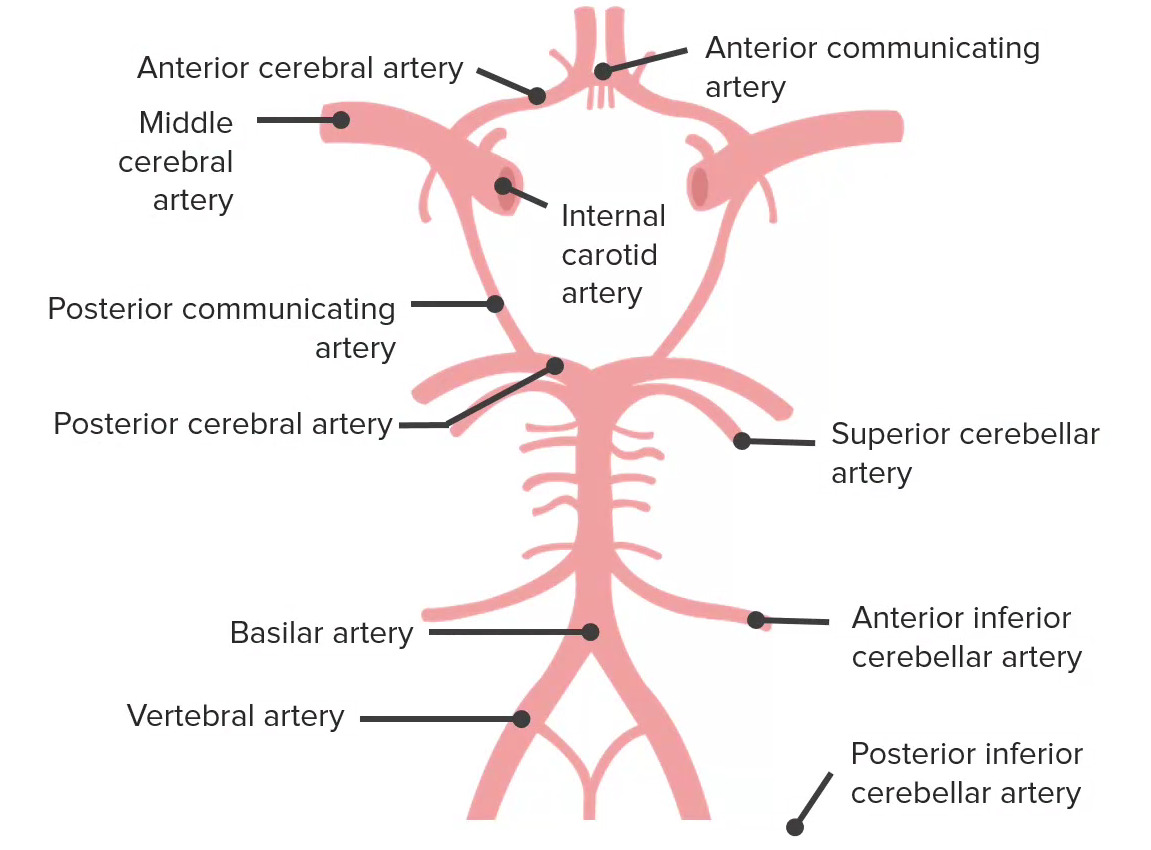
O suprimento sanguíneo para o cérebro é derivado de 2 fontes: 1) as artérias carótidas internas e 2) o sistema vertebrobasilar. Estas fontes interligam-se para formar o círculo de Willis, retratado aqui. O círculo de Willis tem 5 componentes, que incluem a artéria comunicante anterior, as artérias cerebrais anteriores, a artéria carótida interna, a artéria comunicante posterior e as artérias cerebrais posteriores (ACP).
Imagem por Lecturio.O lobo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy é o aspecto mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome anterior/superior do cérebro supratentorial. Controla muitas das funções de ordem superior do cérebro, incluindo função motora, pensamento executivo e fala.
| Nome | Localização | Número de Brodmann |
Função |
|---|---|---|---|
| Córtex motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology primário | Giro pré-central | 4 | Dita o controlo motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology contralateral |
| Córtex pré-motor | Anterior ao córtex motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology primário | 6 | Programação de eventos motores; os neurónios são ativados antes dos neurónios motores primários |
| Córtex motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology suplementar | Superfície da linha média do hemisfério anterior à representação da perna no córtex motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology primário | 6 | Planeamento de movimentos motores complexos |
| Córtex pré-frontal | Porção anterior do lobo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy | 8–14, 24, 25, 32, 44–47 | Olfato e função executiva (resolução de problemas, julgamento, planeamento, comportamento e emoções) |
| Campo ocular frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy | Interseção do giro frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy médio com o giro pré-central | 8 |
|
| Área de Broca | Giro frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy inferior do hemisfério dominante | 44, 45 | Produção de palavras (fala motora) |
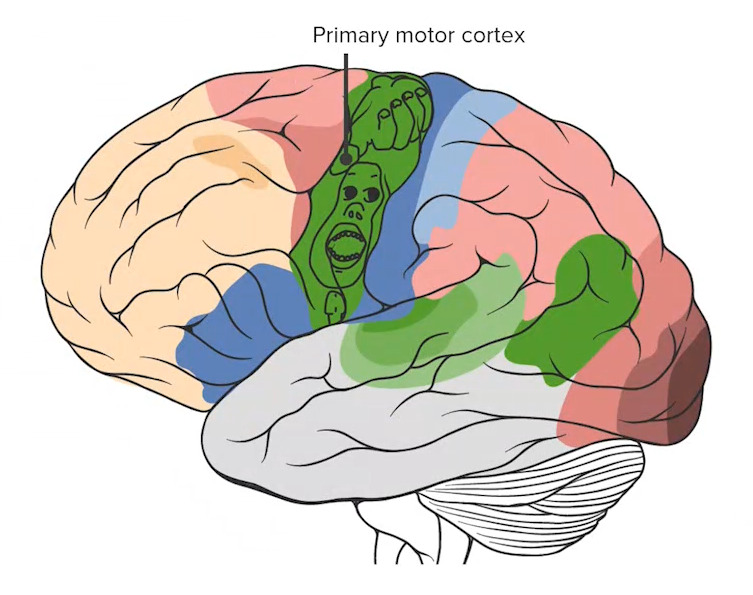
Observar o córtex motor primário (a estrutura mais posterior do lobo frontal) com o homúnculo sobreposto, detalhando as proporções do córtex dedicadas ao processamento de cada função motora específica.
Imagem por Lecturio.O lobo parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy situa-se posteriormente ao lobo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy e superiormente ao lobo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy. Está associado aos processos de sensação e compreensão da linguagem.
| Nome | Localização | Brodmann número |
Função |
|---|---|---|---|
| Córtex somatossensorial primário | Giro pós-central | 3, 1, 2 | Recebe aferência somatossensorial contralateral do núcleo posteromedial ventral e do núcleo posterolateral ventral do tálamo |
| Áreas de associação parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy | Parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy posterior | 5, 7 | Estereognosia e consciência do eu contralateral e arredores |
| Área de Wernicke | Giro supramarginal do hemisfério dominante (para além do giro temporal superior)* | 22, 40 | Compreensão da linguagem |
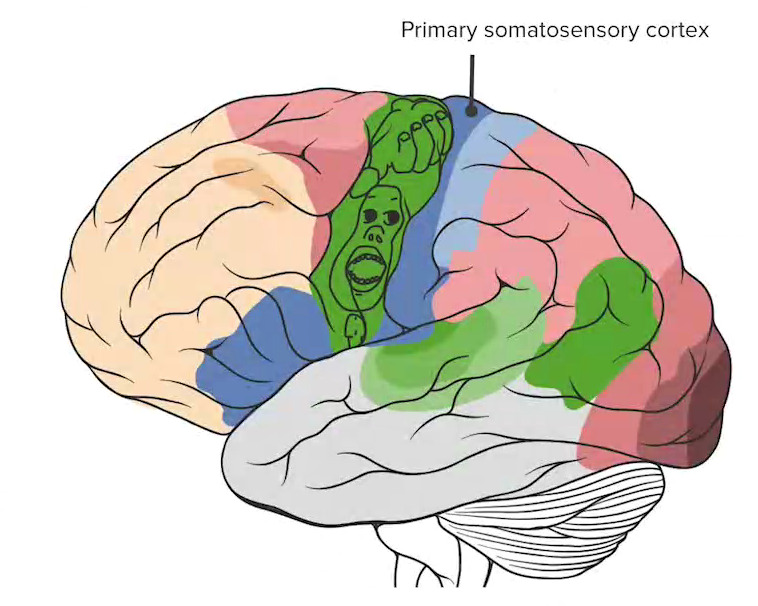
O córtex somatossensorial primário (marcada em azul escuro) marca a região mais anterior do lobo parietal.
Imagem por Lecturio.O lobo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy é o lobo mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome posterior do cérebro supratentorial. Está principalmente envolvido no processamento visual.
| Nome | Localização | Brodmann número |
Função |
|---|---|---|---|
| Córtex visual primário | Lobo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy posterior | 17 | Visão e acuidade visual (entrada do núcleo geniculado lateral via radiações óticas) |
| Córtex de associação visual | Córtex extra-estriado | 18, 19 | Processa informação relacionada com a forma, cor, movimento, profundidade e relações espaciais |
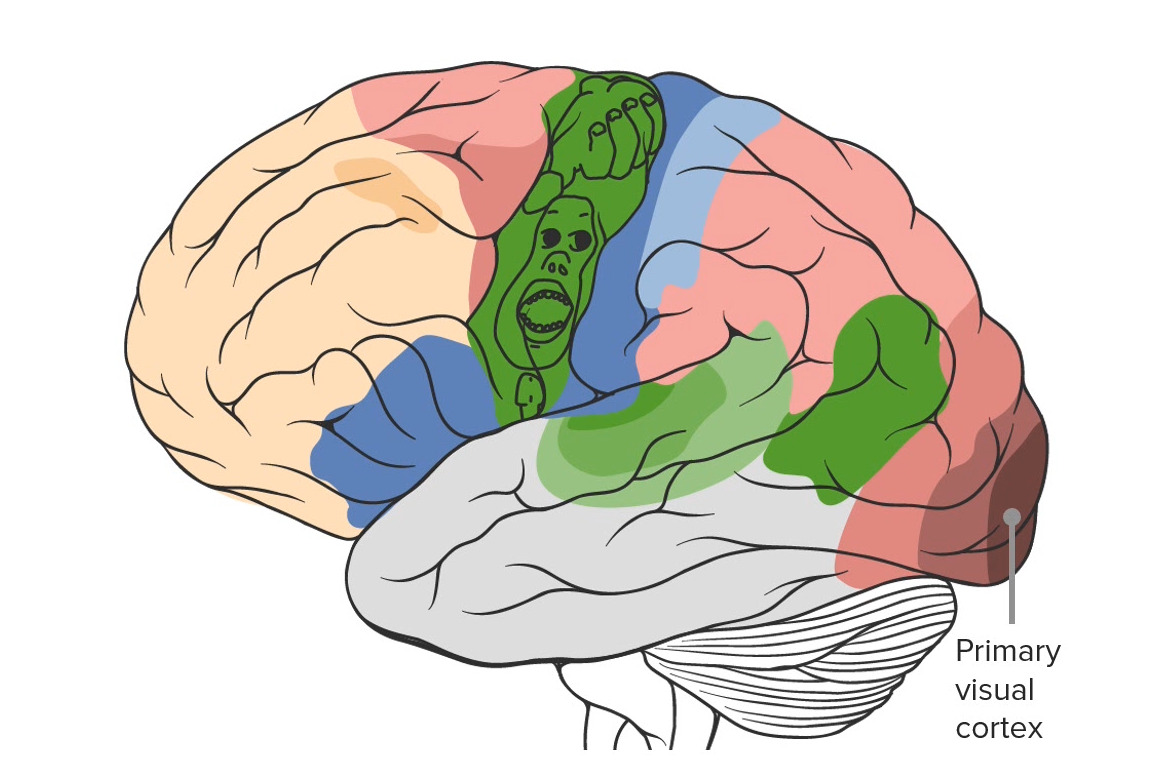
Observar a localização do córtex visual primário na região mais posterior do cérebro no lobo occipital.
Imagem por Lecturio.O lobo temporal é o aspecto mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome anterior/inferior do cérebro supratentorial. Está envolvido nos processos de audição, olfato e memória.
| Nome | Localização | Brodmann número |
Função |
|---|---|---|---|
| Córtex auditivo primário | Plano temporal superior dos lobos temporais dentro do sulco lateral | 40, 41 | Audição |
| Giro temporal médio e inferior | Lobo temporal médio e inferior | 20, 21 | Memória de longo prazo |
| Giro parahipocampal | Localizado medialmente no córtex temporo-occipital inferior | 34 | Memória de curto prazo |
| Uncus Uncus Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy | Contínuo com o giro hipocampal | 35 | Olfato |
| Giro Fusiforme | Giro Medial Occipitotemporal | 37 | Reconhecimento facial |
| Área de Wernicke | Giro temporal superior do hemisfério dominante (para além do giro supramarginal do lobo parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy)* | 22, 40 | Compreensão da linguagem |
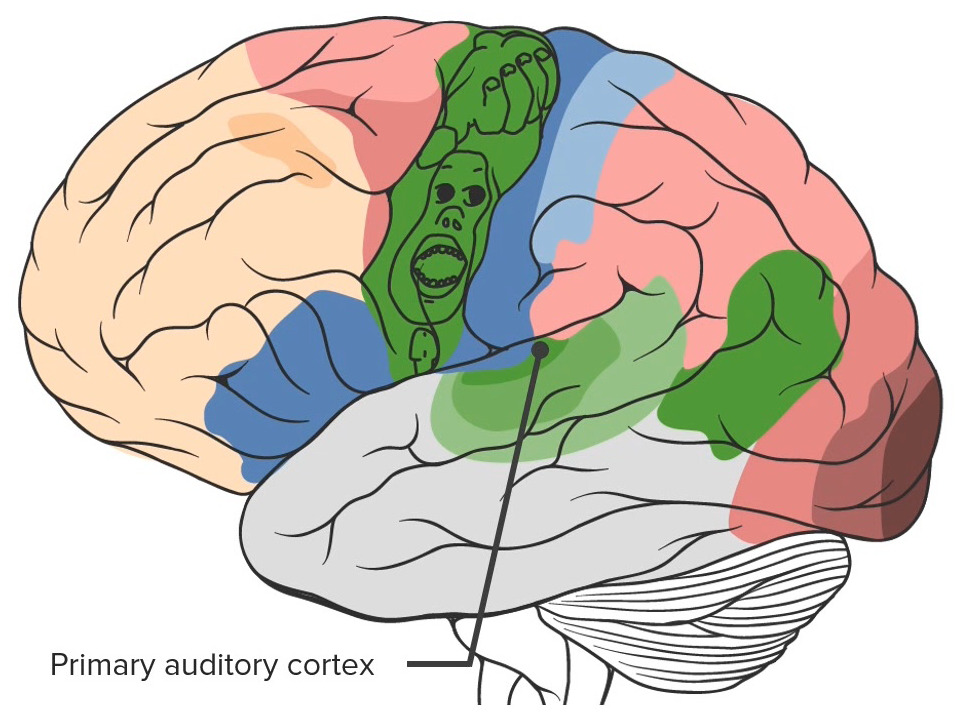
Observar o córtex auditivo primário localizado no lobo temporal
Imagem por Lecturio.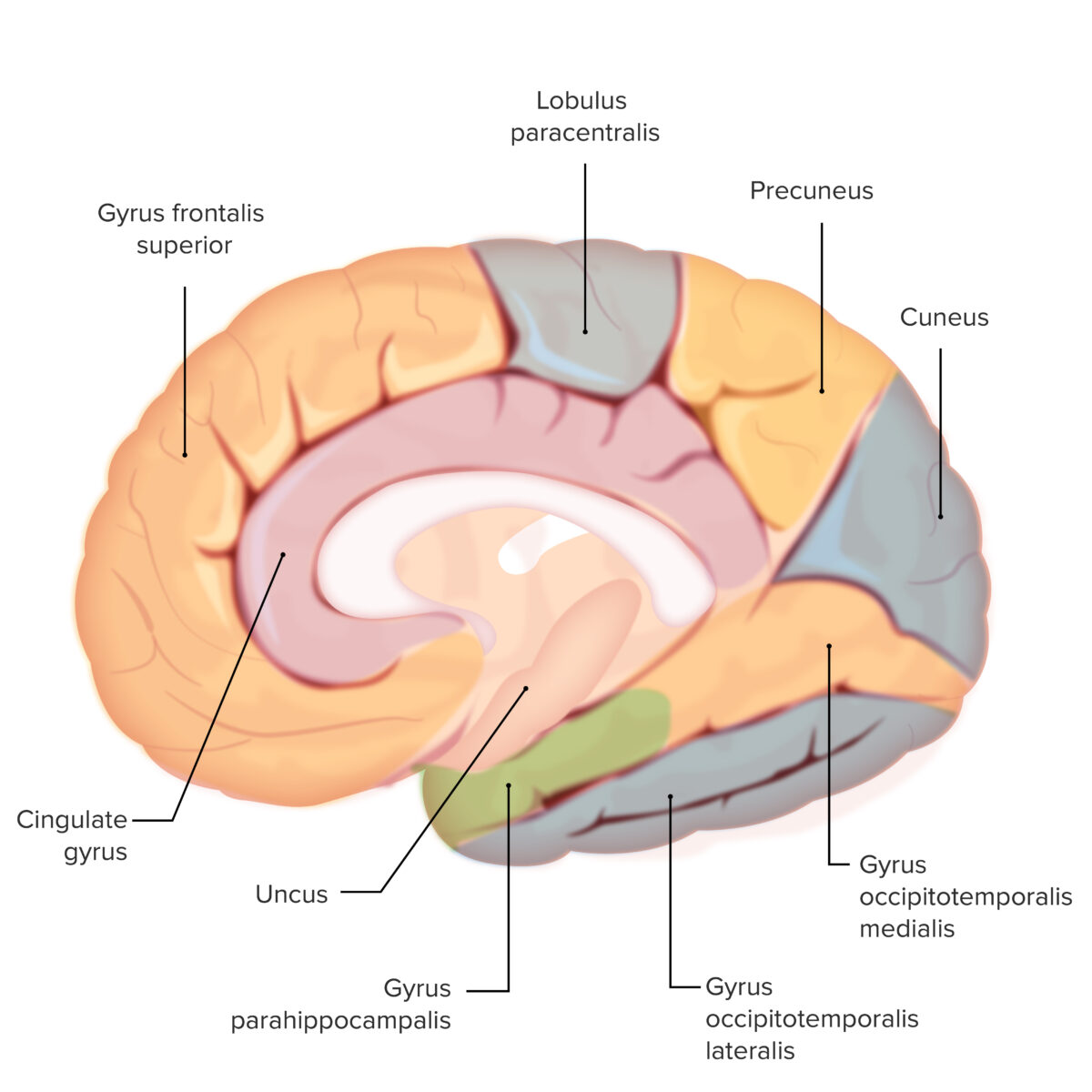
Os vários giros em todo o cérebro: Observar o giro para-hipocampal (sombreado a verde)
Esta estrutura é importante para a formação da memória de curto prazo
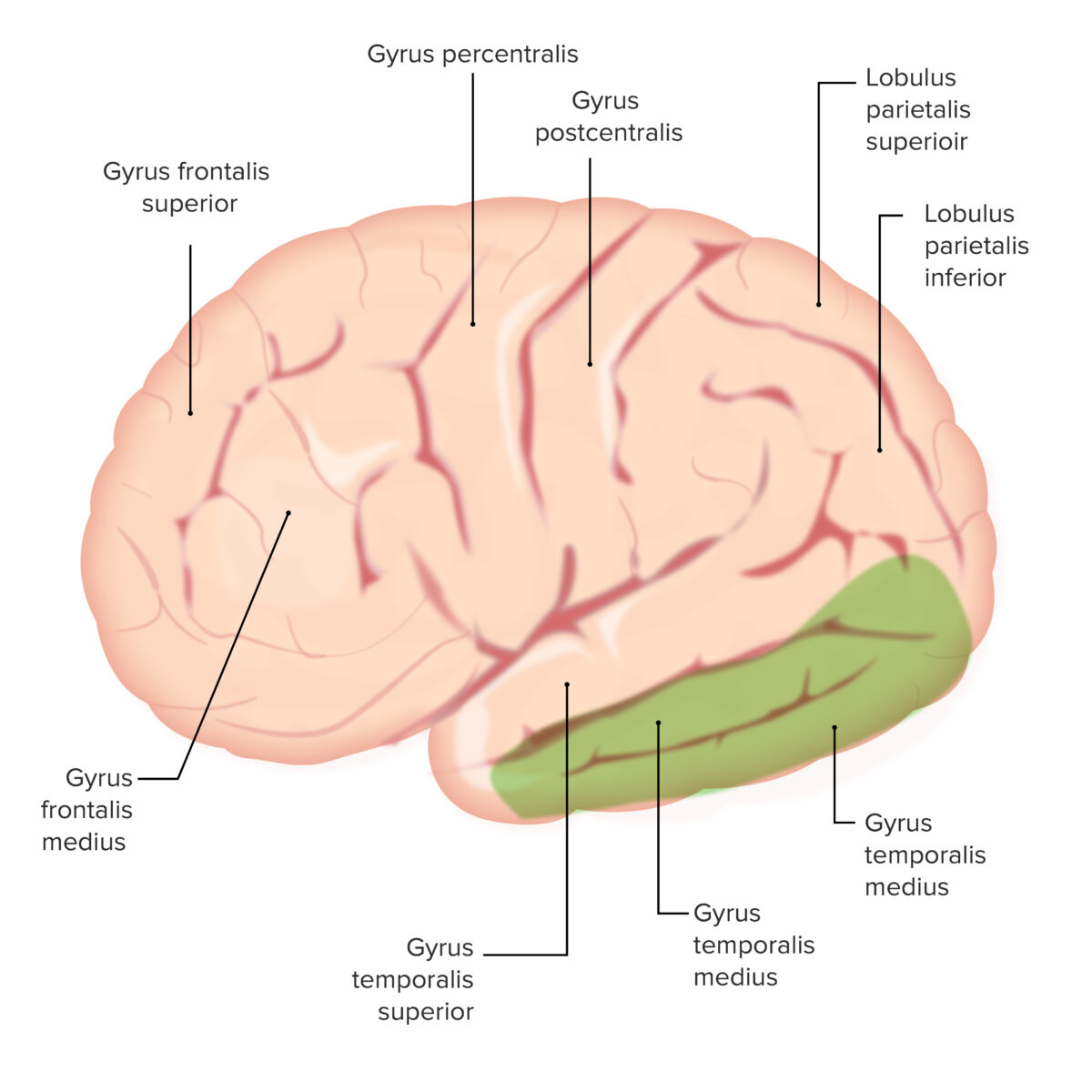
Os vários giros em todo o cérebro: Observar os giros temporais medial e inferior (ambos sombreados a verde).
Estas estruturas são importantes para a memória de longo prazo
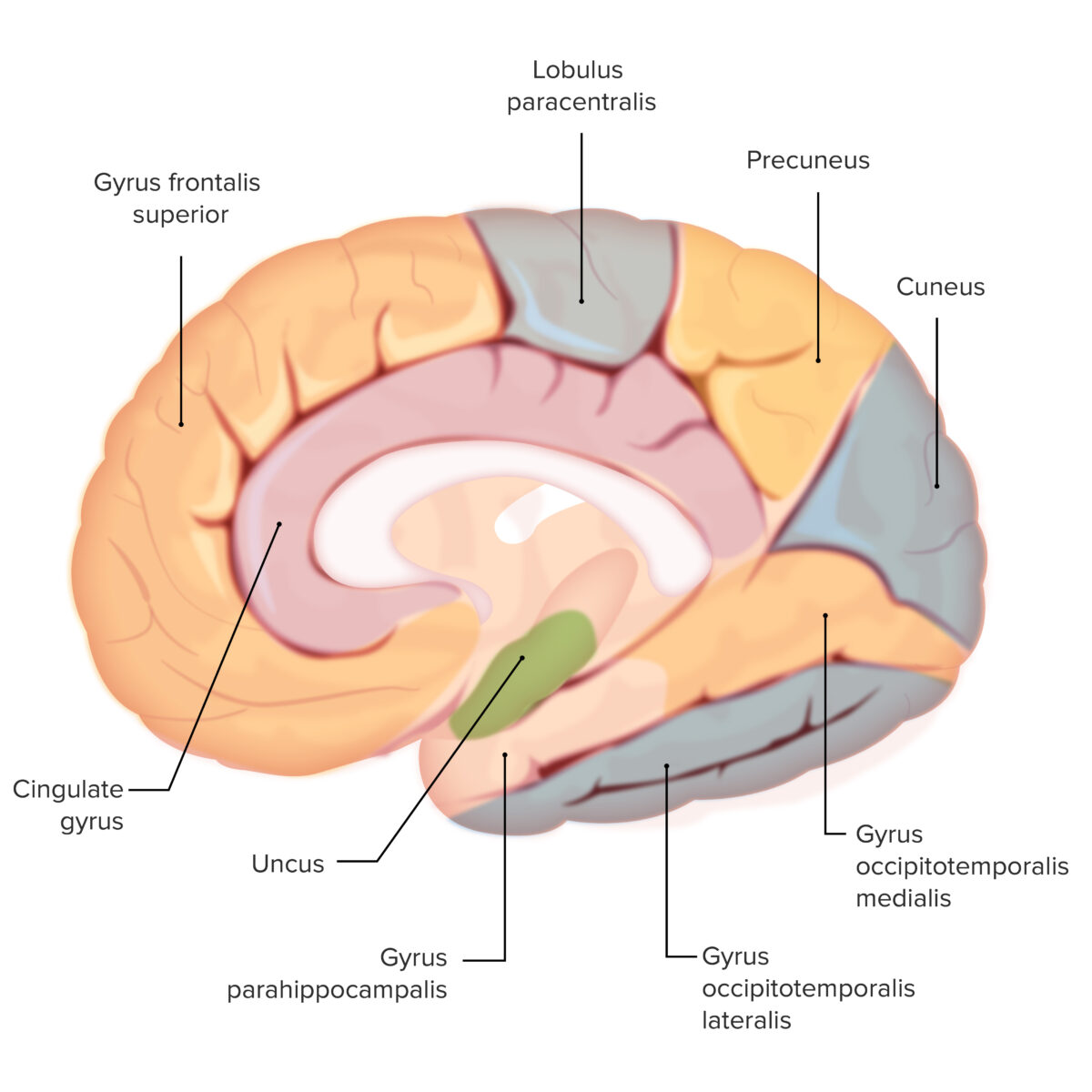
Os vários giros em todo o cérebro: Observar o uncus (sombreado a verde)
Esta é uma estrutura olfativa importante
As seguintes estruturas estão intimamente relacionadas com o córtex cerebral por localização ou função: