Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Regulation of Water and Sodium Balance
-
Slides RegulationofFluidandElectrolyteBalance IntegratedRenalPathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
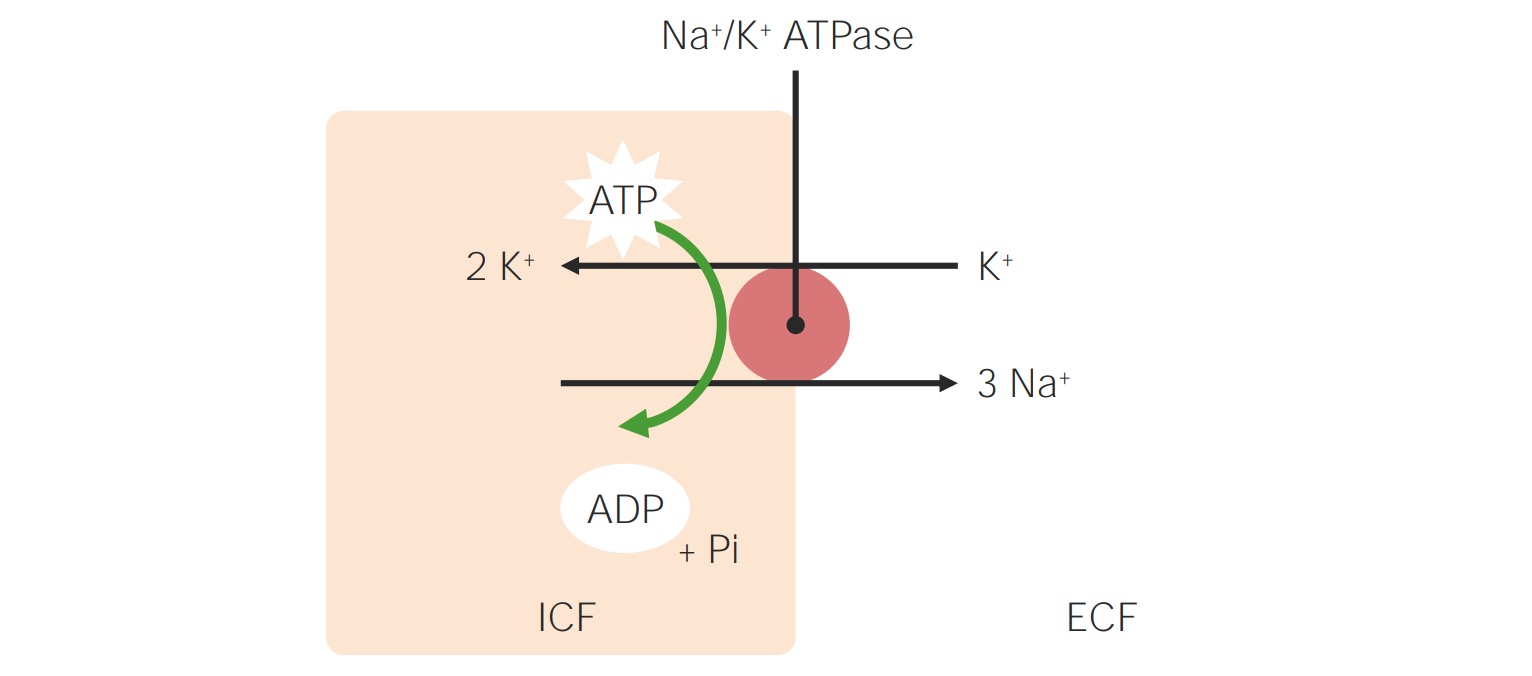
00:02 Continuing our discussion of sodium and water pathophys. Well, we are going to take this information, stuff that we have seen and really put onto clinical setting. That at this point I would say this is more of an advanced type of application of what we have seen earlier. 00:18 But trust me it's not too bad. So two carefully regulated parameters. Regulated. 00:25 We have effective circulating volume. What does that mean to you? The plasma. 00:31 In other words, that is your intravascular volume, isn't it? And you have tonicity. Tonicity, of course, representing the osmolarity. Effective circulating volume is found in the extracellular fluid. The tonicity is then determined by, here you go again, serum sodium concentration. 00:55 The serum sodium concentration as we discussed in previous lectures, was the fact that it is your total body sodium over your total body water. And we went through all of your isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic disorders. Effective circulating volume, the operative term here portion of the intravascular volume that then, of course, perfuses your organs. 01:20 Hence, there has to be constant regulation.
About the Lecture
The lecture Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Regulation of Water and Sodium Balance by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Fluid and Electrolyte Balance.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following body compartments best represents the effective circulating volume?
- The plasma
- The serum
- The intracellular fluid
- The extracellular fluid
- The interstitial fluid
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |