Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Questions – Antifungals
-
Slides Questions Antifungals.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
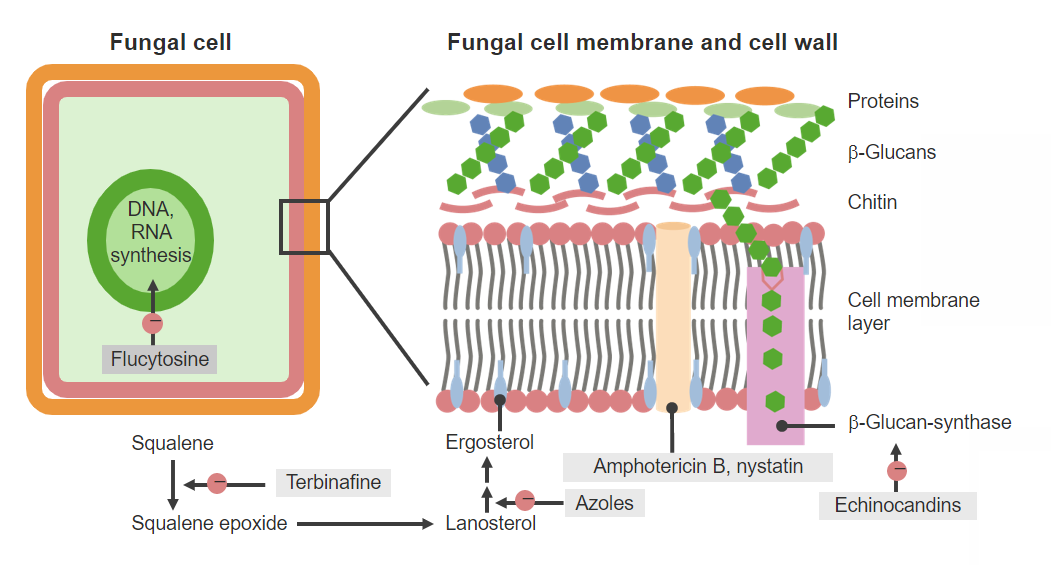
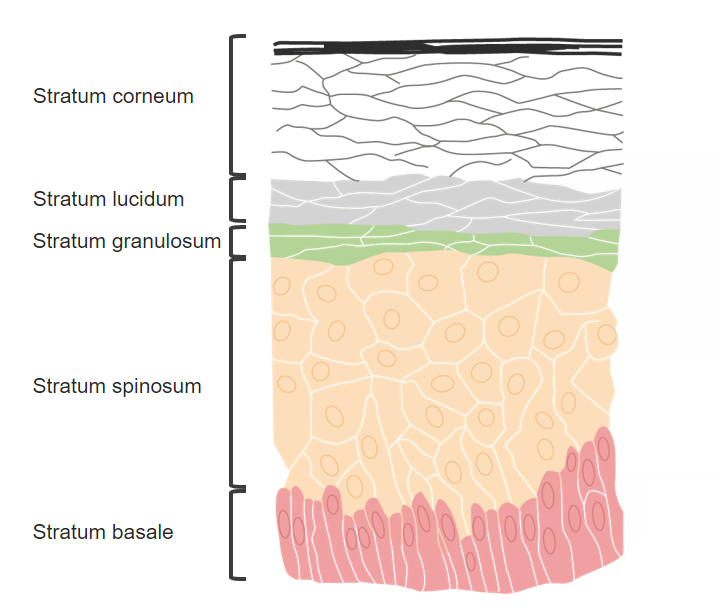
00:00 Okay, let's have a question. 00:03 The following medications act on the fungal cell wall except A) Flucytosine B) Ketoconazole C) Miconazole D) Nystatin and E) Amphotericin B Good you said Flucytosine. 00:23 Which of the following drugs is a drug of choice for cryptococcal pneumonia of mild to moderate severity? A) Ketoconazole B) Fluconazole C) Miconazole D) Terbinafine and E) Griseofulvin Right, fluconazole. 00:42 Now ketoconazole is a narrow spectrum antifungal agent with a significant number of side effects and adverse events. 00:48 It's not available in parenteral form. 00:51 And it's used in really mucocutaneous candidiasis and dermatophyte infections. 00:57 Miconazole is an azole as well. 01:00 It's used against skin infections. 01:03 Terbinafine and griseofulvin are medications that predominantly focus on the skin because they bind to the stratum corneum. 01:10 If you remember where I had a picture of the stratum corneum before. 01:14 Fluconazole is the drug of choice in mild to moderate cryptococcal pneumonia. 01:18 It is also used for the secondary prevention of cryptococcal infections. 01:22 Severe cryptococcal pneumonia and meningoencephalitis are treated with combination therapy, consisting of 5-flucytosine with amphotericin B. 01:32 Which of the following agents act by creating a pore in the cell membrane? Flucytosine. 01:38 Terbinafine. 01:40 The polyenes. 01:41 Ketoconazole. 01:43 Indapamide. 01:46 The polyenes, right. 01:49 Flucytosine interferes with the enzymes that synthesize DNA and RNA. 01:53 Terbinafine binds to the stratum corneum of the skin and inhibits squalene epoxidase, leading to the accumulation of toxic squalene, which disrupts fungal cell function. It does not create pores in the membrane. 02:07 Ketoconazole acts by inhibiting ergosterol synthesis, disrupting the membrane indirectly by depleting ergosterol. It does not create pores. 02:15 Indapamide though is a diuretic. 02:17 This has nothing to do with fungus and is just thrown in there as an extra choice. 02:23 Now the polyenes include amphotericin B and nystatin which create hydrophilic pores in the cell wall allowing the efflux of solutes from the cytoplasm. 02:34 And it also allows for toxic intermediates to develop through free radical formation inside the fungal cell wall. 02:40 That's it. 02:43 That's the fungal agents. 02:45 You did really well to sit through it. 02:47 You can go and write your exam and feel confident and show them what you know.
About the Lecture
The lecture Questions – Antifungals by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following drugs is the drug of choice for treating mild to moderate cryptococcal pneumonia?
- Fluconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Miconazole
- Terbinafine
- Griseofulvin
Which pairing is correct?
- Amphotericin B : Creates hydrophilic pores in the cell wall
- Flucytosine : Disruption of cell wall synthesis
- Griseofulvin : Secondary prevention of cryptococcal infection
- Fluconazole : Binds stratum corneum
- Nystatin : Interferes with DNA synthesis
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |