El tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms es una neoplasia causada por la proliferación del blastema metanéfrico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria riñones y es la neoplasia renal más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. El tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms suele surgir de forma esporádica, pero también puede aparecer como resultado de una anomalía congénita específica como el síndrome WAGR ( tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms, aniridia Aniridia A congenital abnormality in which there is only a rudimentary iris. This is due to the failure of the optic cup to grow. Aniridia also occurs in a hereditary form, usually autosomal dominant. Wilms Tumor, anomalías genitourinarias y retraso mental), el síndrome de Denys-Drash o el síndrome de Beckwith-Wiedemann. El tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms suele presentarse como una masa firme, no sensible y lisa que no cruza la línea media. El tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms también puede presentarse raramente con dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma y/o hipertensión. La malignidad se diagnostica con ultrasonido abdominal y estudios histopatológicos (a partir de una biopsia o resección). El tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms se trata con una terapia multimodal (cirugía, quimioterapia y/o radiación). Dependiendo de la edad del paciente, los LOS Neisseria marcadores moleculares y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos patológicos, el pronóstico es generalmente favorable, con tasas de supervivencia a los LOS Neisseria 5 años cercanas al AL Amyloidosis 90%.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
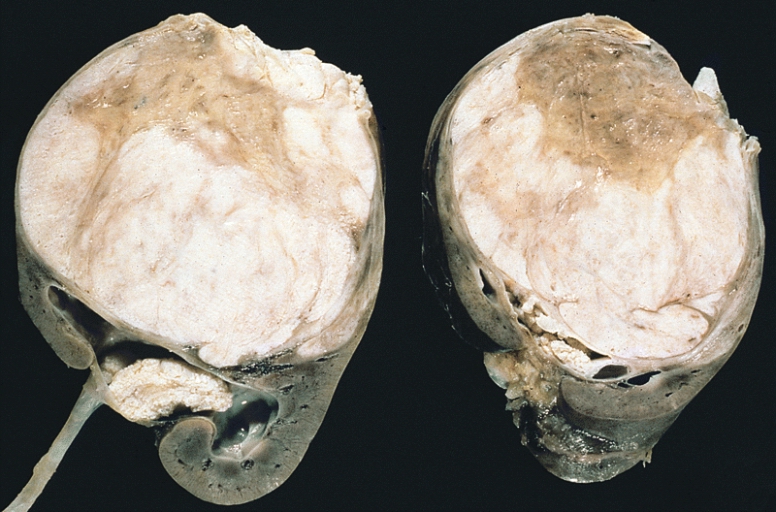
Tumor de Wilms:
Obsérvense los prominentes septos que subdividen la superficie seccionada y la protrusión del tumor en la pelvis renal, que se asemeja a un rabdomiosarcoma botrioide.
Ultrasonido abdominal seriado para los LOS Neisseria que tienen riesgo de tumor Tumor Inflammation de Wilms:
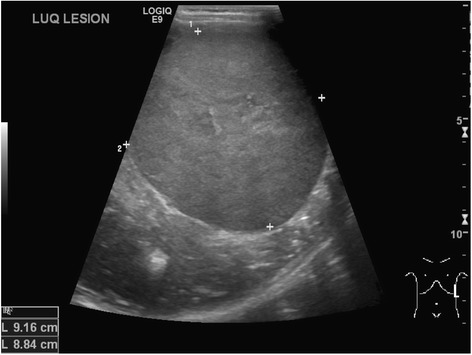
Ultrasonido abdominal que revela un tumor de Wilms del lado izquierdo en un niño de 4 años
Imagen: “Neuroblastoma and nephroblastoma: a radiological review” por Dumba M, Jawad N, McHugh K. Licencia: CC BY 4.0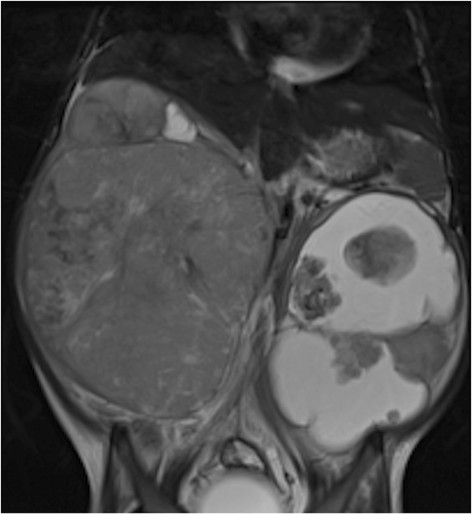
RM de un tumor de Wilms: niña de 4 años con tumor de Wilms bilateral, más quístico en la izquierda
Imagen: “Figure 11” por Dumba, M. et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0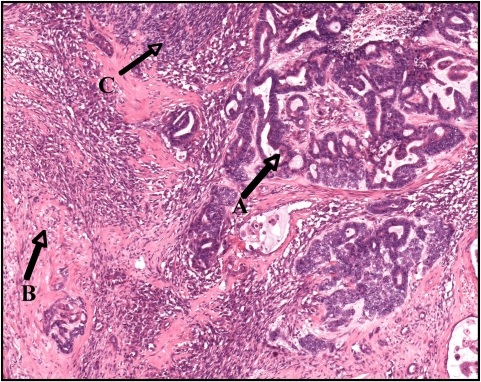
Tumor de Wilms con componente epitelial (A), componente estromal (B) y pequeñas áreas de blastema (C)
Imagen: “Wilms tumor in a 37-year-old” por Thevendran G, Farne HA, Kaisary AV. Licencia: CC BY 2.0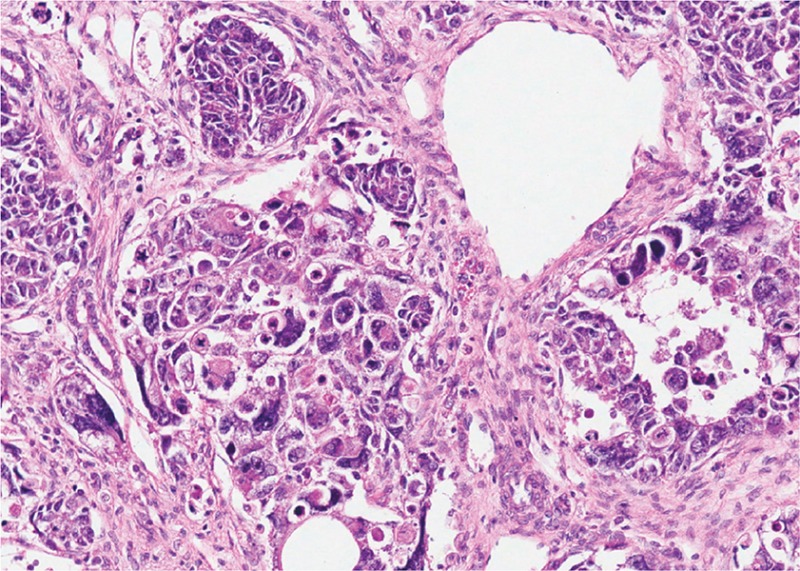
Examen histopatológico de la biopsia de un tumor de Wilms con anaplasia
Imagen: “Wilms tumour with anaplasia” por van den Heuvel-Eibrink, MM. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Del National Wilms Tumor Tumor Inflammation Study (NWTS, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)/Children’s Oncology Group (COG, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Recomendaciones basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ensayos del NWTS/COG: