El sistema arterial carotídeo es el encargado de la irrigación sanguínea a la cabeza y cuello. El sistema arterial comienza con la arteria carótida común, que nace directamente del arco aórtico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lado izquierdo y del tronco/arteria braquiocefálica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lado derecho. Posteriormente, ambas arterias carótidas comunes ascienden por el cuello y se dividen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las arterias carótidas internas y externas. La primera abastece las estructuras del cerebro y las órbitas, mientras que la segunda abastece las estructuras superficiales y partes del cuello y la cara.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La arteria carótida común posee diferentes orígenes dependiendo de cada lado del cuerpo:
La arteria carótida común se bifurca a nivel del cartílago tiroides (vértebra C4) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
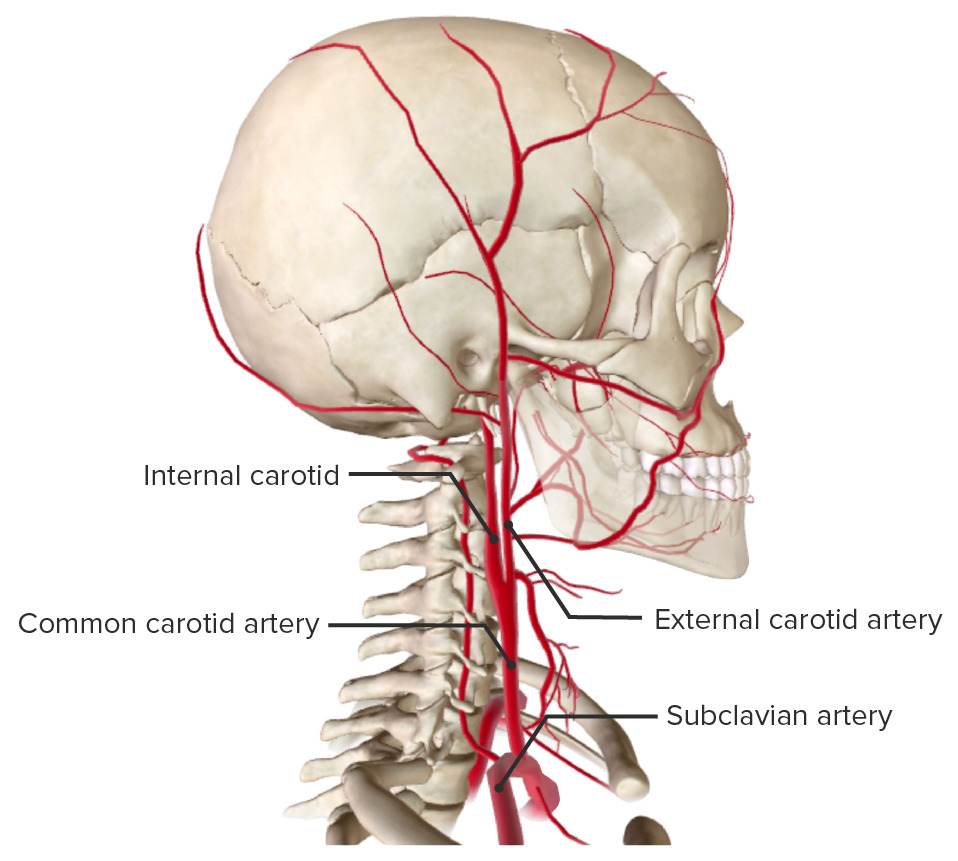
Bifurcación de la arteria carótida
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por LecturioGlomus o cuerpo carotídeo:
Seno carotídeo:

Arteria carótida común dentro de la vaina carotídea
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio| Parte torácica (izquierda) | Parte inferior del cuello (ambas) | Parte superior del cuello (ambas) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior |
|
|
|
| Posterior |
|
|
|
| Lateral |
|
|
|
| Medial | Tronco/arteria braquiocefálica | Tráquea |
|
La arteria carótida externa irriga las siguientes estructuras:
Superficial, dentro del triángulo carotídeo, y a nivel del cartílago tiroides (C4)
| Rama | Estructuras irrigadas |
|---|---|
| Tiroidea superior |
|
| Faríngea ascendente |
|
| Lingual |
|
| Facial |
|
| Occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy | Región posterior del cuero cabelludo |
| Auricular posterior |
|
| Maxilar |
|
| Temporal superficial | Región temporal del cuero cabelludo |
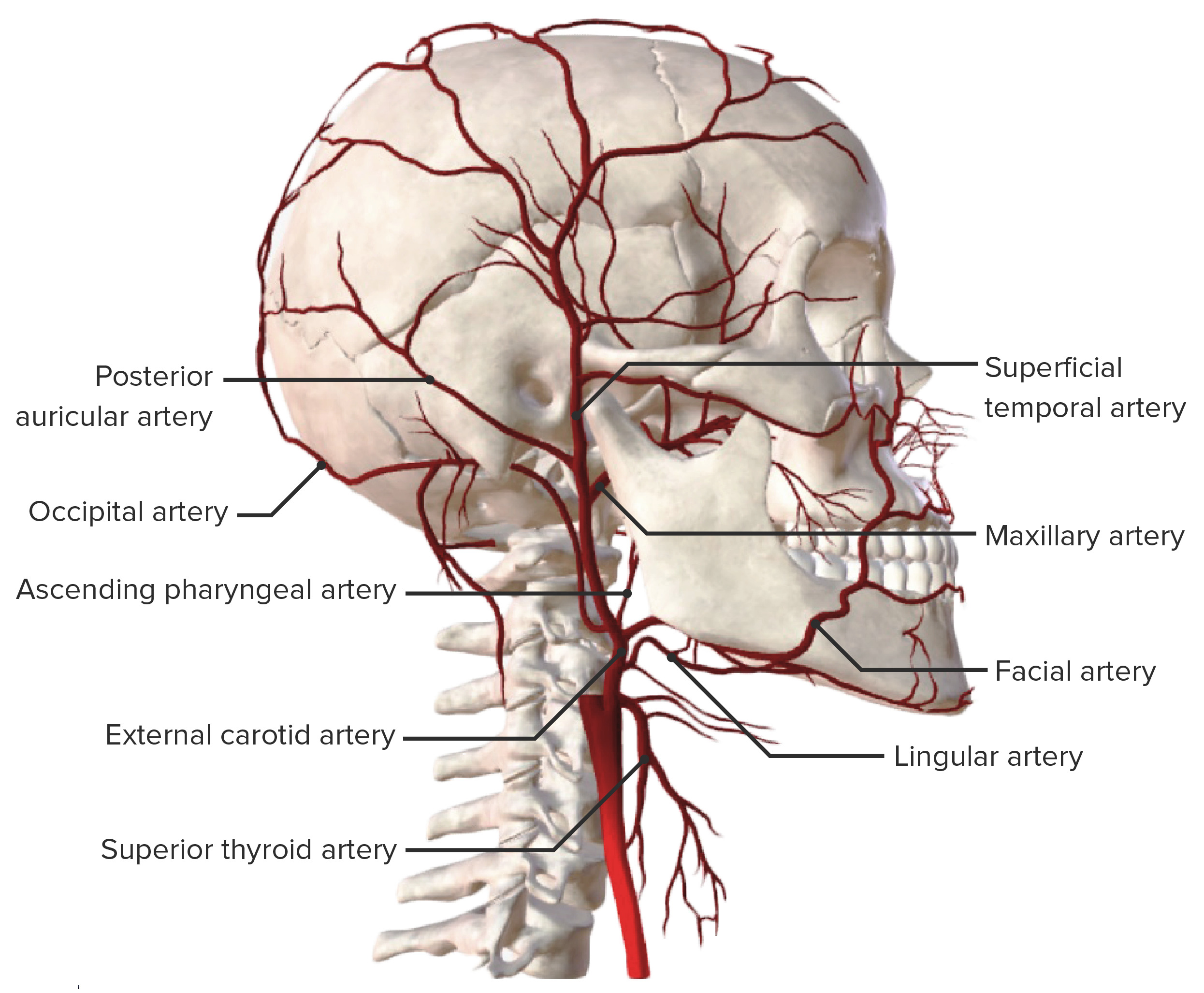
Principales ramas de la arteria carótida externa
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por LecturioLa arteria carótida interna irriga las siguientes estructuras:
La arteria carótida interna se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum segmentos:
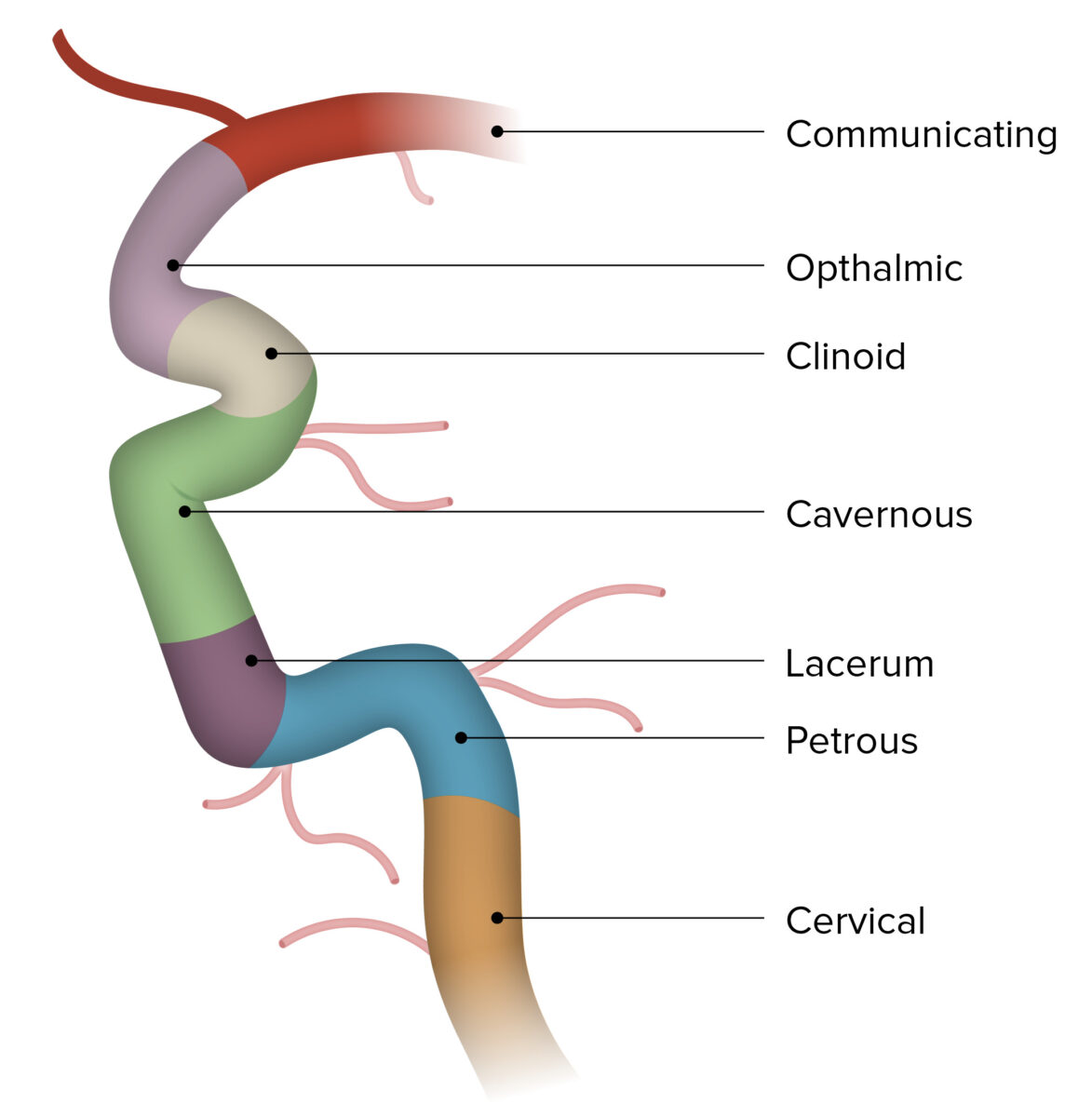
Segmentos de la arteria carótida interna
Imagen por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio