Los LOS Neisseria trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal son un grupo de trastornos pediátricos neonatales causados por el consumo de alcohol de la madre durante el embarazo. El término implica una serie de efectos físicos y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el desarrollo neurológico. La clasificación se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gravedad y la presentación clínica. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria antecedentes de exposición prenatal al AL Amyloidosis alcohol y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presencia de anomalías físicas y del desarrollo características. El tratamiento implica la corrección quirúrgica de las anomalías estructurales y el inicio temprano de las medidas de soporte para promover los LOS Neisseria mejores resultados.
Last updated: Jan 7, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal consisten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria déficits físicos, de desarrollo, cognitivos y psiquiátricos postnatales observados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente que ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia estado expuesto al AL Amyloidosis alcohol mientras estaba en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el útero.
Al AL Amyloidosis ser un término paraguas, los LOS Neisseria trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal comprende múltiples condiciones:
El alcohol es un teratógeno que tiene efectos irreversibles:
Factores que contribuyen a la patogénesis:
La variación de la susceptibilidad del feto está afectada por:
Puede haber varias combinaciones de características.
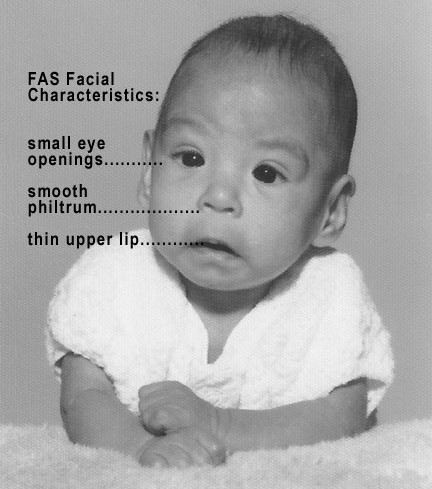
Trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal: bebé con rasgos faciales característicos
Imagen: “Male baby with FAS syndrome” por Teresa Kellerman. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0El diagnóstico preciso y precoz los LOS Neisseria trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal realizado < 6 años de edad es importante para permitir las intervenciones y mejorar los LOS Neisseria resultados.
Actualmente, no existe ningún tratamiento para los LOS Neisseria trastornos del espectro alcohólico fetal; el tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la intervención temprana y la prevención.