El síndrome de X frágil, también conocido como síndrome de Martin-Bell, es una enfermedad genética de herencia ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X. Tanto los LOS Neisseria niños como las niñas pueden verse afectados, pero la gravedad es mucho mayor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. Los LOS Neisseria rasgos característicos son cara alargada, frente y barbilla prominentes, orejas grandes, pies planos y testículos grandes después de la pubertad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. El síndrome de X frágil es la causa más común de discapacidad intelectual hereditaria y también se asocia al AL Amyloidosis autismo. Las pruebas genéticas confirman el diagnóstico. El tratamiento está dirigido a mejorar los LOS Neisseria síntomas asociados.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de X frágil se produce debido a una mutación de pérdida de función en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen del retraso mental del cromosoma X frágil 1 (FMR1). El FMR1 codifica la proteína del retraso mental del X frágil, que es importante para el desarrollo del cerebro y las gónadas (testículos y ovarios).
Más del 99% de los LOS Neisseria casos se deben a una expansión inestable de repeticiones de trinucleótidos (CGG) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la región promotora del gen FMR1:
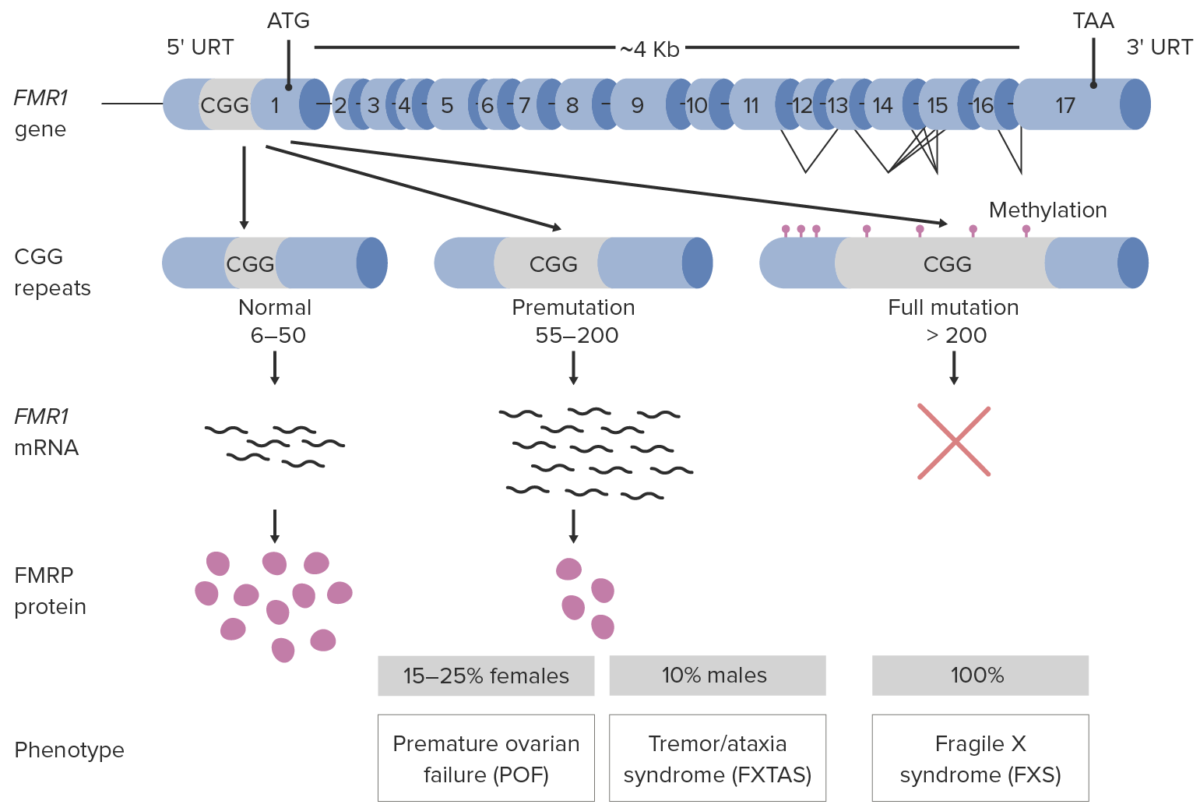
Fisiopatología del síndrome de X frágil
FXTAS: Síndrome de temblor/ataxia asociado al X frágil
El patrón de herencia es dominante ligado al AL Amyloidosis X:
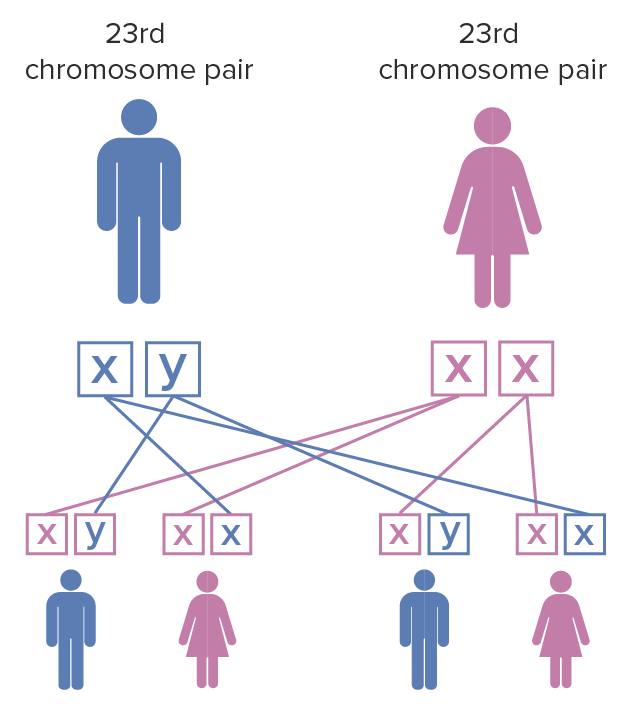
Patrón de herencia del síndrome del cromosoma X frágil:
La madre tiene un par de cromosomas X que han sufrido una mutación; el padre tiene cromosomas X e Y no afectados. Cuando la mujer con la mutación del cromosoma X frágil en ambos cromosomas X tiene hijos, cada hijo tiene un 100% de posibilidades de heredar la enfermedad. Las mujeres se ven menos afectadas por el síndrome del cromosoma X frágil que los hombres debido a la inactivación del cromosoma X.
Las niñas y las personas con premutaciones tienen manifestaciones clínicas variables y a menudo menos graves. Las siguientes son las características clínicas de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síndrome de X frágil clásico (mutación completa).
Niño con síndrome de Down y mutación completa de síndrome de X frágil
Imagen: “Boy with cooccurrence DS and full mutation FXS” por Emory University, Department of Human Genetics, 2165 N. Decatur Road, Decatur, GA 30033, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0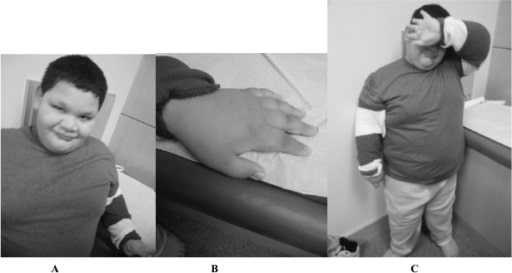
Un niño de 9 años con síndrome de X frágil de mutación completa: Obsérvese la cara redonda y las orejas prominentes (A), dedos cortos (B), y la obesidad troncal (C).
Imagen: “Fragile X boy with the Prader-Willi phenotype” por Medical Investigation of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (M.I.N.D.) Institute, University of California Davis Health System, Sacramento, California, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.5No existe un tratamiento curativo para el síndrome de X frágil. El tratamiento se adapta a los LOS Neisseria síntomas presentes. La terapia de soporte incluye lo siguiente:
Las siguientes afecciones son diagnósticos diferenciales del síndrome de X frágil:
Las siguientes son afecciones que preocupan a quienes tienen premutaciones para el síndrome de X frágil.