El síndrome de ovario poliquístico (SOP) es el trastorno endocrino más común de las mujeres en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum edad reproductiva y afecta a casi 5‒10% de las mujeres en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ese grupo de edad. Caracterizado por el hiperandrogenismo, la anovulación crónica que conduce a la oligomenorrea (o amenorrea) y la disfunción metabólica, el SOP aumenta el riesgo de infertilidad, hiperplasia o carcinoma endometrial y enfermedades cardiovasculares. La fisiopatología no se comprende completamente, pero se cree que tiene una base genética multifactorial que causa una liberación pulsátil alterada de la hormona liberadora de gonadotropina (GnRH), así como aumentos de la hormona luteinizante ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle), andrógenos y estrógenos (debido a la aromatización periférica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tejido adiposo). El resultado es la anovulación crónica y el hirsutismo, los LOS Neisseria cuales definen la enfermedad. El diagnóstico es de exclusión, por lo que hay que descartar otras causas de hemorragia uterina anormal e hirsutismo. El tratamiento incluye el intento de restablecer la ovulación normal mediante la pérdida de peso, los LOS Neisseria anticonceptivos orales (ACO) y el apoyo a la fertilidad.
Last updated: Jan 13, 2025
Se desconocen los LOS Neisseria mecanismos exactos, pero se cree que son complejos e incluyen tanto factores genéticos como ambientales. El síndrome metabólico y la obesidad están presentes a menudo, pero no siempre, y probablemente contribuyen a la fisiopatología en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos individuos.
El síndrome de ovario poliquístico (SOP) debe sospecharse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier mujer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum edad reproductiva con menstruaciones irregulares y/o síntomas de hiperandrogenismo, especialmente si es obesa o presenta infertilidad.
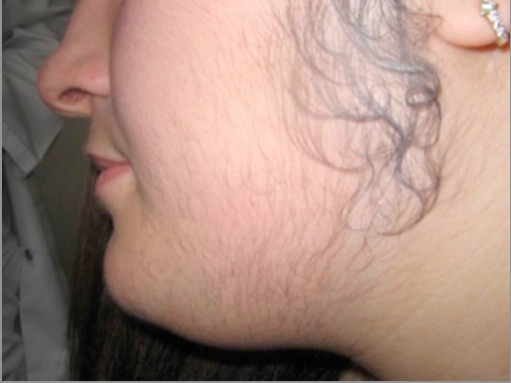
Hirsutism in PCOS:
Hair is noted along the side burns, chin, and upper lip; signs of hyperandrogenism.
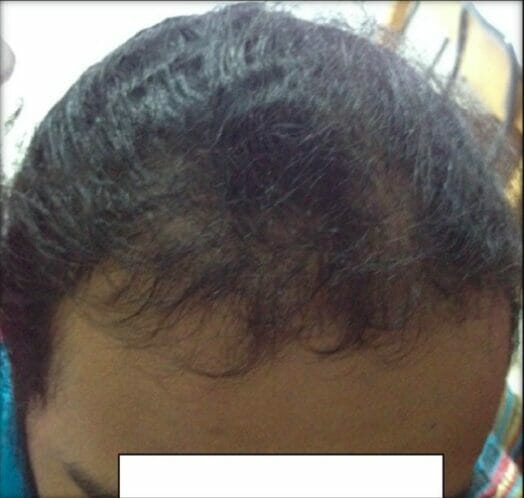
Male-pattern alopecia in PCOS:
The patient has frontal hair thinning, which is a sign of hyperandrogenism.
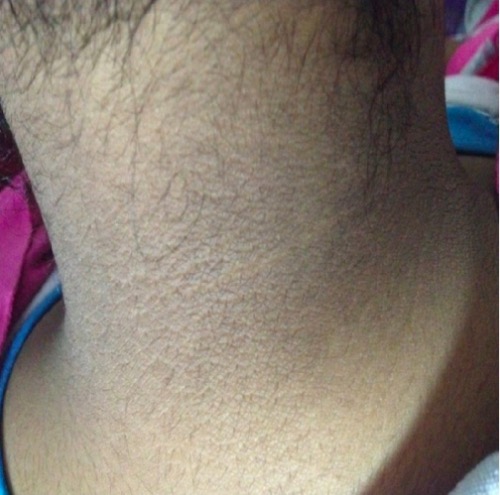
Acantosis nigricans en el SOP:
La piel engrosada y oscurecida puede aparecer en la nuca, las axilas o los pliegues de la piel como signo de niveles elevados de insulina por la resistencia a la misma.
El síndrome de ovario poliquístico (SOP) es un diagnóstico de exclusión, por lo que deben descartarse otras causas de oligo o amenorrea e hiperandrogenismo. Los LOS Neisseria criterios de Rotterdam se utilizan habitualmente para hacer el diagnóstico una vez que se han excluido otras causas.
El diagnóstico requiere 2 de los LOS Neisseria 3 criterios siguientes:
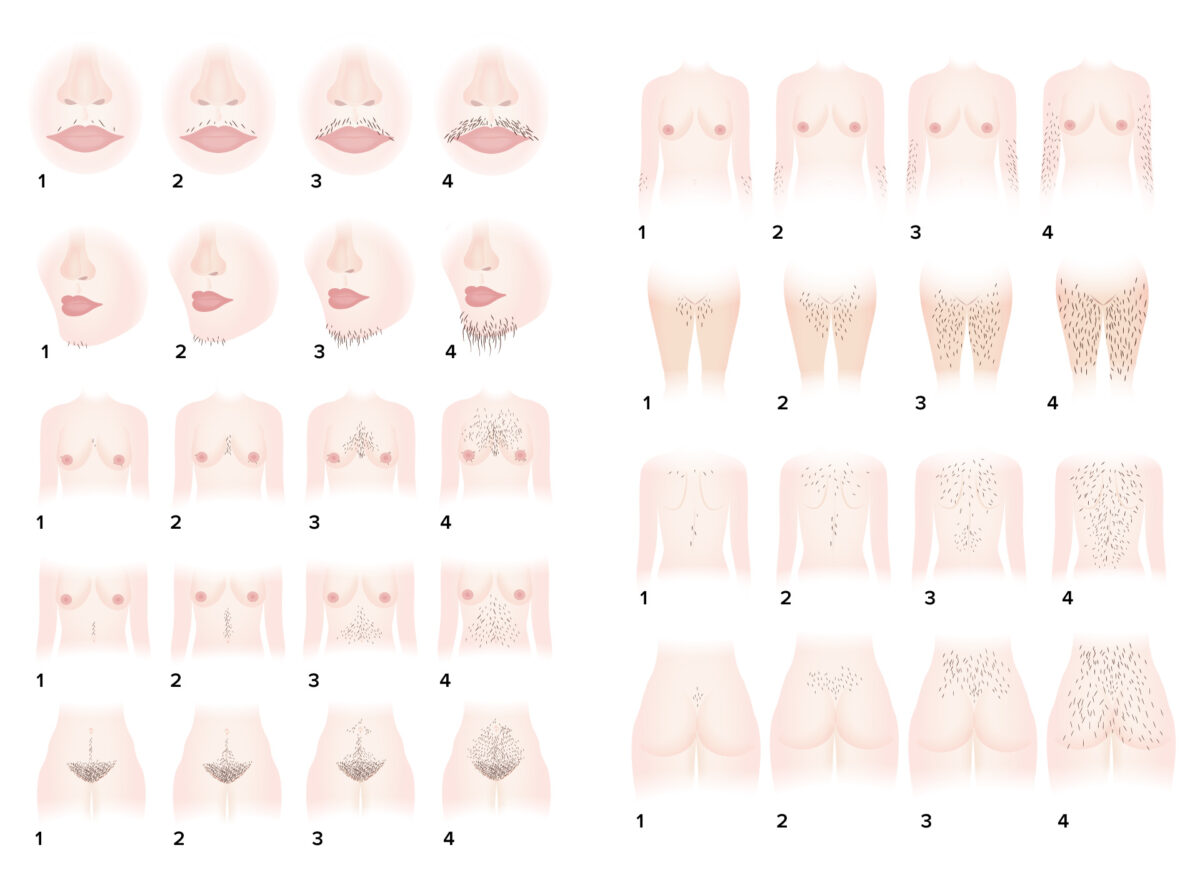
Sistema de puntuación del hirsutismo de Ferriman-Gallwey: un sistema de evaluación objetiva del grado de hirsutismo
Imagen por Lecturio.| Hormonas ↑ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SOP | Hormonas ↓ en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SOP |
|---|---|
|
|
FSH: hormona estimulante del folículo
HDL: lipoproteínas de alta densidad
LDL: lipoproteínas de baja densidad
LH: hormona luteinizante
SOP: síndrome de ovario poliquístico
SHBG: globulina transportadora de hormonas sexuales
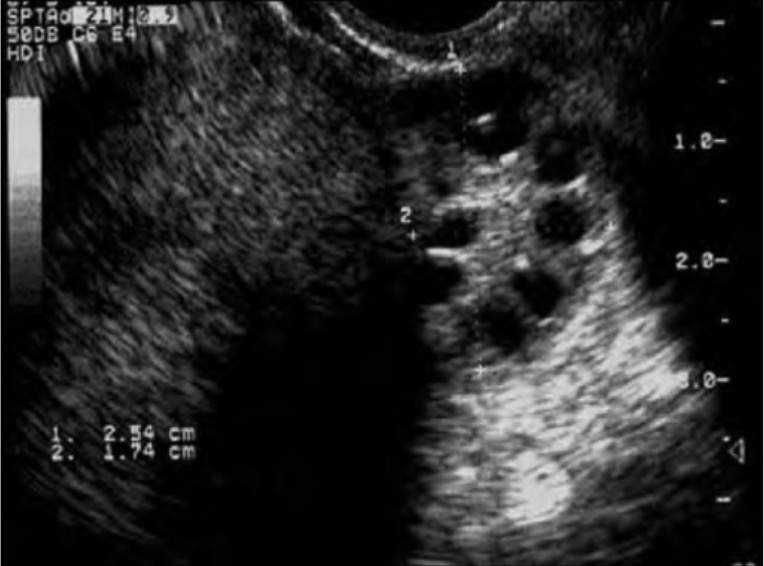
Ecografía de un ovario de apariencia poliquística:
Observe el clasico “collar de perlas” alrededor de la periferia del ovario que identifican los folículos de desarrollo anormal que se observan en el SOP. Los ovarios de apariencia poliquística se observan en aproximadamente ⅔ de las pacientes con SOP y es uno de los 3 criterios diagnósticos de Rotterdam.
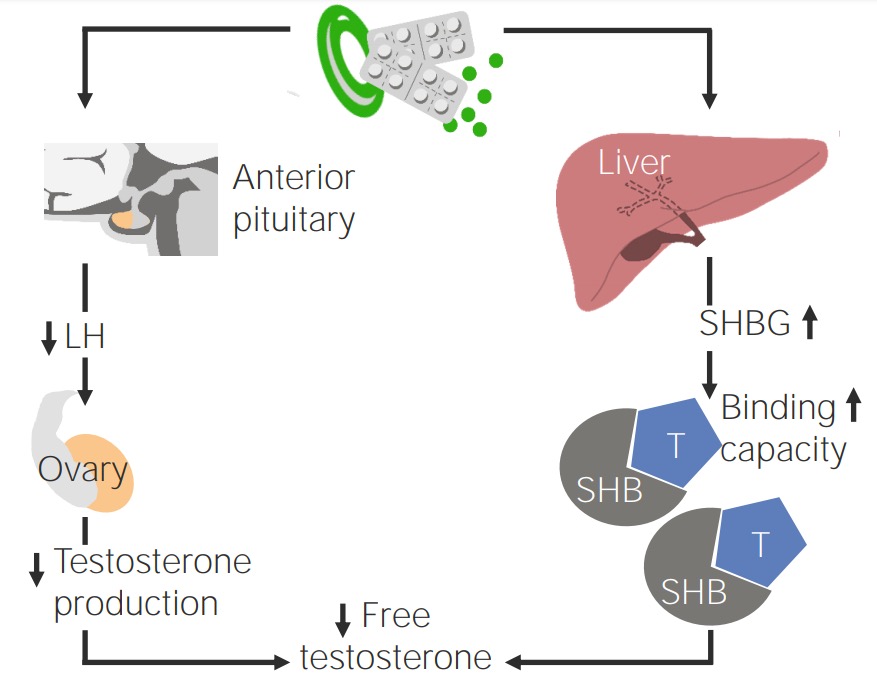
Efecto de los anticonceptivos orales en pacientes con SOP
Imagen por Lecturio.