El síndrome de Lynch, también llamado cáncer colorrectal hereditario no polipósico, es el síndrome de cáncer de colon hereditario más común, y conlleva un riesgo significativamente mayor de cáncer de endometrio y otras neoplasias. El síndrome de Lynch tiene un patrón de herencia autosómico dominante que implica variantes patogénicas en uno de los genes reparadores de desajustes (MMR, por sus siglas en inglés) o el gen de la molécula de adhesión de células epiteliales (EpCAM, por sus siglas en inglés). El diagnóstico se realiza mediante pruebas genéticas del paciente índice y de sus familiares. El tratamiento consiste en un tamizaje más temprano de los individuos con genes MMR defectuosos, así como una colectomía total si se descubre una neoplasia colorrectal. La histerectomía y salpingooforectomía profiláctica se recomiendan para las mujeres que superan la edad reproductiva.
Last updated: Jan 18, 2024
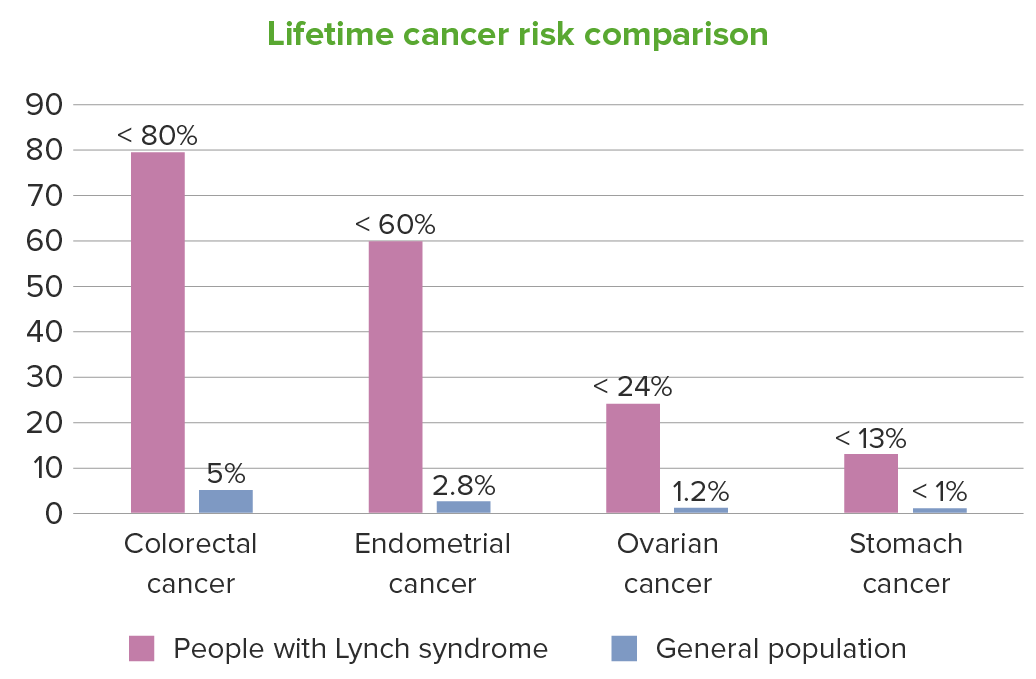
En el caso de las personas con síndrome de Lynch, el riesgo de cáncer a lo largo de la vida también aumenta en menor medida para otros tipos de cáncer, como: pelvis renal, uréteres, vejiga, cerebro, intestino delgado, tracto hepatobiliar, páncreas, próstata y piel. En la figura, se indican los rangos superiores de los riesgos individuales.
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con síndrome de Lynch heredan uno o más genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome mutantes y los LOS Neisseria respectivos alelos normales; el 2do alelo muta o pierde su función por silenciamiento epigenético con tanta frecuencia que el patrón de herencia es efectivamente autosómico dominante.
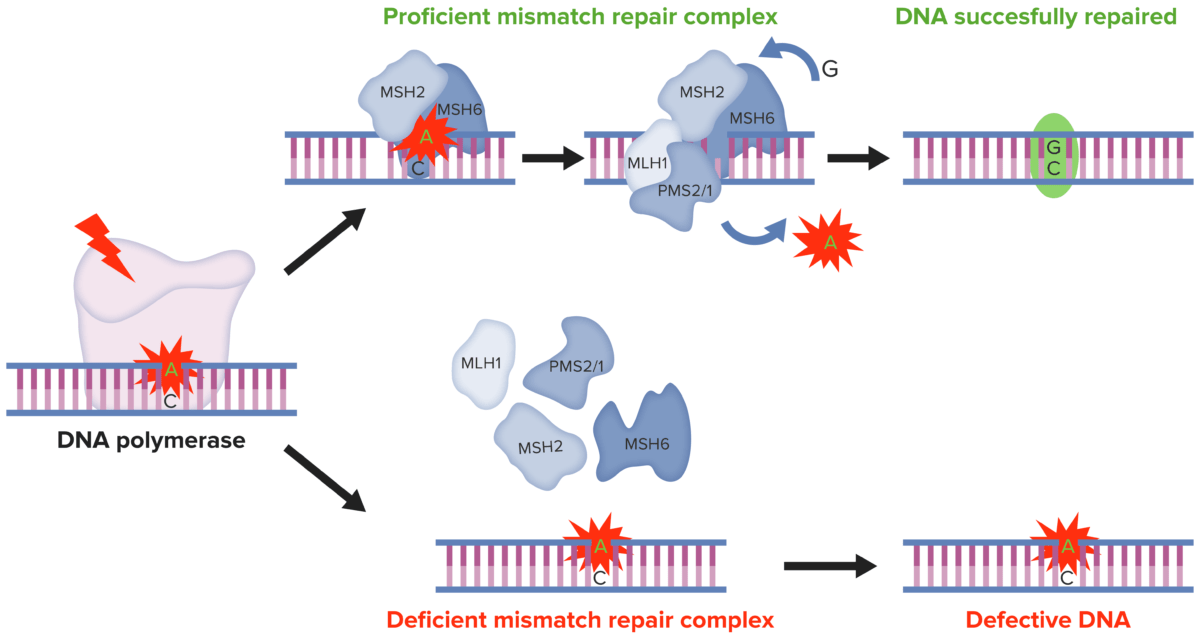
ADN MMR:
En las células normales, el ADN MMR reconoce y repara los desajustes genéticos generados durante la replicación del ADN. Por el contrario, en las células tumorales MSI la presencia de un sistema MMR deficiente da lugar a una MMR del ADN defectuosa en los microsatélites, lo que determina la acumulación de mutaciones en diferentes codones genómicos.
MMR: reparación de desajustes
MSI: inestabilidad de microsatélites
Para CCR:
Para el cáncer de endometrio:
Quimioprevención:
Inmunoterapia: