Las queratosis seborreicas son la neoplasia epitelial cutánea benigna más común. La afección consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum queratinocitos inmaduros. Las queratosis seborreicas son el tumor Tumor Inflammation cutáneo benigno más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos de mediana edad y ancianos y se presenta como una lesión cutánea exofítica bien delimitada que puede ser de color marrón o negra y tiene un aspecto “de estar pegada”. Puede haber prurito o dolor Dolor Inflammation si estas lesiones se inflaman secundariamente por un trauma, especialmente si están dentro de los LOS Neisseria pliegues cutáneos. Se cree que la genética juega un papel, pero la patogenia es incierta. Las mutaciones más comunes involucran dos oncogenes Oncogenes Genes whose gain-of-function alterations lead to neoplastic cell transformation. They include, for example, genes for activators or stimulators of cell proliferation such as growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein kinases, signal transducers, nuclear phosphoproteins, and transcription factors. A prefix of 'v-' before oncogene symbols indicates oncogenes captured and transmitted by retroviruses; the prefix 'c-' before the gene symbol of an oncogene indicates it is the cellular homolog (proto-oncogenes) of a v-oncogene. Carcinogenesis: el receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors 3 del factor de crecimiento de fibroblastos (FGFR3) y PIK3CA. Existe una predisposición familiar a desarrollar un elevado número de queratosis seborreicas. El tratamiento no es necesario, ya que se trata de una afección benigna, pero se puede realizar crioterapia, curetaje o electrodesecación por molestias o problemas estéticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las queratosis seborreicas son tumores benignos de la piel que consisten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una proliferación de queratinocitos inmaduros.
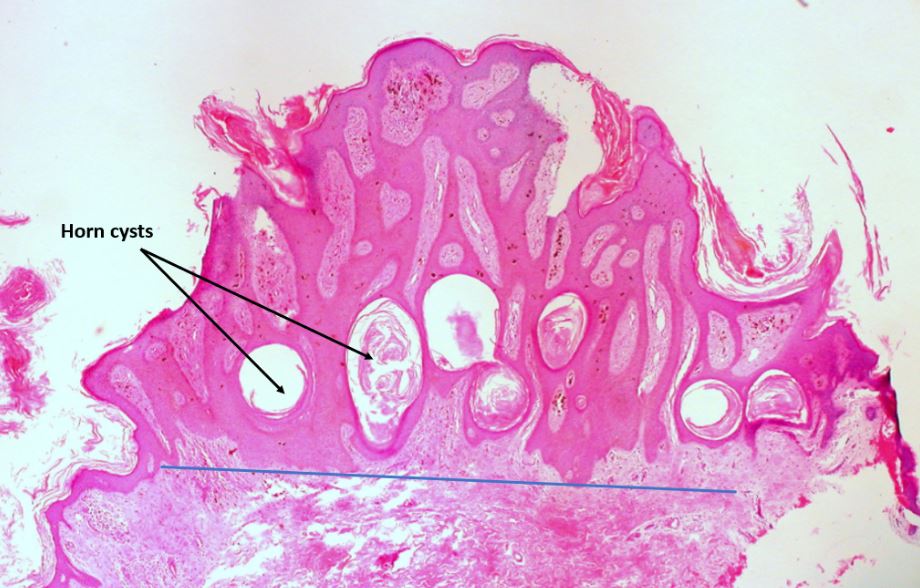
Queratosis seborreica pigmentada de la vulva:
Obsérvese la forma abovedada, la circunscripción nítida de la piel circundante, los quistes córneos y el pigmento de melanina marrón dentro de la epidermis y en la dermis adyacente (dentro de los macrófagos).
La línea azul debajo de la lesión demuestra el “signo de la cuerda” de la queratosis seborreica visto con un aumento de baja potencia: se puede dibujar una línea horizontal paralela a la superficie epidérmica subyacente a la lesión porque la queratosis seborreica se extiende uniformemente a una profundidad.
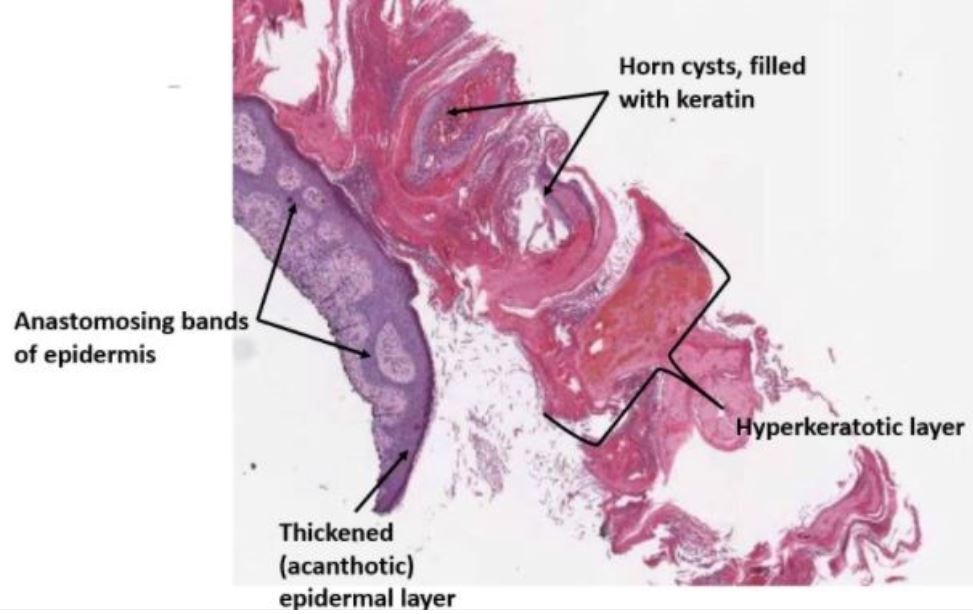
Microfotografía de bajo aumento de una biopsia por afeitado de una queratosis seborreica hiperqueratósica que muestra el material queratinoso superficial teñido de rosa parcialmente desprendido de la superficie.
Obsérvese la epidermis engrosada con hebras anastomosadas de células basaloides proliferantes dentro de la epidermis.
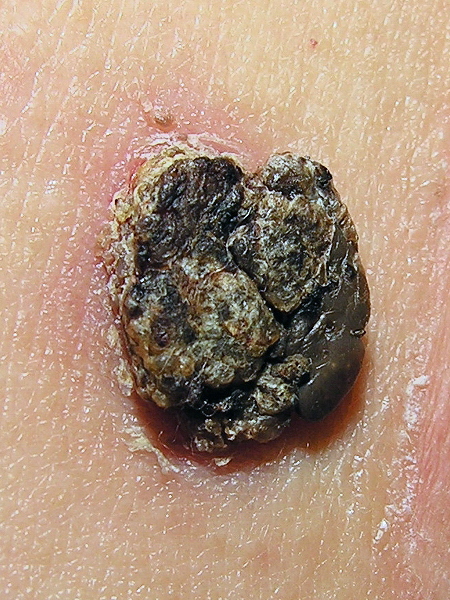
Queratosis seborreica con superficie rugosa:
Obsérvese el aspecto ceroso típico, el borde bien delimitado y el aspecto “de estar pegada”.
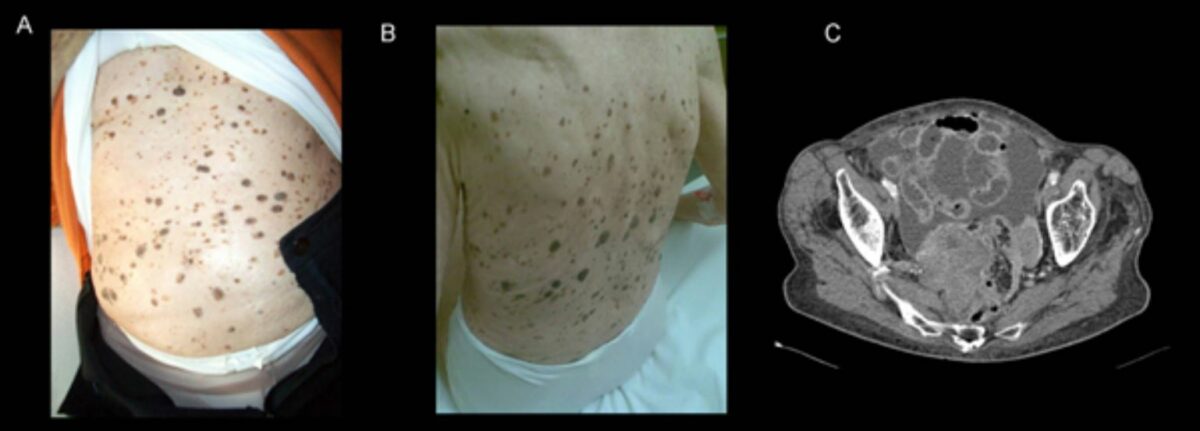
A y B: Signo de Leser-Trélat en una mujer de 92 años con cáncer de ovario avanzado. Las queratosis seborreicas eruptivas múltiples habían aumentado drásticamente en tamaño y número durante los 2 años anteriores.
C: TC que muestra un tumor ovárico necrótico acompañado de signos de carcinomatosis peritoneal
Examen físico:
Dermatoscopia:
Biopsia: