La poliposis juvenil familiar, también conocida como síndrome de poliposis juvenil, es una enfermedad autosómica dominante caracterizada por el crecimiento de pólipos hamartomatosos (tipo juvenil) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal, la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria cuales surgen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. Los LOS Neisseria síndromes de poliposis son un grupo de condiciones hereditarias o adquiridas que se caracterizan por el crecimiento de pólipos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal y que se asocian a otras características extracolónicas. Estos síndromes están causados por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure específicos asociados a la supresión de tumores o a la regulación del ciclo celular. La poliposis juvenil familiar está comúnmente asociada a mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure SMAD4 (cromosoma 18q) y BMPR1A BMPR1A A subtype of bone morphogenetic protein receptors with high affinity for bone morphogenetic proteins. They can interact with and undergo phosphorylation by type II bone morphogenetic protein receptors. They signal primarily through receptor-regulated SMAD proteins. Familial Juvenile Polyposis (cromosoma 10q). El diagnóstico se realiza al AL Amyloidosis visualizar 5 o más pólipos juveniles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la colonoscopia, múltiples pólipos juveniles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otras áreas del tracto gastrointestinal o cualquier número de pólipos juveniles más antecedentes familiares positivos. El tratamiento es quirúrgico para reducir la probabilidad de hemorragia y obstrucción gastrointestinal.
Last updated: Dec 26, 2025
La poliposis juvenil familiar o síndrome de poliposis juvenil, es una enfermedad autosómica dominante caracterizada por el crecimiento de pólipos hamartomatosos (tipo juvenil) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy.
Otras manifestaciones pueden incluir:
Criterios
El diagnóstico se realiza al AL Amyloidosis visualizar > 5 pólipos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la colonoscopia, múltiples pólipos juveniles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otras áreas del tracto gastrointestinal o cualquier número de pólipos con antecedentes familiares positivos.
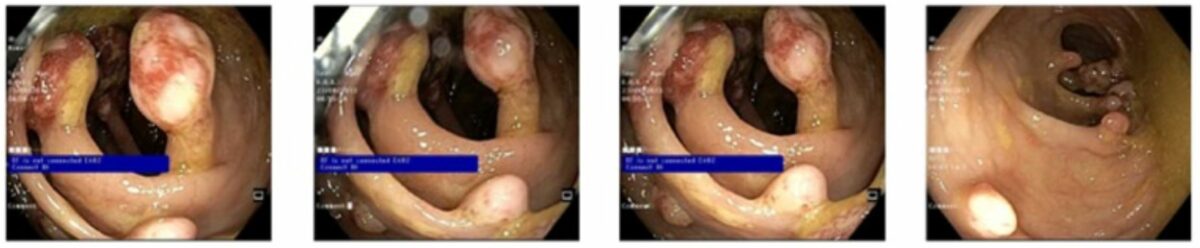
Múltiples pólipos juveniles pedunculados y sésiles, no sangrantes
Imagen: “Multiple pedunculated and sessile, nonbleeding polyps” por Amna Ahmed and Badr Alsaleem. Licencia: CC BY 4.0