Las malformaciones de Chiari son un grupo de afecciones del sistema nervioso central (SNC) que se caracterizan por el subdesarrollo de la fosa craneal posterior con la consiguiente protrusión de estructuras neurales a través del foramen magnum. Existen 4 tipos de malformaciones de Chiari, siendo la tipo I la más común. El síntoma más frecuente es la cefalea. El diagnóstico se realiza por medio de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos y se confirma con una resonancia magnética (RM). El tratamiento es quirúrgico, y se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la descompresión de la fosa posterior y el restablecimiento del flujo del SNC. El pronóstico depende del tipo de malformación.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las malformaciones de Chiari son un grupo de trastornos definidos por déficits estructurales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cerebro y la médula espinal que conducen a un espacio limitado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa posterior, lo que obliga a las estructuras cerebelosas a sobresalir a través del foramen magnum.
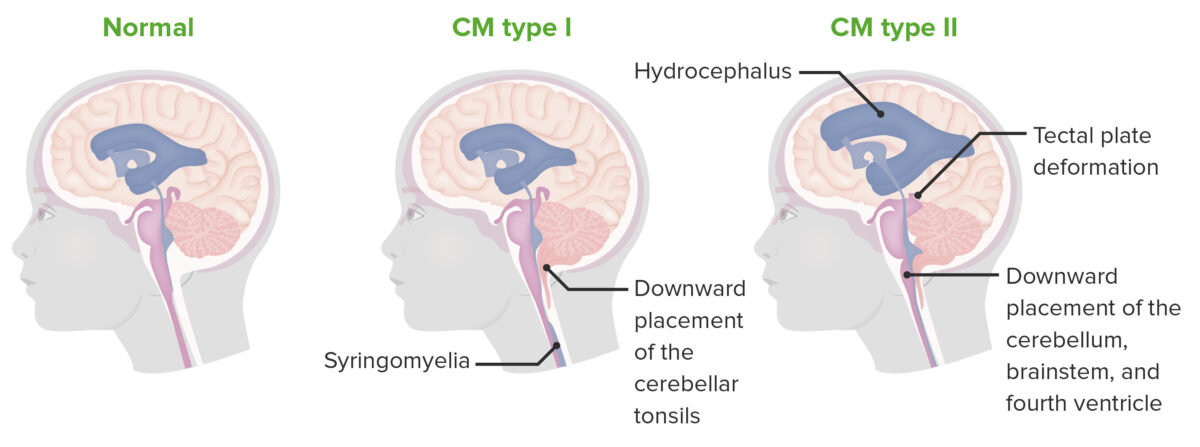
Chiari tipo I y II
Las malformaciones de Chiari se caracterizan por una fosa craneal posterior subdesarrollada, con la consiguiente protrusión de las estructuras neurales a través del foramen magnum. La tipo 1 se caracteriza por la herniación de las amígdalas cerebelosas únicamente, mientras que la tipo 2 afecta a más estructuras.
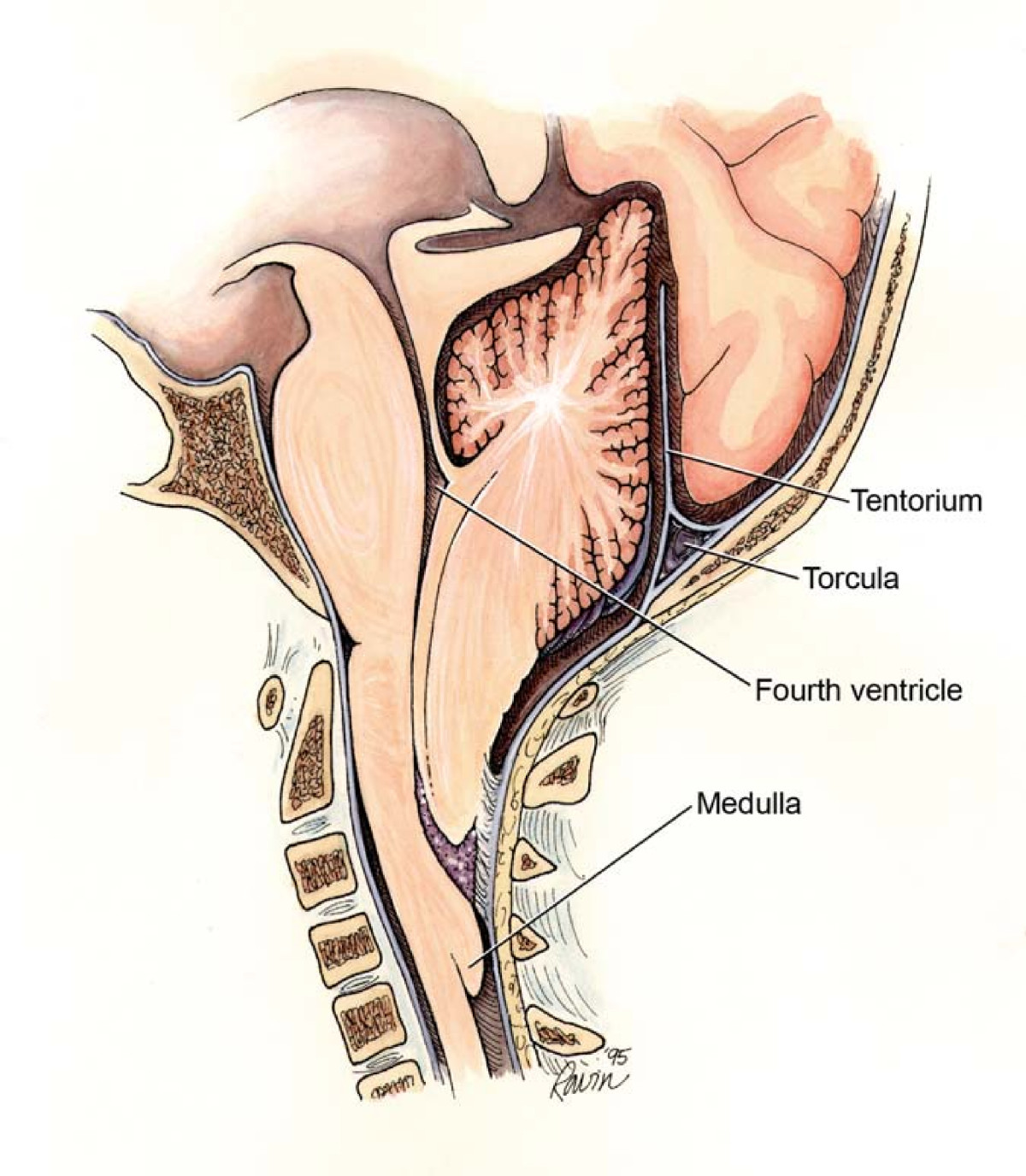
Malformación de Chiari II mostrando los puntos de obstrucción potencial que dan lugar a diferentes subtipos de hidrocefalia
Imagen: “Chiari2” por Rekate HL. Licencia:CC BY 2.0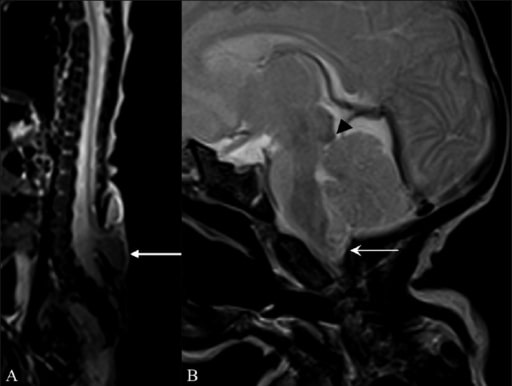
Hallazgos en la resonancia magnética (RM) que sugieren una malformación de Arnold-Chiari II
RM sagital T2W de toda la columna vertebral (A) muestra un meningomielocele (flecha) frente a las vértebras L5 y S1. RM Sagital T2W del cerebro (B) muestra una pequeña fosa craneal posterior, con herniación del vermis cerebeloso y de las amígdalas (flecha) a través del foramen magnum, con un pico tectal (cabeza de flecha).
Incidencia:
Condiciones asociadas:
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas neurológicos son causados por:
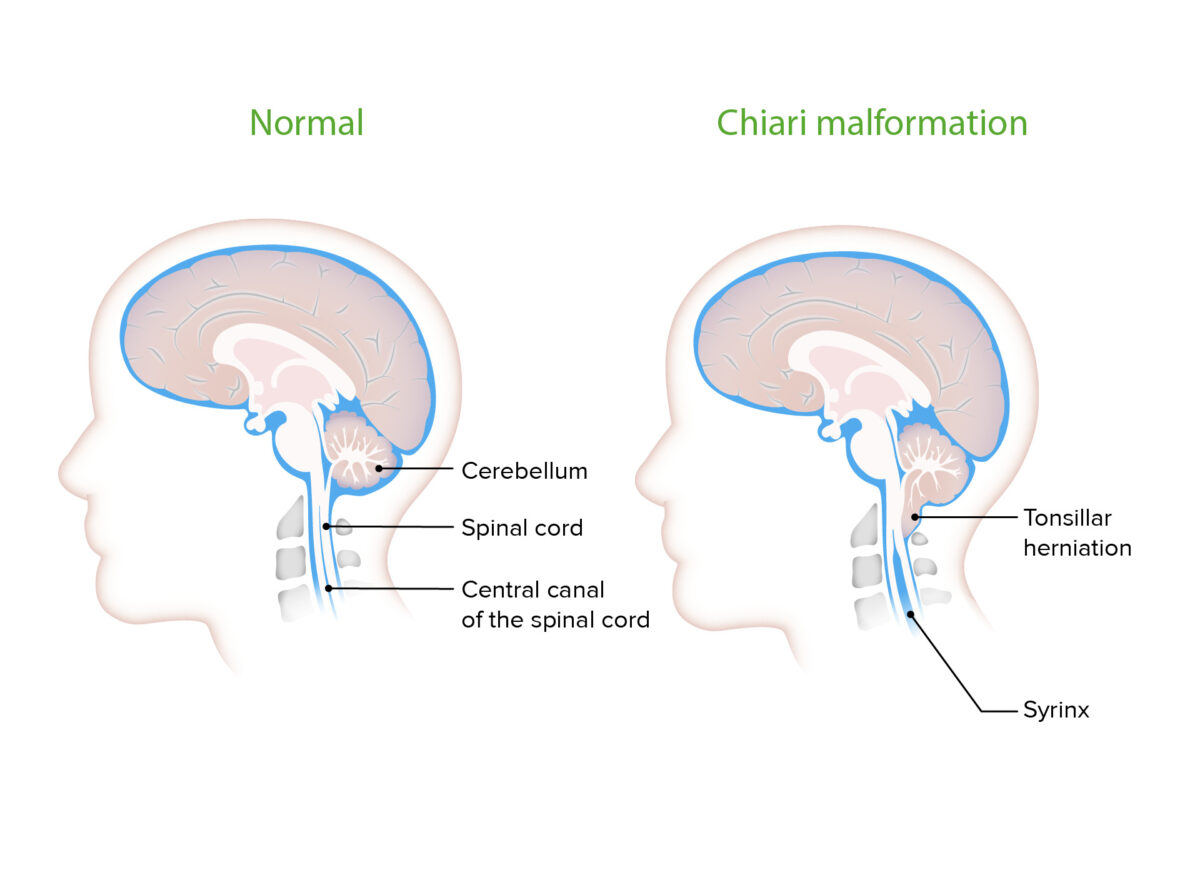
Siringomielia observada con malformación de Chiari
Las cavidades llenas de líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) se observan con frecuencia en las malformaciones de Chiari. Provocan la sintomatología comúnmente asociada a la malformación al ejercer presión sobre el tejido neural circundante.
Síntomas:
Signos físicos:
Síntomas:
Signos físicos:
Hay una alta mortalidad infantil con este tipo.
Síntomas:
Signos físicos:
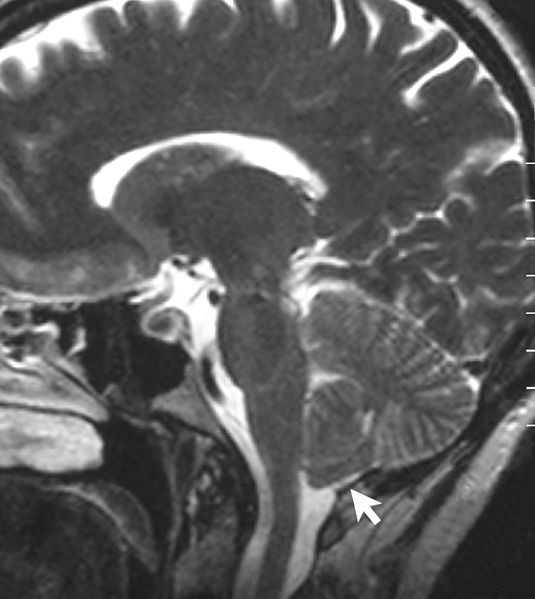
Resonancia magnética que muestra una malformación de Chiari tipo I. Observe la hernia amigdalina.
Imagen: “Sagittal MRI scan of brain of patient with Chiari malformation” por Raymond F Sekula Jr et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0