Un hemotórax es una acumulación de sangre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cavidad pleural. El hemotórax ocurre con mayor frecuencia debido al AL Amyloidosis daño de las arterias intercostales o por una laceración pulmonar después de un traumatismo torácico. El hemotórax también puede ocurrir como complicación de una enfermedad, o puede ser espontáneo o iatrogénico. Los LOS Neisseria hemotórax grandes pueden poner en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum peligro la vida al AL Amyloidosis provocar colapso pulmonar. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan disnea y dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen físico incluyen hipotensión, taquicardia, disminución de los LOS Neisseria ruidos pulmonares y matidez a la percusión del tórax. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante una radiografía de tórax en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum bipedestación. El tratamiento implica drenaje pleural, cirugía toracoscópica asistida por video o toracotomía cuando hay un hemotórax masivo o hemorragia persistente.
Last updated: Feb 19, 2025
Un hemotórax se define como una colección de líquido con un hematocrito de al AL Amyloidosis menos 50% acumulado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio potencial entre la pleura Pleura The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura. Pleura: Anatomy parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy y visceral de los LOS Neisseria pulmones.
La fuente de sangre puede ser la pared torácica, el parénquima pulmonar, el corazón o los LOS Neisseria grandes vasos por causas tanto traumáticas como no traumáticas.
Causas traumáticas:
Causas no traumáticas:
Componente hemodinámico:
La pérdida de gran volumen (cada hemotórax puede contener hasta el 40% del volumen total de sangre circulante) hacia la pleura Pleura The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura. Pleura: Anatomy puede provocar una disminución de la función cardíaca debido a:
Componente respiratorio:
La acumulación de sangre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pleura Pleura The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura. Pleura: Anatomy disminuye la capacidad vital funcional de los LOS Neisseria pulmones al AL Amyloidosis:
El diagnóstico se establece utilizando los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, el examen físico y la imagenología apropiada. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de traumatismo, el uso de la evaluación primaria es primordial para un rápido diagnóstico y tratamiento.
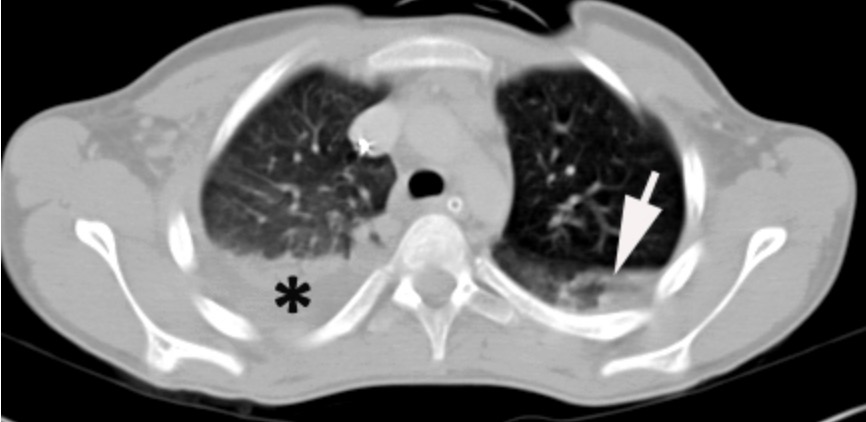
TC de tórax que muestra un hemotórax en el pulmón derecho
La flecha indica una contusión pulmonar y una acumulación de líquido que se cree que es un hemotórax.
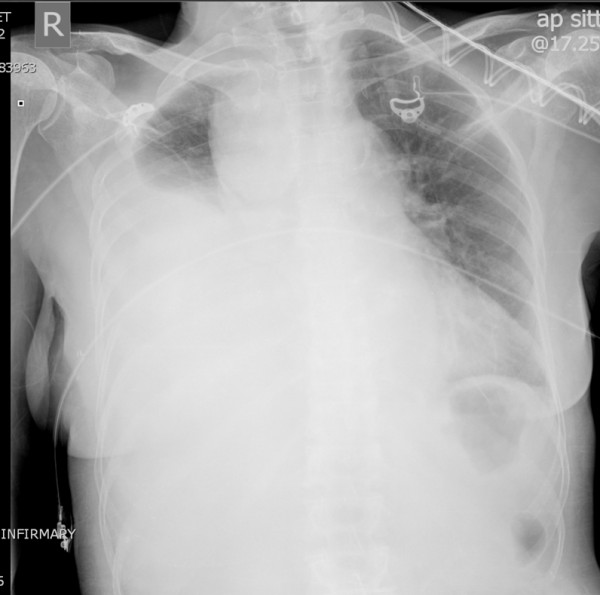
Hemotórax derecho masivo
Radiografía de tórax que muestra una acumulación de líquido en el espacio pleural derecho, como lo ilustra el pulmón opacificado
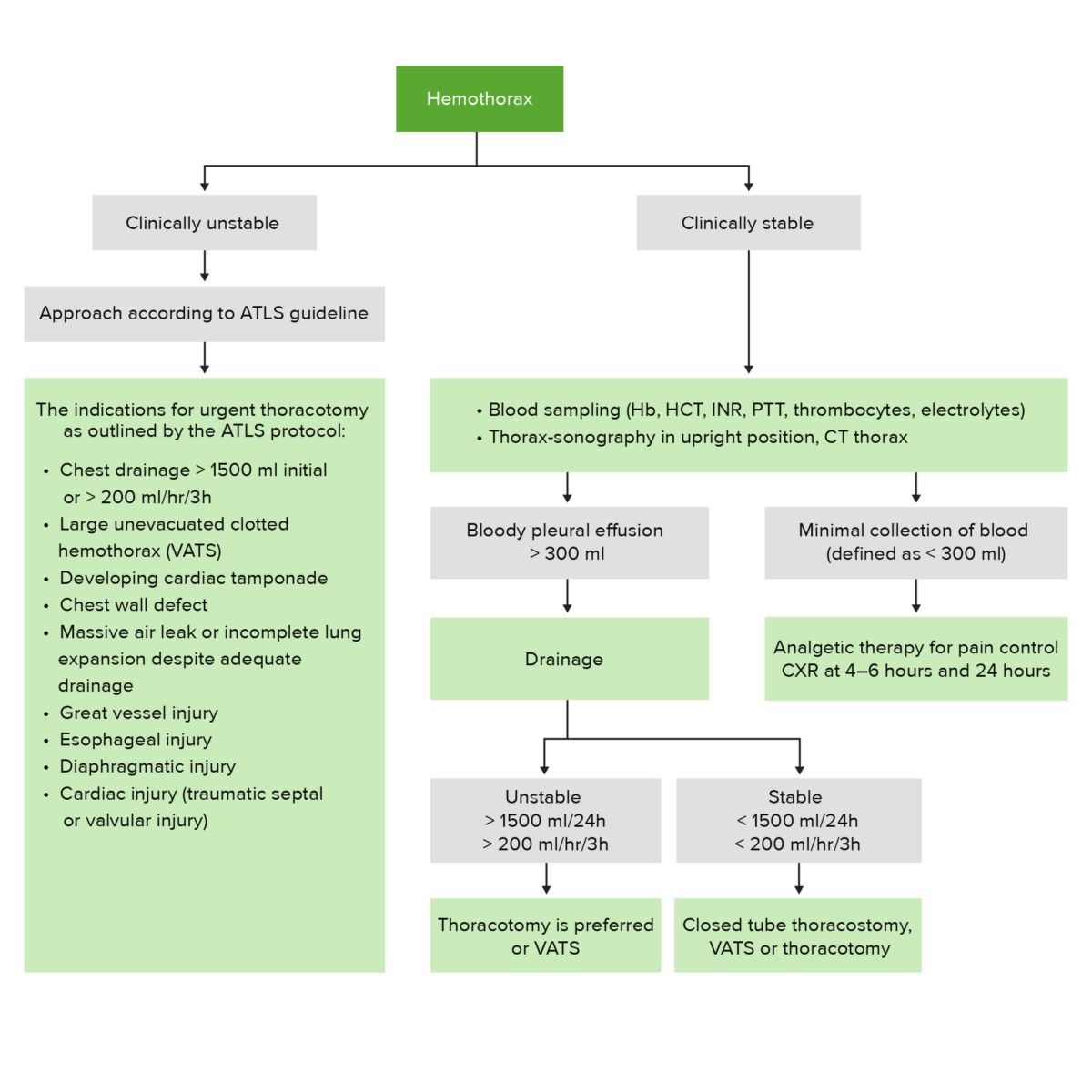
Algoritmo de tratamiento del hemotórax
ATLS: Soporte Vital Avanzado para Traumatismos (por sus siglas en inglés)
CXR: Radiografía de tórax (por sus siglas en inglés)
Hb: Hemoglobina
HCT: hematocrito
INR: razón internacional normalizada (por sus siglas en inglés)
PTT: tiempo de protrombina (por sus siglas en inglés)
VATS: cirugía toracoscópica asistida por video (por sus siglas en inglés)
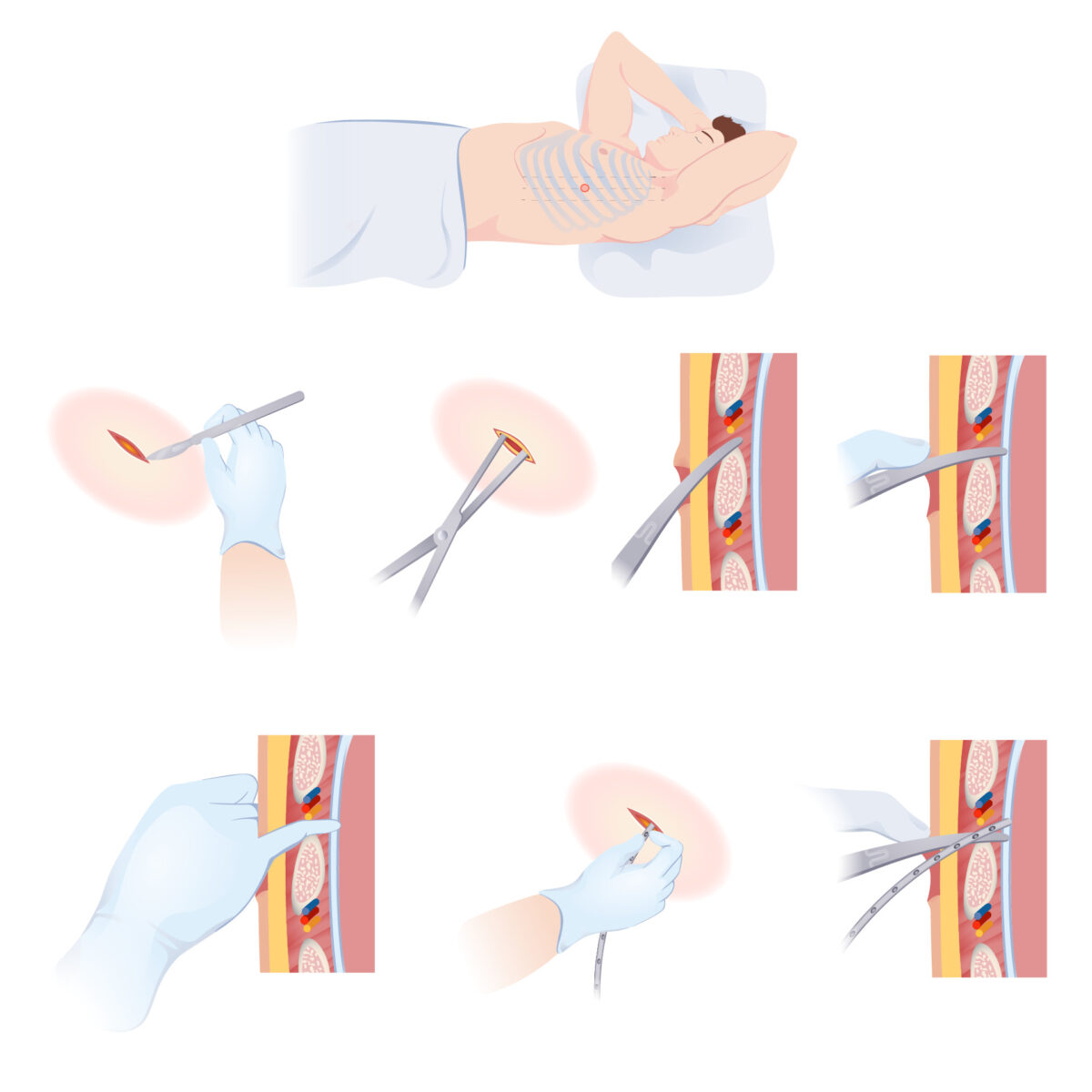
Cómo insertar un drenaje pleural
Ilustración paso a paso sobre cómo insertar un drenaje pleural para drenar la acumulación de líquido del espacio pleural