Una "fractura de Toddler" es una fractura en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum espiral u oblicua de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy distal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños pequeños, resultante de un traumatismo de baja energía con un componente de rotación/torsión. Estas fracturas se observan a menudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños que están aprendiendo a caminar y que no tienen un antecedente específico de traumatismos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones, el niño puede presentar una claudicación dolorosa o rechazo a soportar peso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la extremidad afectada. El tratamiento incluye analgesia Analgesia Methods of pain relief that may be used with or in place of analgesics. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts e inmovilización de la pierna lesionada durante varias semanas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las fracturas espirales no desplazadas de la tibia distal suelen denominarse “fracturas de Toddler”, ya que suelen observarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños que acaban de empezar a caminar.
El diagnóstico de la fractura de Toddler puede ser difícil debido a la falta de documentación del traumatismo y a la incapacidad del niño para localizar la lesión:
Signos:
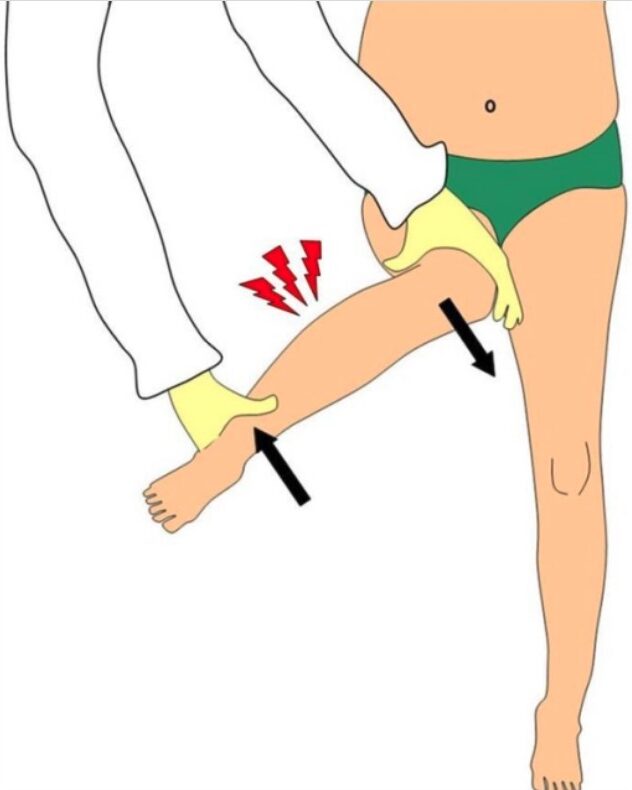
Hallazgo en el examen físico de la fractura de Toddler:
La torsión suave del tobillo y la rodilla en direcciones opuestas provoca dolor tibial. Durante la exploración de la cadera, las fuerzas de cizallamiento rotativo que actúan sobre la pierna (flechas) pueden provocar dolor en una tibia lesionada y esto puede confundirse con una sensibilidad en la cadera.
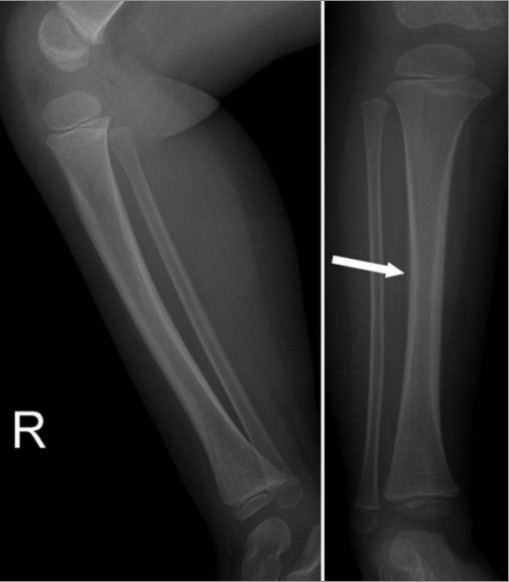
Fractura del Toddler:
Las imágenes iniciales en casos de fracturas en espiral de tibia pueden ser sutiles o negativas. En los casos con alta sospecha clínica, las radiografías de las extremidades inferiores repetidas después de 1–2 semanas pueden mostrar una nueva formación de hueso perióstico (flecha blanca), lo que sugiere la curación de una fractura del niño.
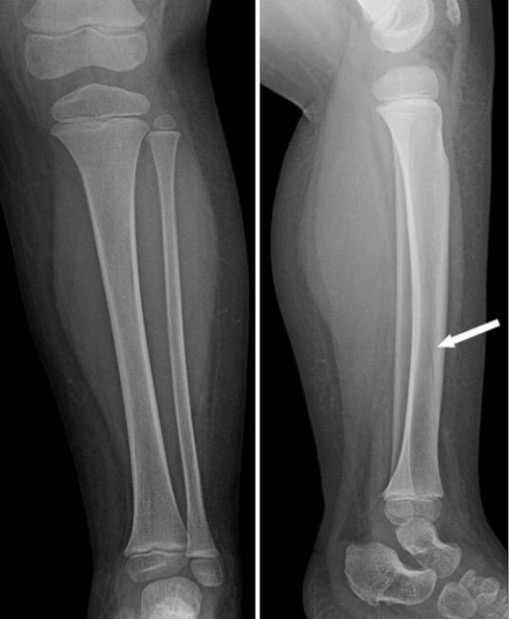
Fractura en espiral en la tibia distal izquierda:
Las fracturas espirales de la tibia pueden verse a veces en la vista anterior y lateral como una tenue línea oscura (flecha blanca), que a menudo puede confundirse con un vaso nutricio.
Estas fracturas no suelen estar desplazadas y se tratan de forma no quirúrgica.
Consideraciones esenciales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico diferencial de un niño que presenta claudicación:
Fracturas frecuentes observadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el grupo de edad pediátrico: