Las fracturas de radio distal son una de las fracturas más comunes que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la práctica y, a menudo, se asocian con una caída sobre una mano extendida. Estas fracturas se observan con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas mayores, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esta población, estas fracturas se relacionan con un aumento de las caídas por la inestabilidad de la marcha con el envejecimiento y la osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis asociada. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas más jóvenes, las fracturas de radio distal suelen estar relacionadas con traumatismos de alta energía. Los LOS Neisseria individuos a menudo se presentan con dolor Dolor Inflammation y una deformidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de tenedor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el antebrazo distal. El diagnóstico es clínico y se confirma con radiografías de la muñeca. El tratamiento puede ser quirúrgico o conservador según la edad del individuo, la afectación articular y el grado de desplazamiento o angulación.
Last updated: Dec 26, 2025
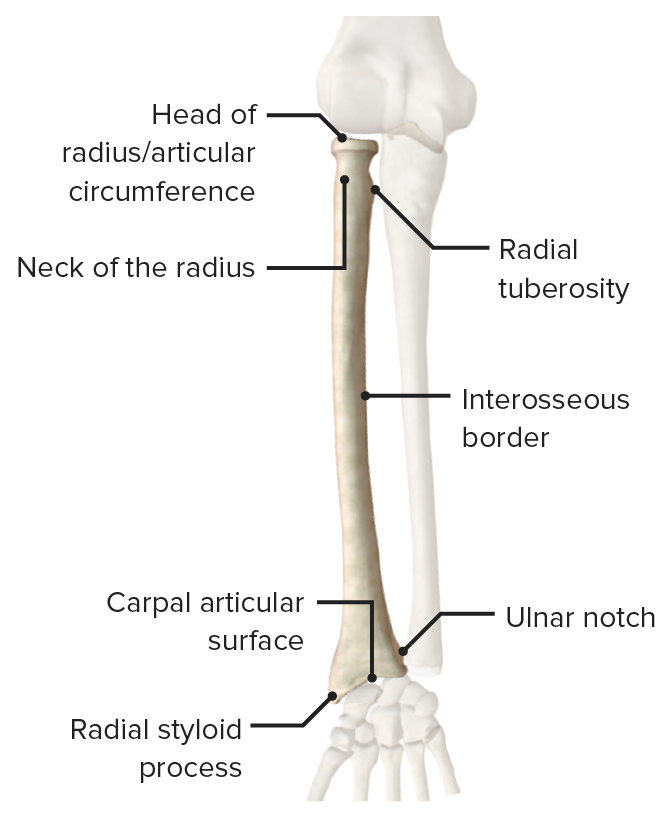
Vista anterior del radio con sus puntos de referencia óseos y superficies articulares
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio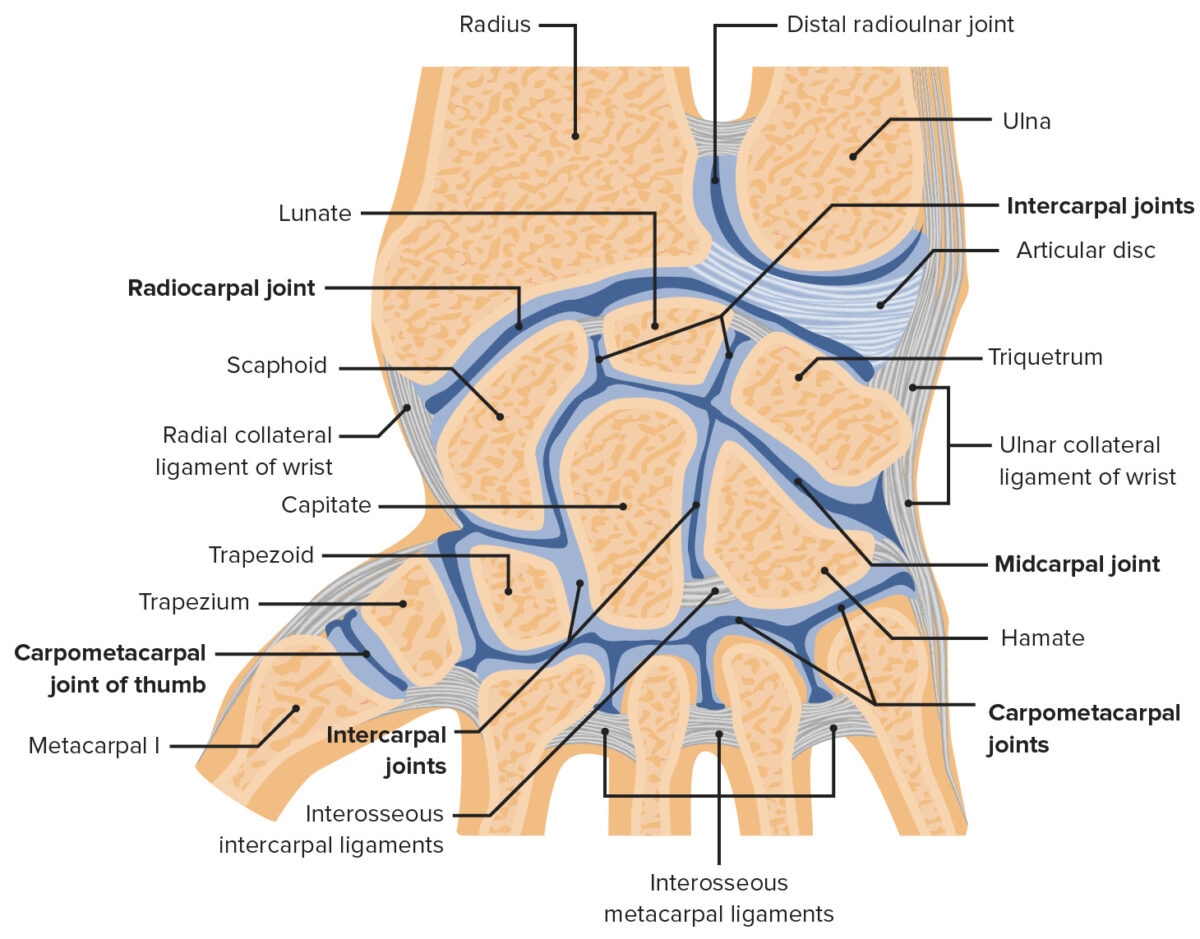
Articulación de la muñeca y sus articulaciones con el radio y el cúbito:
El radio distal se articula con los huesos escafoides y semilunar de la muñeca en la articulación radiocarpiana. El radio distal también se articula con el cúbito en la articulación radiocubital.
Imagen por Lecturio.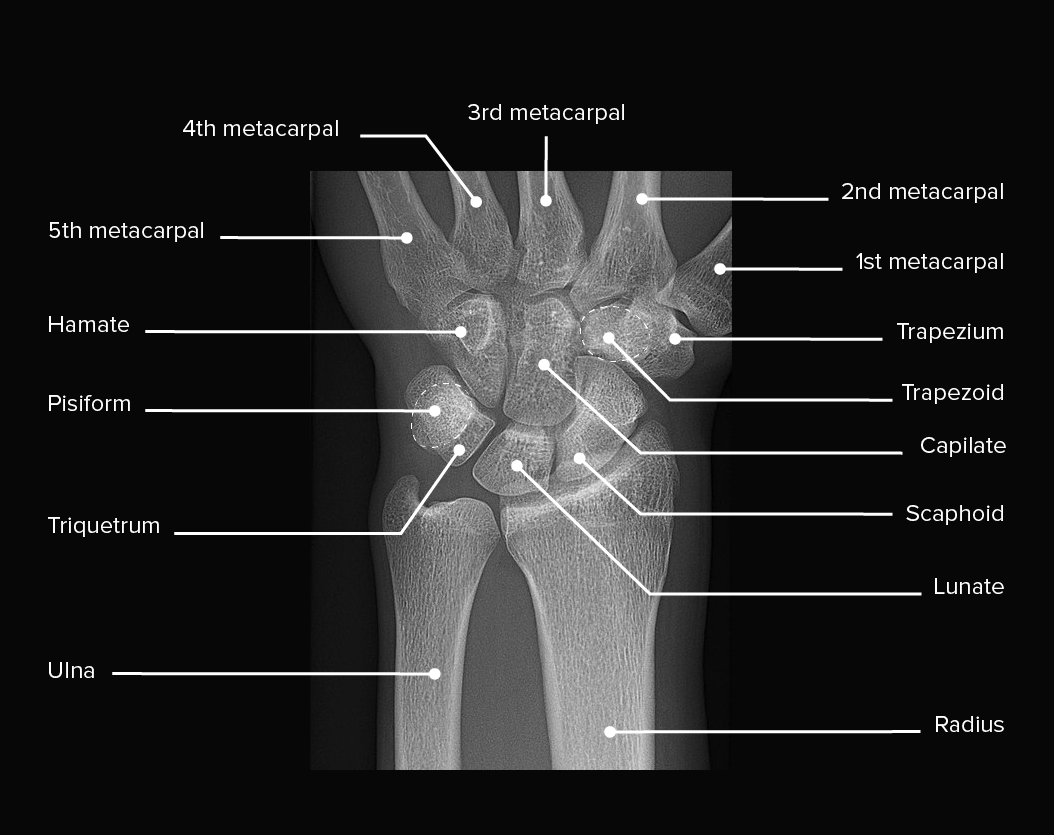
Radiografía de una muñeca izquierda, que muestra una anatomía normal y sin lesiones
Imagen: “X-ray of normal wrist” por Mikael Häggström, MD Licencia: CC0 1.0, editado por Lecturio.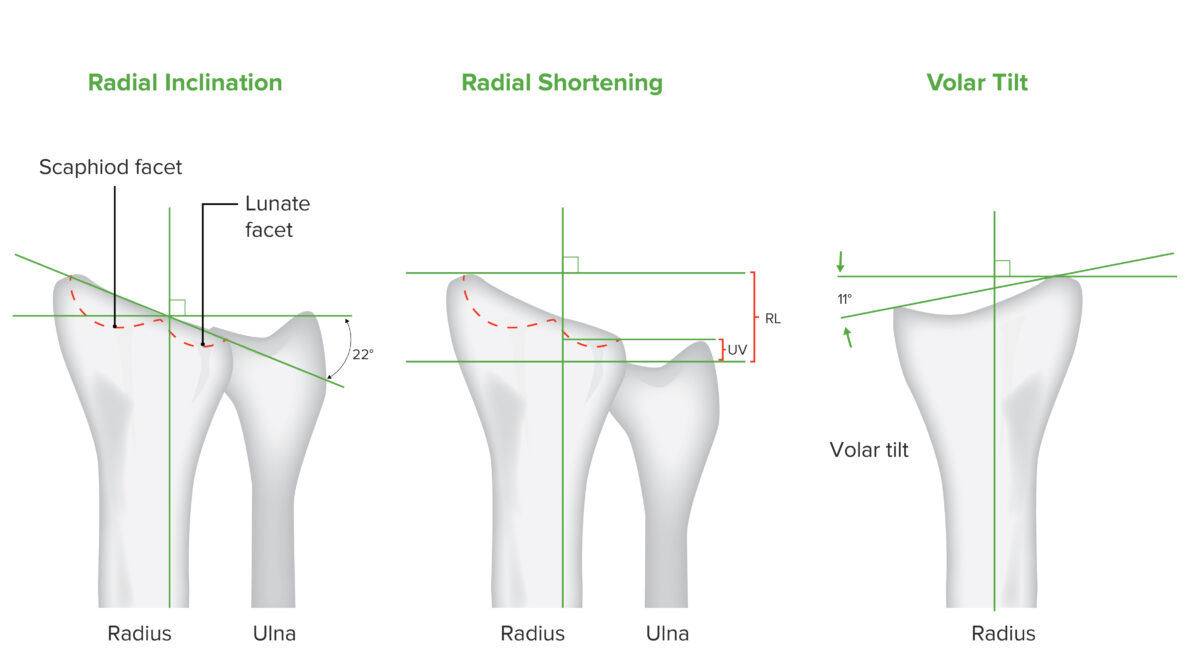
Movimientos del radio distal:
La inclinación del radio, el acortamiento del radio y la inclinación volar son valores medidos radiológicamente que se utilizan para evaluar la articulación radial en el contexto de una fractura de radio distal.
Antecedentes:
Examen físico:
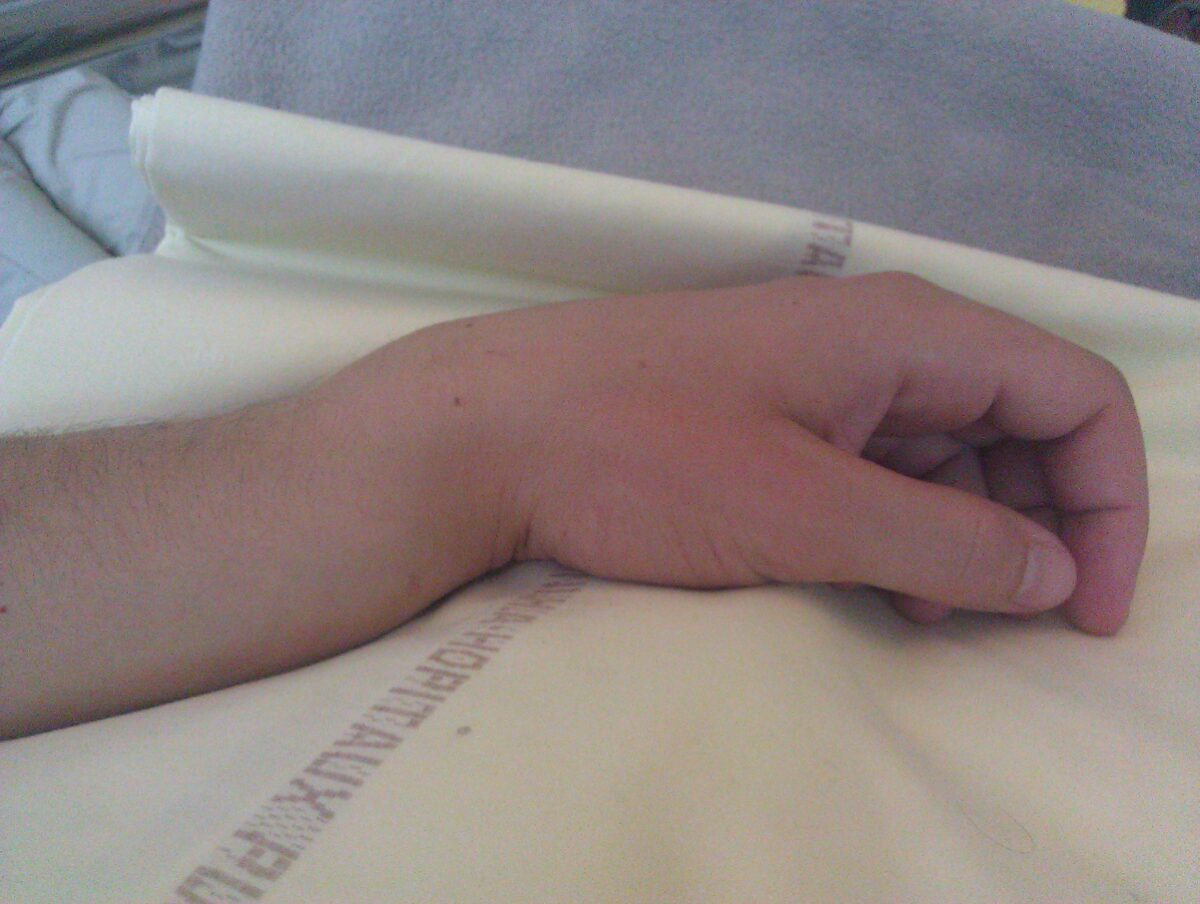
Fractura de Colles de la mano izquierda:
Deformidad clásica en tenedor con desplazamiento posterior claramente visible.
El diagnóstico es clínico; sin embargo, se necesita imagenología para confirmar y evaluar la gravedad.
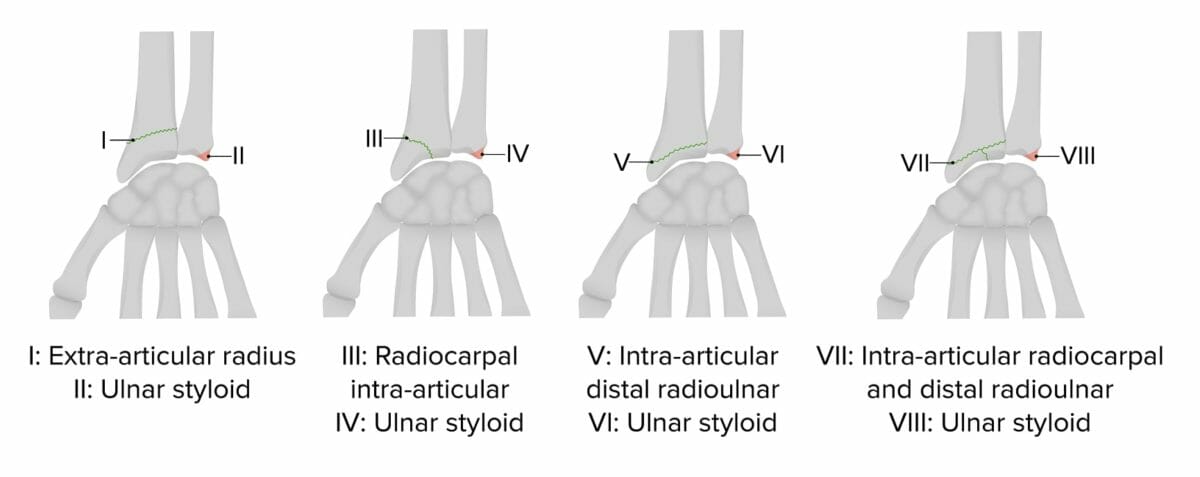
Clasificación de Frykman de las fracturas de radio distal
Imagen por Lecturio.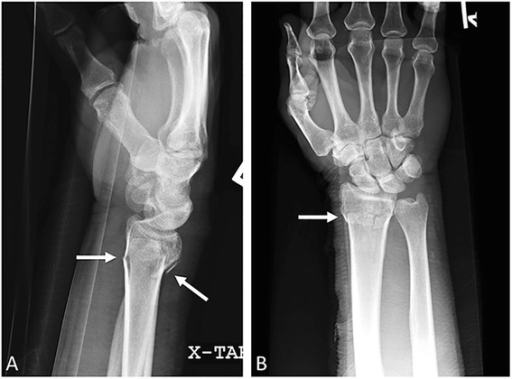
Fractura de Colles:
Radiografías lateral (a) y anteroposterior (b) de la muñeca. Se muestra una fractura metafisaria radial distal transversal (flechas) sin extensión intraarticular.
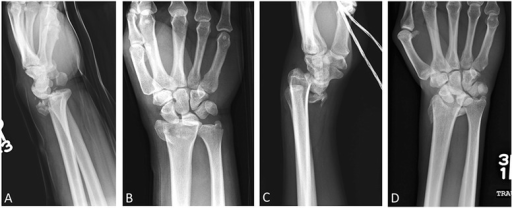
Fracturas de Barton y de Barton inversa:
Radiografías lateral (a) y anteroposterior (b) de la muñeca derecha. Se muestra una fractura intraarticular oblicua conminuta con migración dorsal del carpo, compatible con una fractura de Barton.
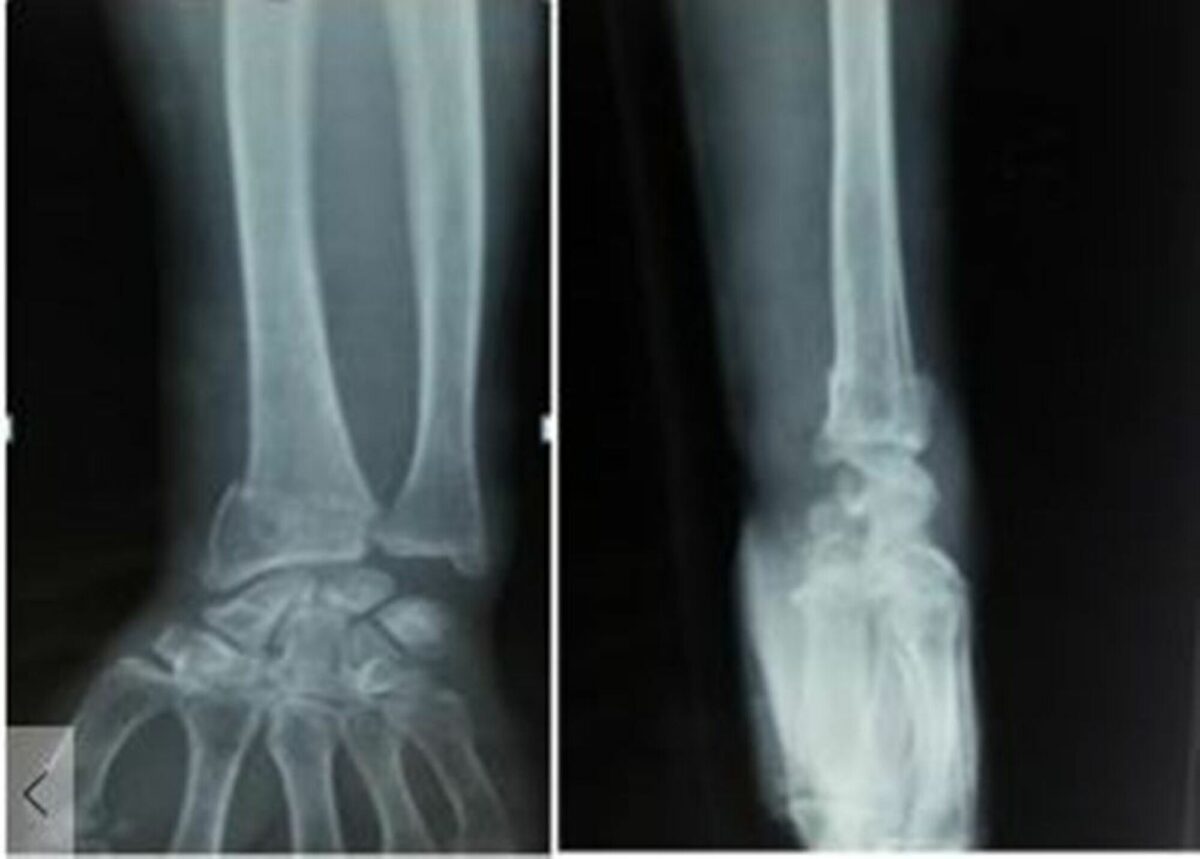
Radiografías (vistas anteroposterior y lateral) que muestran fractura de radio distal
Imagen: “Radiographs anteroposterior and lateral view showing distal radius fracture” por Panthi S, et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0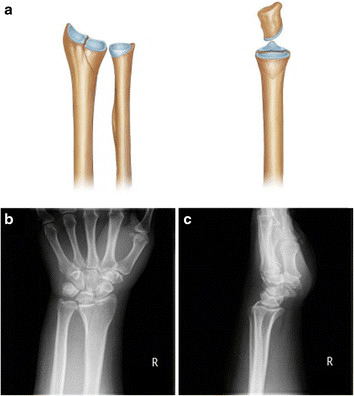
La fractura por die-punch del radio muestra una fractura por depresión vertical:
a: Toda la fosa semilunar está deprimida verticalmente (izquierda, vista anterior; derecha, vista lateral).
b y c: radiografías anteroposterior (izquierda) y lateral (derecha)
El tratamiento, ya sea quirúrgico o no quirúrgico, se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tipo de fractura (basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el compromiso y el desplazamiento articular) y la edad y el nivel de actividad del individuo.
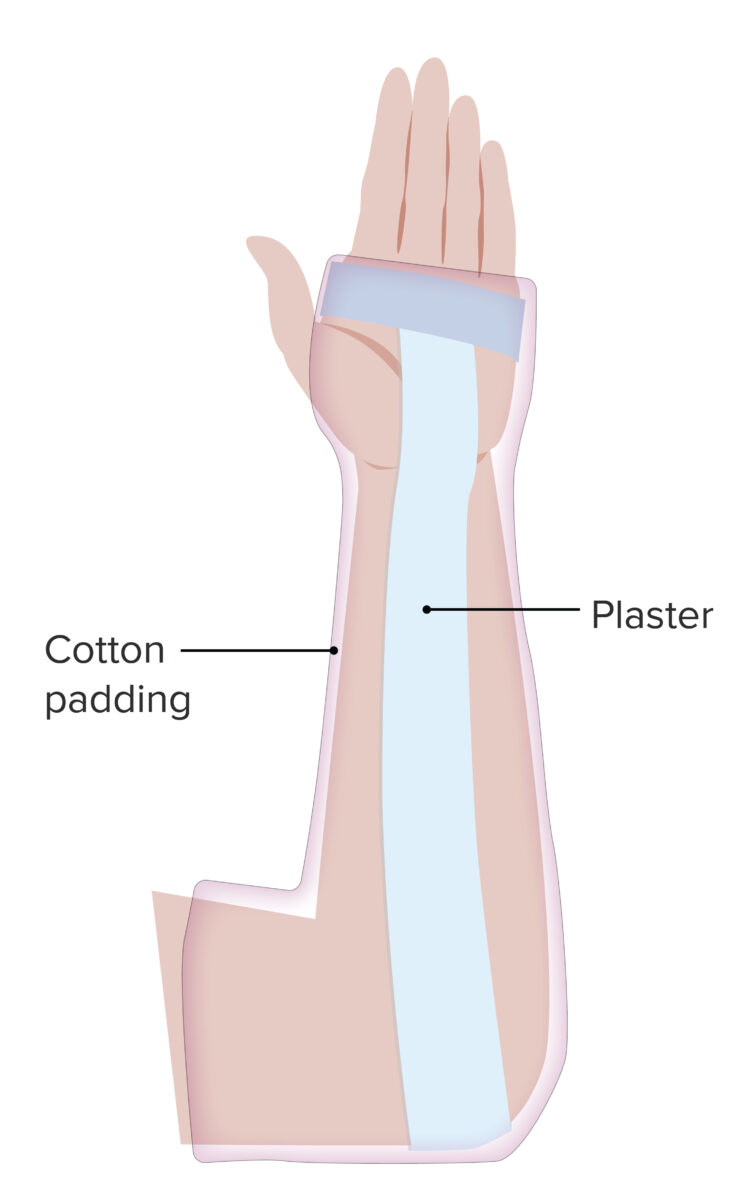
Férula estilo sugar tong en el antebrazo:
Una férula simple, la férula estilo sugar tong, está indicada en fracturas de radio distal y cubital que no están desplazadas. La férula impide la pronación/supinación e inmoviliza la articulación del codo.
El tratamiento quirúrgico está indicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de: