El estreñimiento es un motivo de consulta común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños, que está relativamente definido para cada grupo etario en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la frecuencia y la dificultad de la defecación y la consistencia de las heces. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de estreñimiento son funcionales o no orgánicos. La presentación clínica puede variar, desde una evacuación insuficiente observada por los LOS Neisseria padres, pasando por quejas de dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, hasta la incontinencia secundaria. A menudo, se necesita una combinación de tratamiento no farmacológico y farmacológico para evacuar el contenido intestinal, eliminar el dolor Dolor Inflammation al AL Amyloidosis defecar y mejorar los LOS Neisseria hábitos intestinales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Lactantes y niños pequeños (≤4 años de edad de desarrollo) | Niños (>4 años de edad de desarrollo) |
|---|---|
| Al AL Amyloidosis menos 2 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes hallazgos durante más de 1 mes: | Al AL Amyloidosis menos 2 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes hallazgos durante más de 1 mes, que se presenten al AL Amyloidosis menos 1 vez por semana: |
|
|
Criterios adicionales para niños que ya van
al
AL
Amyloidosis baño:
|
| No orgánicas (funcionales o retentivas) | No hay causas patológicas subyacentes |
|---|---|
| Anatómicas |
|
| Musculatura anormal |
|
| Anomalías intestinales nerviosas o musculares |
|
| Trastornos metabólicos |
|
| Trastornos intestinales |
|
| Medicamentos |
|
| Psiquiátrica | Anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa nerviosa |
El estreñimiento funcional es la causa más común de estreñimiento:
Los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen físico se realizan para descartar cualquier causa orgánica y asegurar al AL Amyloidosis profesional que los LOS Neisseria síntomas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuestión se deben al AL Amyloidosis estreñimiento funcional.
Hábitos evacuatorios:
Momento de aparición de los LOS Neisseria síntomas:
Estresores psicosociales:
Pistas conductuales:
Pistas que apuntan a etiologías orgánicas:
General:
Examen abdominal:
Examen rectal:
Examen neurológico:
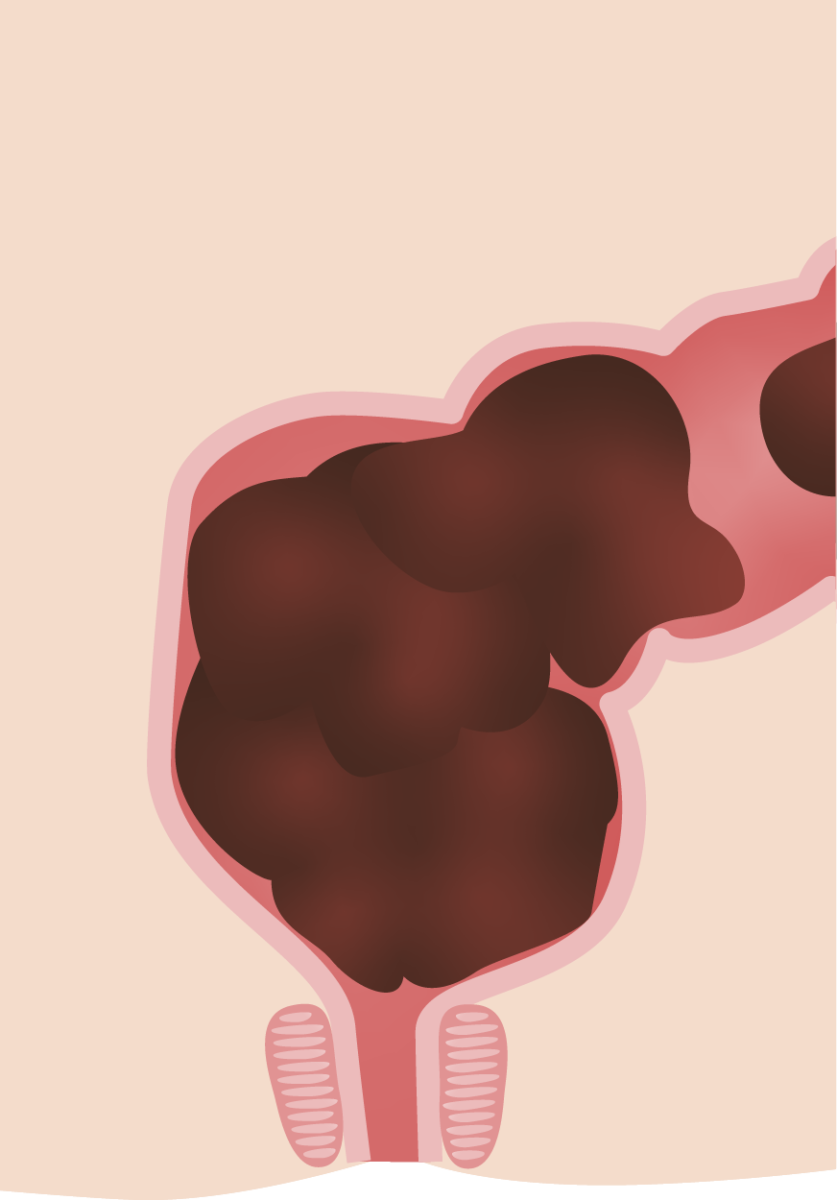
Representación de la sección transversal de la bóveda rectal en el estreñimiento con gran carga fecal que se observa a menudo en el estreñimiento funcional en niños
Imagen por Lecturio.En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un niño por lo demás sano, el estreñimiento funcional se diagnostica clínicamente. El examen de laboratorio debe estar dirigido por indicios que sugieran otras causas patológicas:
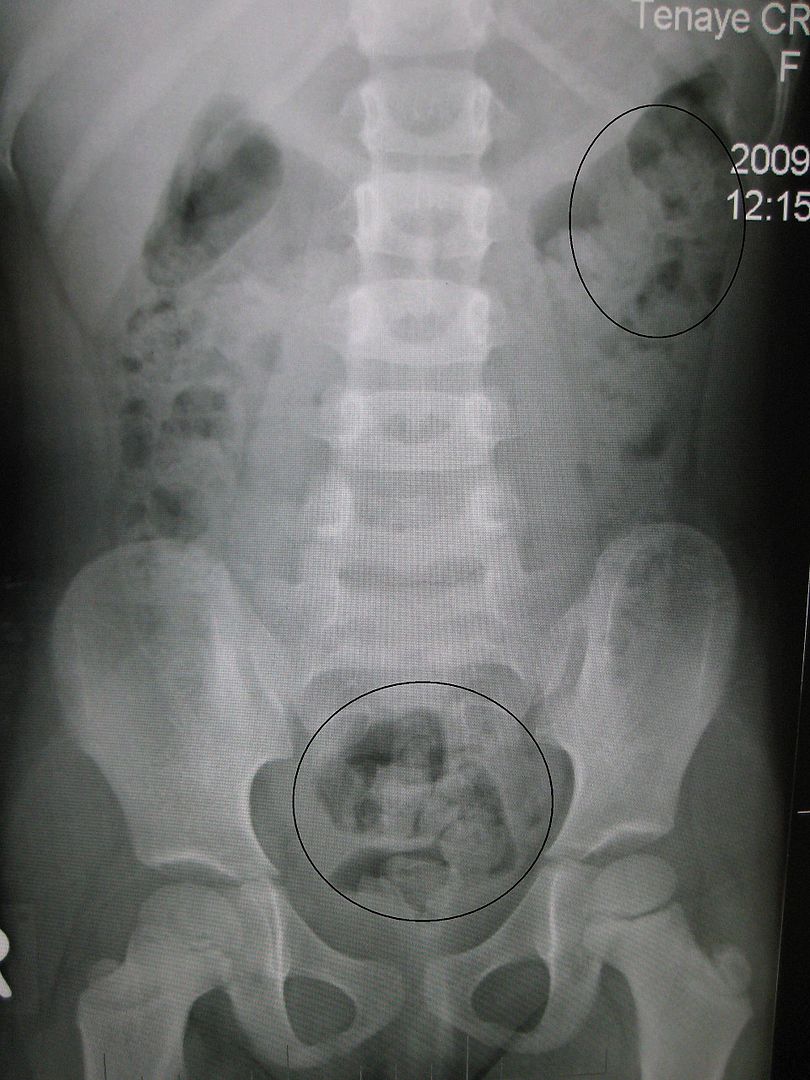
Vista anterior de una radiografía de un joven que muestra una importante carga fecal en el recto que sugiere estreñimiento
Imagen: “Constipation in a young child as seen on X-ray” por James Heilman, MD. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.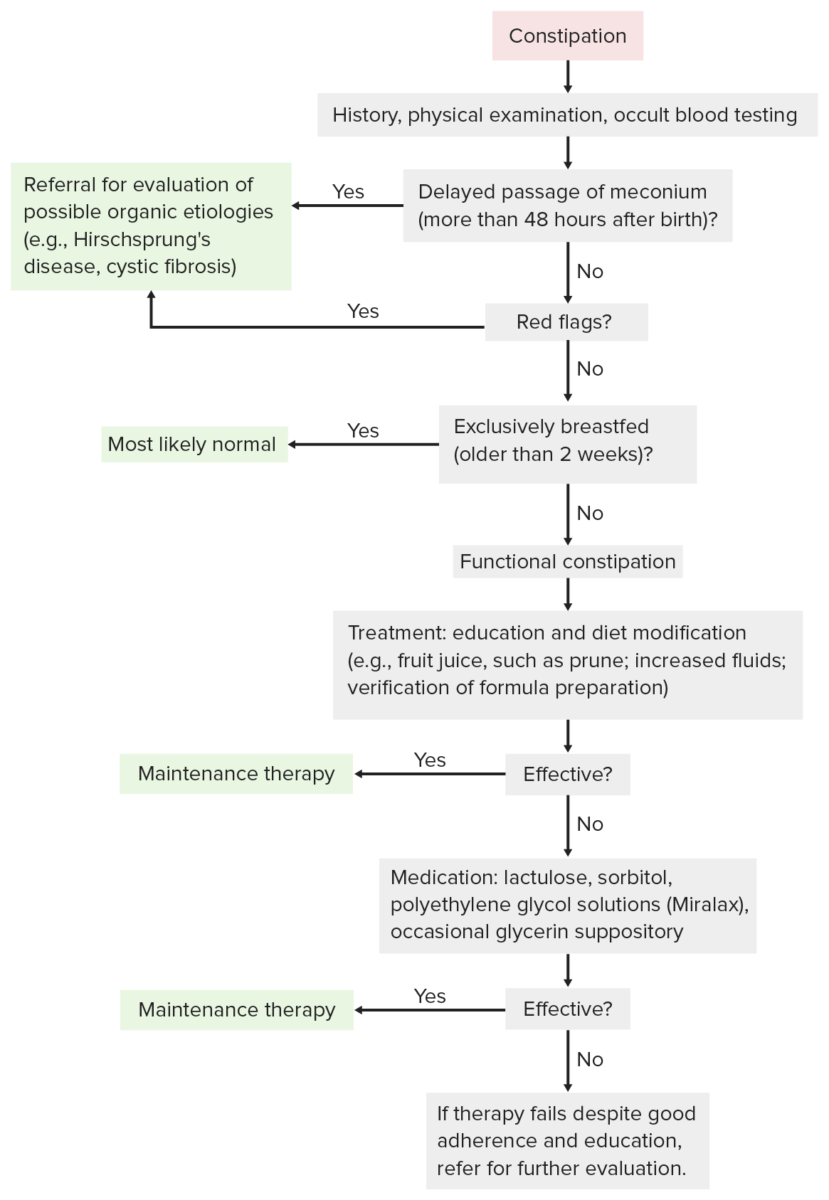
Diagramas de flujo del diagnóstico y tratamiento del estreñimiento.
Imagen por Lecturio.