La distonía es un trastorno de movimiento hipercinético caracterizado por la contracción involuntaria de los LOS Neisseria músculos, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum posturas anormales o movimientos repetitivos y tortuosos. La distonía puede presentarse de varias maneras y puede afectar a muchos grupos de músculos esqueléticos diferentes. La distonía puede ser hereditaria, adquirida o idiopática. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y se recomiendan pruebas genéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con antecedentes familiares de distonía. El tratamiento es con toxina botulínica u otros medicamentos que actúan sobre los LOS Neisseria diversos neurotransmisores implicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la patogenia de la distonía.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La distonía es un grupo de trastornos del movimiento caracterizados por contracciones musculares involuntarias que provocan un control anormal del movimiento y la postura. La distonía es un trastorno hipercinético focal o generalizado que se presenta con una respuesta de contracción muscular excesiva.
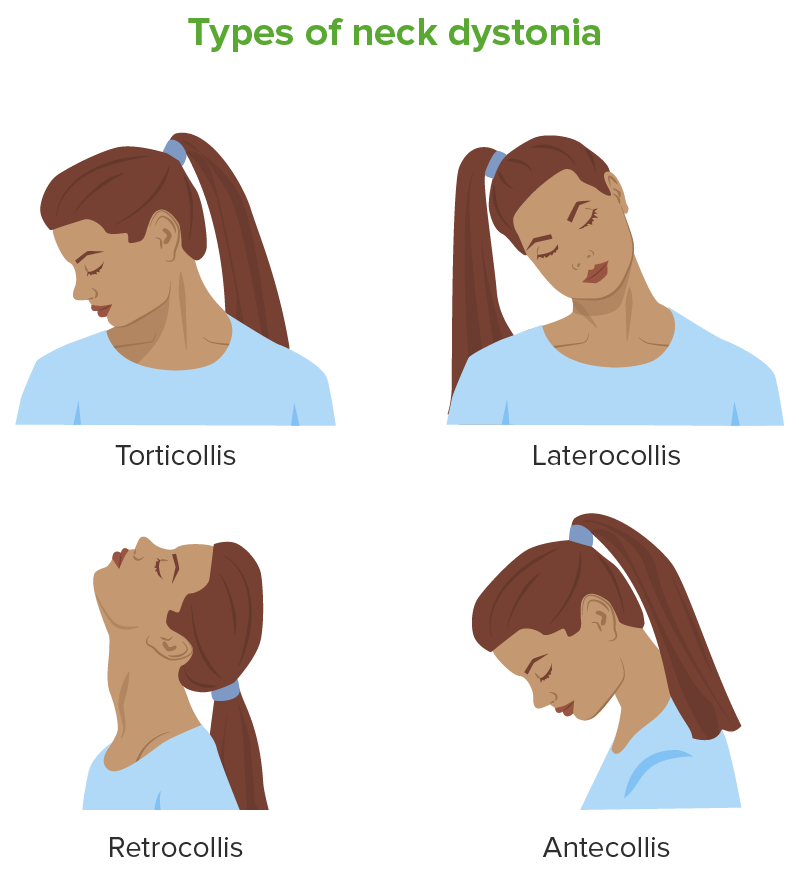
Presentaciones de distonía cervical
Imagen por Lecturio.| Nombre | Tipo | Inicio | Caracteristicas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distonía de inicio temprano | Primaria (heredada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un patrón autosómico dominante) generalizada | Infancia |
|
| Distonía DYT-TOR1A | Primaria (heredada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un patrón autosómico dominante) generalizada | Infancia |
|
| Distonía DYT-THAP1 | Primaria (heredada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un patrón autosómico dominante) generalizada | Adolescencia |
|
| Distonía DYT-KMT2B | Primaria (generalmente mutaciones de novo) | Infancia |
|
| Distonía cervical (tortícolis espasmódica) |
|
Edad: 30–50 años |
|
| Distonía de extremidades |
|
Adultez |
|
| Distonía laríngea (aislada) |
|
Adultez | |
| Blefaroespasmo (aislado) |
|
Adultez | |
| Distonía de torsión generalizada primaria |
|
Infancia |
|
| Síndrome de Meige | Segmentario primario | Por lo general, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la adultez |
|
| Distonía inducida por medicamentos | Secundario | Después de exposición a medicamentos desencadenantes |
|
| Trastornos heredodegenerativos | Secundario | Varía |
|
| Síndromes de distonía-plus | Secundario | Generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la infancia |
Las contracciones musculares excesivas y frecuentes que conducen a posturas anormales y/o movimientos repetitivos son el sello distintivo de la distonía.
Pueden afectar cualquier parte del cuerpo:
Empeoradas por la acción voluntaria:
Ocurre con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sitios anatómicamente distintos:
Pueden presentarse temprano en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida (distonía de inicio temprano):
Pueden presentarse más tarde en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida (distonía de inicio tardío):
Pueden tener dominancia temporal:
Pueden tener características dinámicas:
Pueden presentarse con trastornos del movimiento comórbidos:
La distonía se diagnostica clínicamente sobre la base de una toma de antecedentes y un examen físico completos, con un enfoque particular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen musculoesquelético y del sistema nervioso.
El tratamiento es en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida sintomático, ya que no existe una cura para la distonía.