La corteza cerebral es la parte más grande y desarrollada del cerebro humano y del sistema nervioso central (SNC). Ocupando la parte superior de la cavidad craneal, la corteza cerebral tiene 4 lóbulos y está dividida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 2 hemisferios que están unidos centralmente por el cuerpo calloso. La corteza está organizada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum circunvoluciones que están separadas por surcos. La corteza cerebral proporciona el sustrato neural para la experiencia consciente de los LOS Neisseria estímulos sensoriales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La corteza cerebral es la capa más externa del encéfalo:
El cerebro es la porción más grande del encéfalo. El cerebro se compone de materia gris (corteza cerebral) y las estructuras subyacentes de la materia blanca:
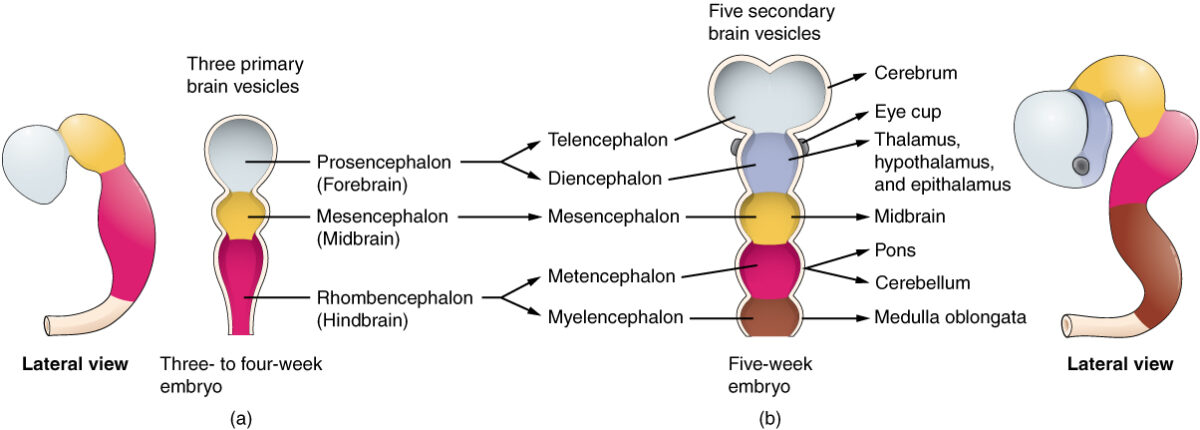
El desarrollo embrionario del cerebrum: nótese el linaje que inicia a partir del tubo neural → prosencéfalo → telencéfalo → cerebrum
Imagen: “Brain Vesicle” por Phil Schatz. Licencia: CC BY 4.0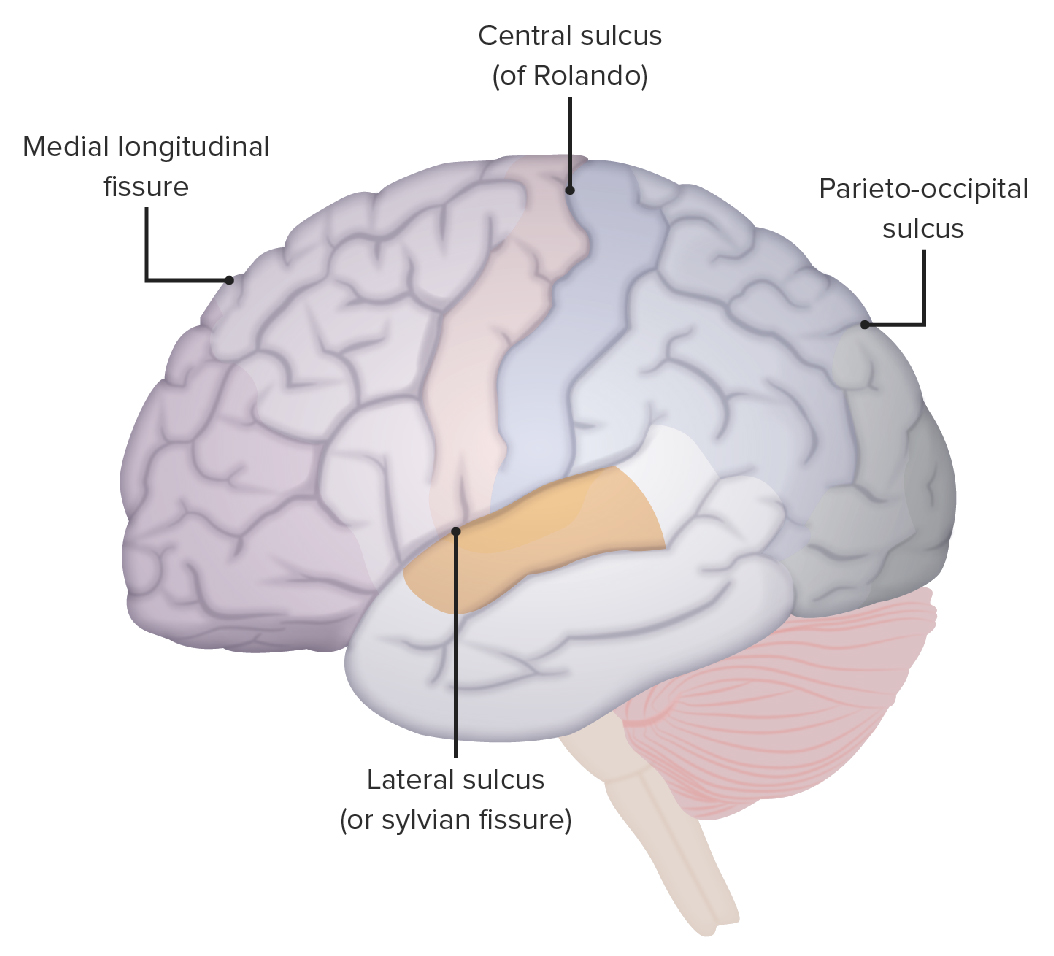
Localización del surco lateral, surco central y surco parietooccipital
Imagen por Lecturio.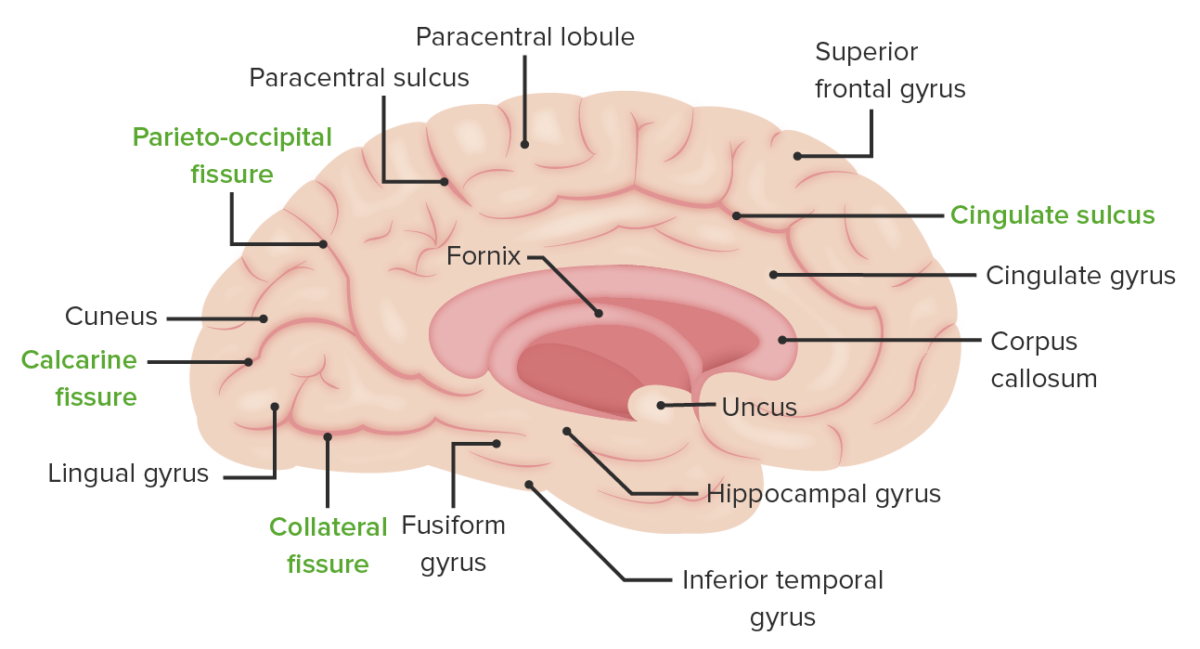
La superficie medial del hemisferio cerebral izquierdo: obsérvese la localización del surco colateral que separa la circunvolución lingual de la fusiforme, la fisura calcarina que separa la circunvolución cuneiforme de la lingual y el surco parietooccipital que separa el lóbulo parietal del occipital.
Imagen por Lecturio.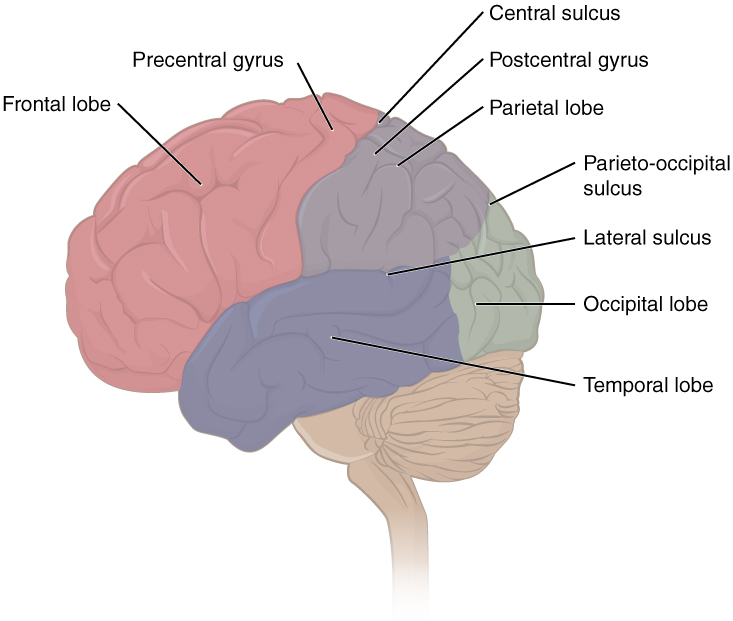
La imagen muestra la ubicación de algunas estructuras clave, incluyendo cada uno de los 4 lóbulos, la circunvolución precentral y postcentral, y los surcos central, lateral y parietooccipital.
Imagen: “Lobes of Cerebral Cortex” por OpenStax Anatomy and Physiology. Licencia: CC BY 4.0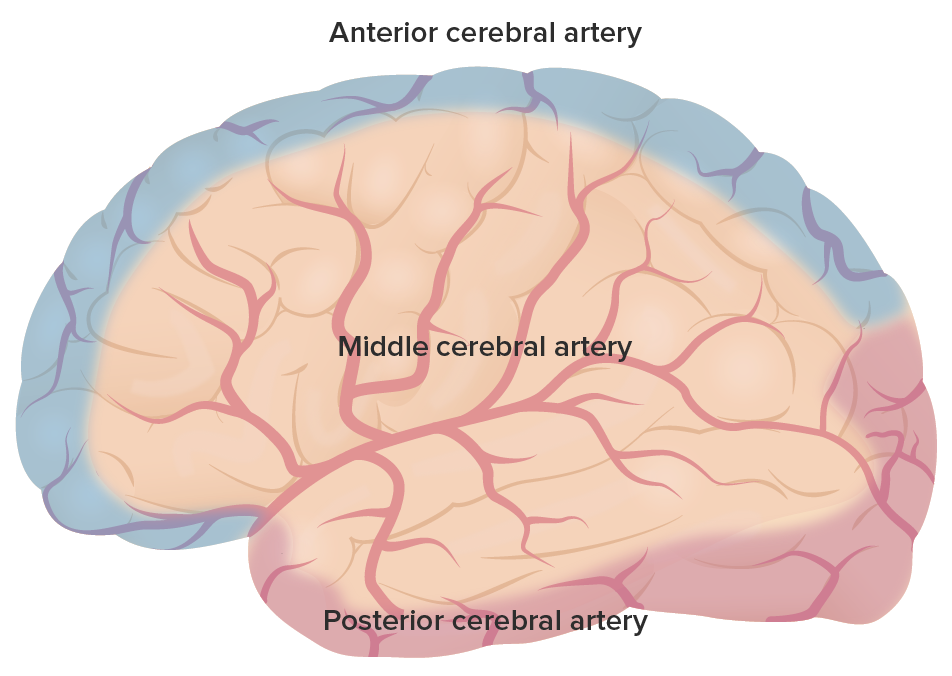
La irrigación primaria de todo el cerebrum: Obsérvense las regiones cubiertas por la arteria cerebral anterior en púrpura, la arteria cerebral media en rojo y la arteria cerebral posterior en rosa.
Imagen por Lecturio.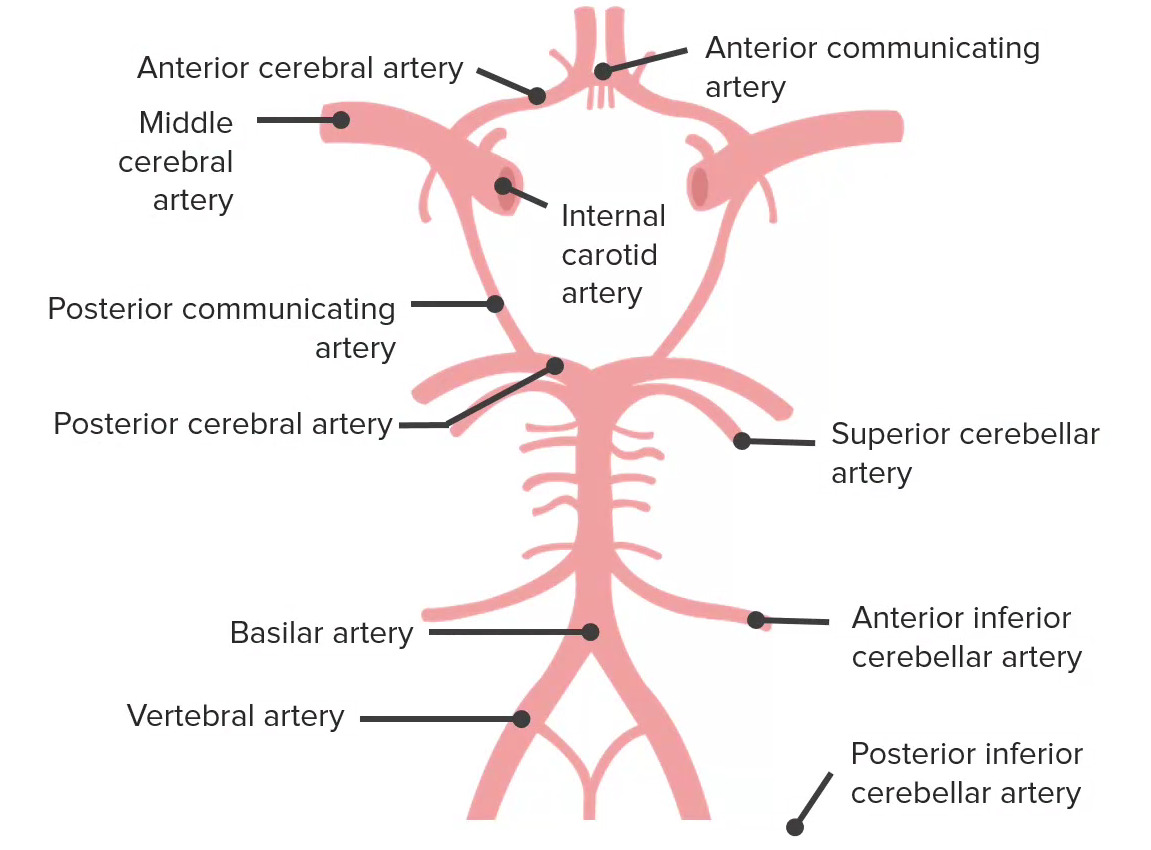
La irrigación al cerebro proviene de 2 fuentes: 1) las arterias carótidas internas y 2) el sistema vertebrobasilar. Estos sistemas se interconectan para formar el polígono de Willis, que se representa aquí. El polígono de Willis tiene 5 componentes, que incluyen la arteria comunicante anterior, arterias cerebrales anteriores, arteria carótida interna, arteria comunicante posterior y arterias cerebrales posteriores.
Imagen por Lecturio.El lóbulo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy es la cara más anterior/superior del cerebro supratentorial. Controla muchas de las funciones de orden superior del cerebro, como la función motora, el pensamiento ejecutivo y el habla.
| Nombre | Localización | Área de Brodmann |
Función |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corteza motora primaria | Circunvolución precentral | 4 | Dictamina el control motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology contralateral |
| Corteza premotora | Anterior a la corteza motora primaria | 6 | Programación de eventos motores; sus neuronas se activan antes que las neuronas motoras primarias |
| Corteza motora suplementaria | Superficie de la línea media del hemisferio, anterior a la representación de la pierna de la corteza motora primaria | 6 | Planificación de movimientos motores complejos |
| Corteza prefrontal | Porción anterior del lóbulo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy | 8–14, 24, 25, 32, 44–47 | Olfato y función ejecutiva (resolución de problemas, juicio, planificación, comportamiento y emociones) |
| Campo ocular frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy | Intersección de la circunvolución frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy media con la circunvolución precentral | 8 |
|
| Área de Broca | Circunvolución frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy inferior del hemisferio dominante | 44, 45 | Producción de palabras (habla motora) |
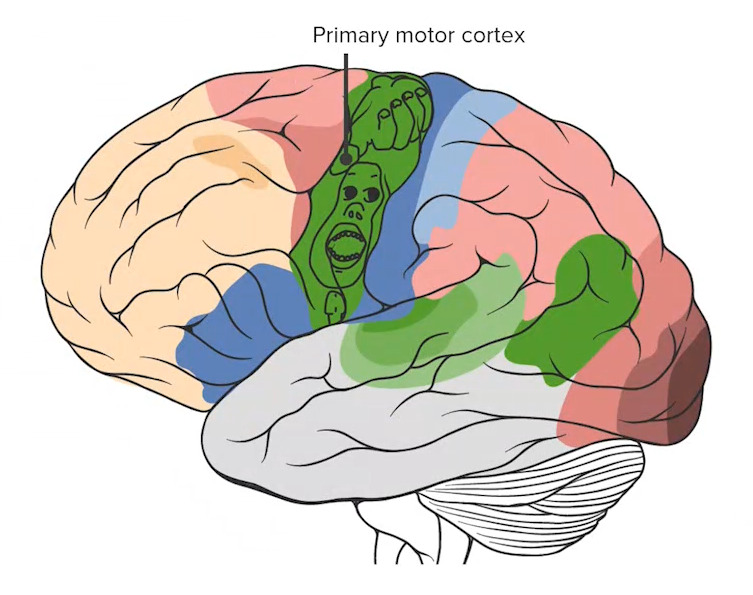
Obsérvese la corteza motora primaria (la estructura más posterior del lóbulo frontal) con el homúnculo superpuesto, que detalla las proporciones de la corteza dedicadas al procesamiento de cada función motora específica.
Imagen por Lecturio.El lóbulo parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy se encuentra posterior al AL Amyloidosis lóbulo frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy y superior al AL Amyloidosis lóbulo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy. Se asocia a los LOS Neisseria procesos de sensación y comprensión del lenguaje.
| Nombre | Localización | Área de Brodmann |
Función |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corteza somatosensorial primaria | Circunvolución postcentral | 3, 1, 2 | Recibe información somatosensorial contralateral del núcleo ventral posteromedial y del núcleo ventral posterolateral del tálamo |
| Áreas de asociación parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy | Parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy posterior | 5, 7 | Estereognosis y conciencia del yo contralateral y del entorno |
| Área de Wernicke | Circunvolución supramarginal del hemisferio dominante (además de la circunvolución temporal superior)* | 22, 40 | Comprensión del lenguaje |
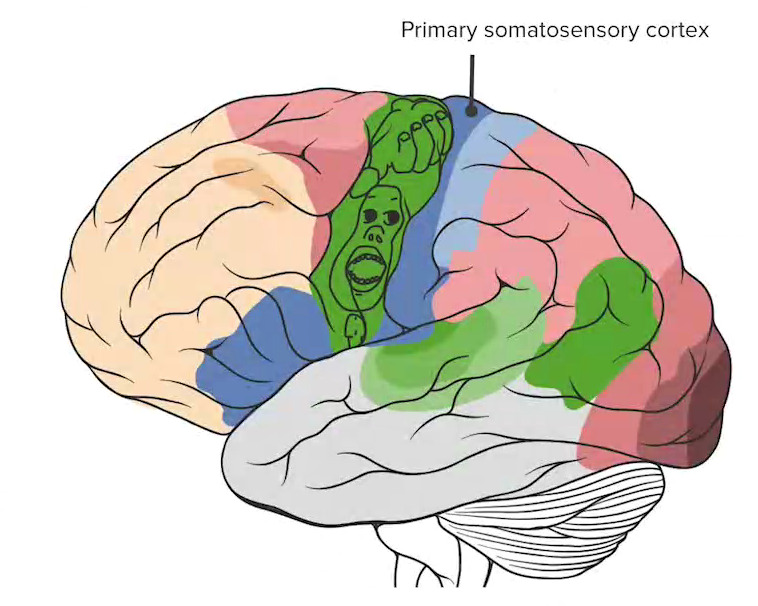
La corteza somatosensorial primaria (señalada en azul oscuro) marca la región más anterior del lóbulo parietal.
Imagen por Lecturio.El lóbulo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy es el lóbulo más posterior del cerebro supratentorial. Participa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el procesamiento de la visión.
| Nombre | Localización | Área de Brodmann |
Función |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corteza visual primaria | Lóbulo occipital Occipital Part of the back and base of the cranium that encloses the foramen magnum. Skull: Anatomy posterior | 17 | Visión y agudeza (información del núcleo geniculado lateral a través de las radiaciones ópticas) |
| Corteza de asociación visual | Corteza extraestriada | 18, 19 | Procesa información relacionada con la forma, color, movimiento, profundidad y relaciones espaciales |
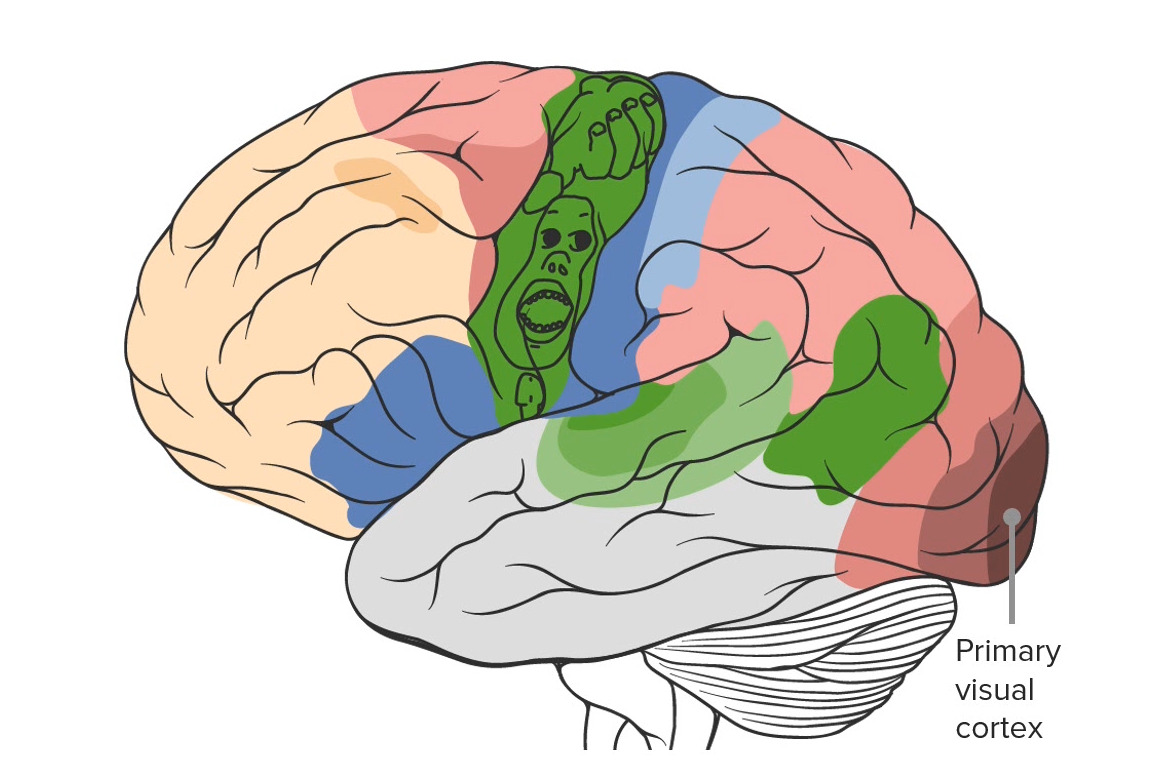
Obsérvese la ubicación de la corteza visual primaria en la región más posterior del cerebro, en el lóbulo occipital.
Imagen por Lecturio.El lóbulo temporal es la cara más anterior/inferior del cerebro supratentorial. Participa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria procesos de audición, olfato y memoria.
| Nombre | Localización | Área de Brodmann |
Función |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corteza auditiva primaria | Plano temporal superior de los LOS Neisseria lóbulos temporales dentro del surco lateral | 40, 41 | Audición |
| Circunvolución temporal media e inferior | Lóbulo temporal medio e inferior | 20, 21 | Memoria a largo plazo |
| Circunvolución parahipocampal | Localizada medialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la corteza temporooccipital inferior | 34 | Memoria a corto plazo |
| Uncus Uncus Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy | Continuo con la circunvolución del hipocampo | 35 | Olfato |
| Circunvolución fusiforme | Circunvolución medial occipitotemporal | 37 | Reconocimiento facial |
| Área de Wernicke | Circunvolución temporal superior del hemisferio dominante (además del giro supramarginal del lóbulo parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy)* | 22, 40 | Comprensión del lenguaje |
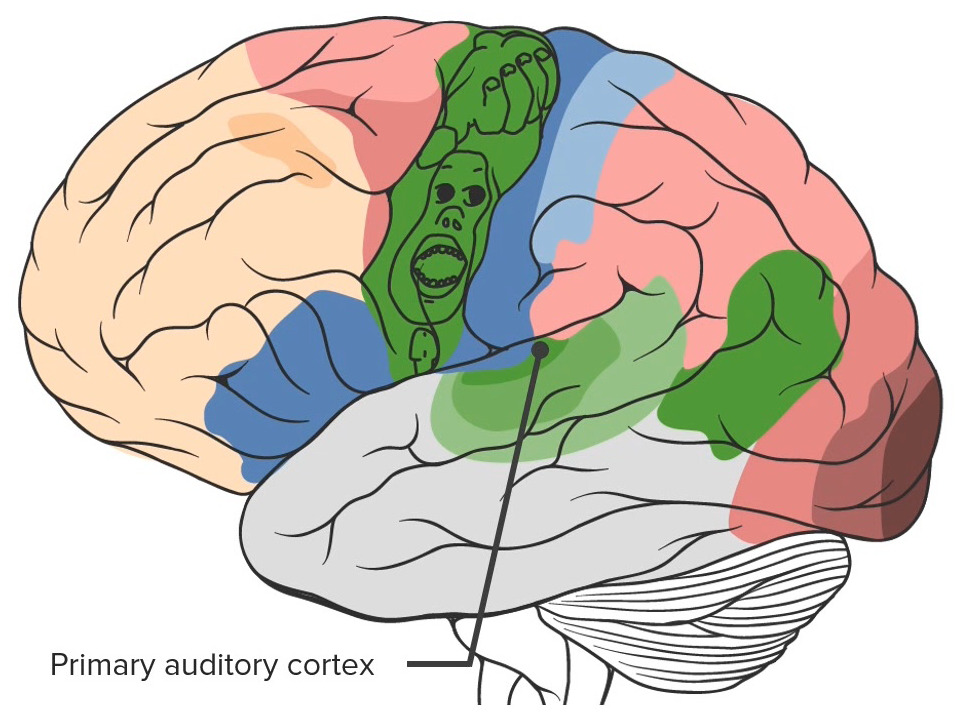
Obsérvese la corteza auditiva primaria situada en el lóbulo temporal
Imagen por Lecturio.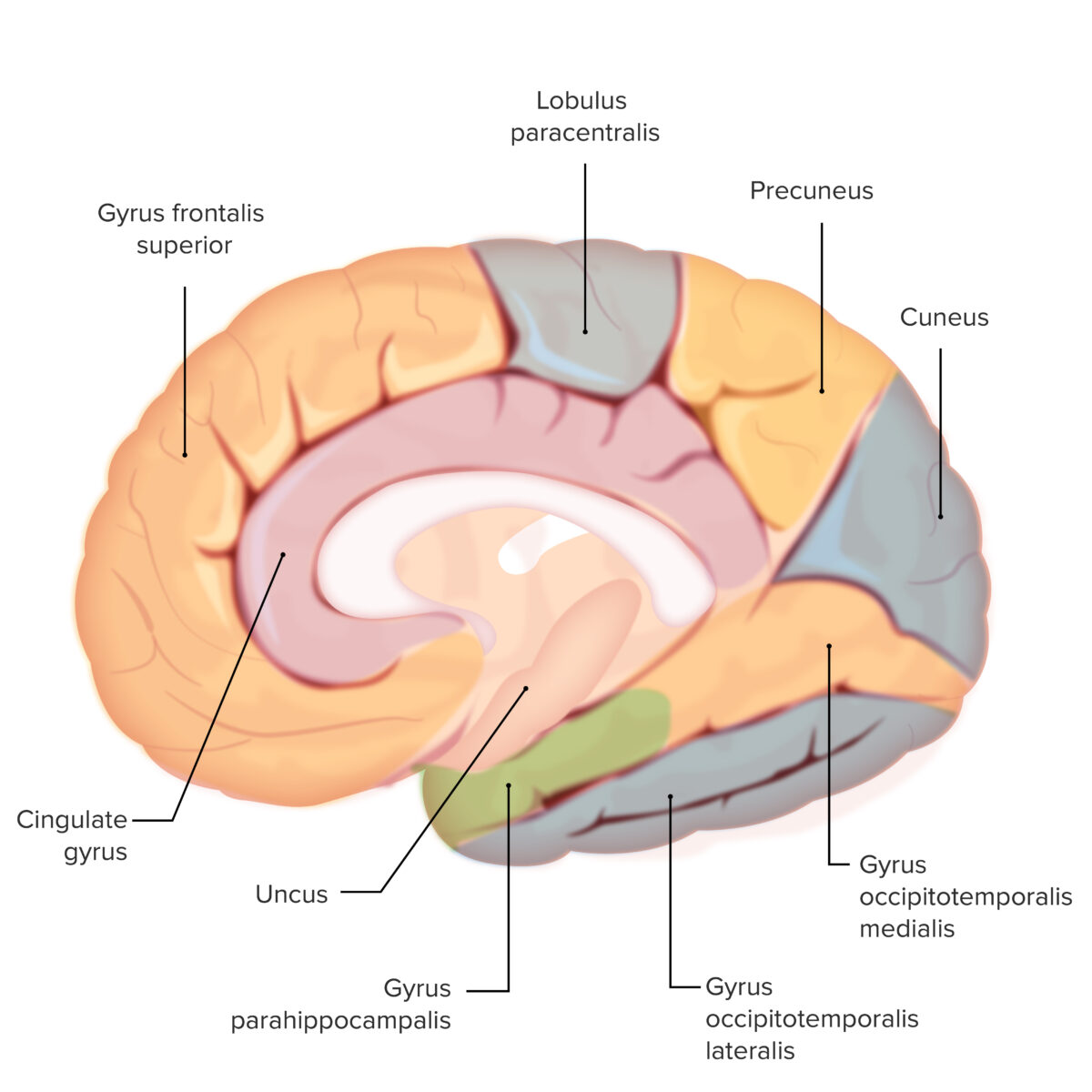
Las distintas circunvoluciones del cerebro: obsérvese la circunvolución parahipocampal (sombreada en verde)
Esta estructura es importante para la formación de la memoria a corto plazo
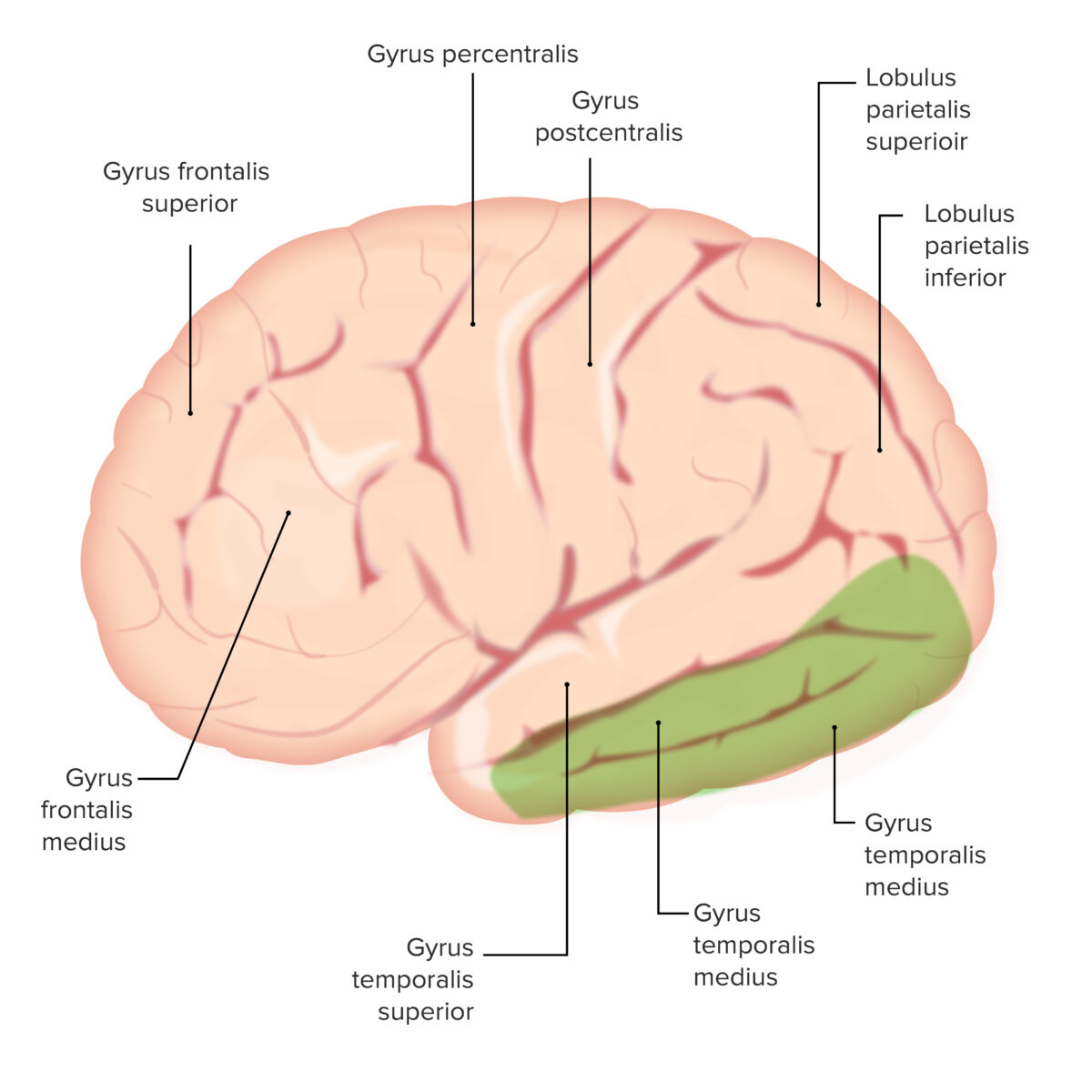
Las distintas circunvoluciones del cerebro: observe las circunvoluciones temporales medial e inferior (ambas sombreadas en verde).
Estas estructuras son importantes para la memoria a largo plazo
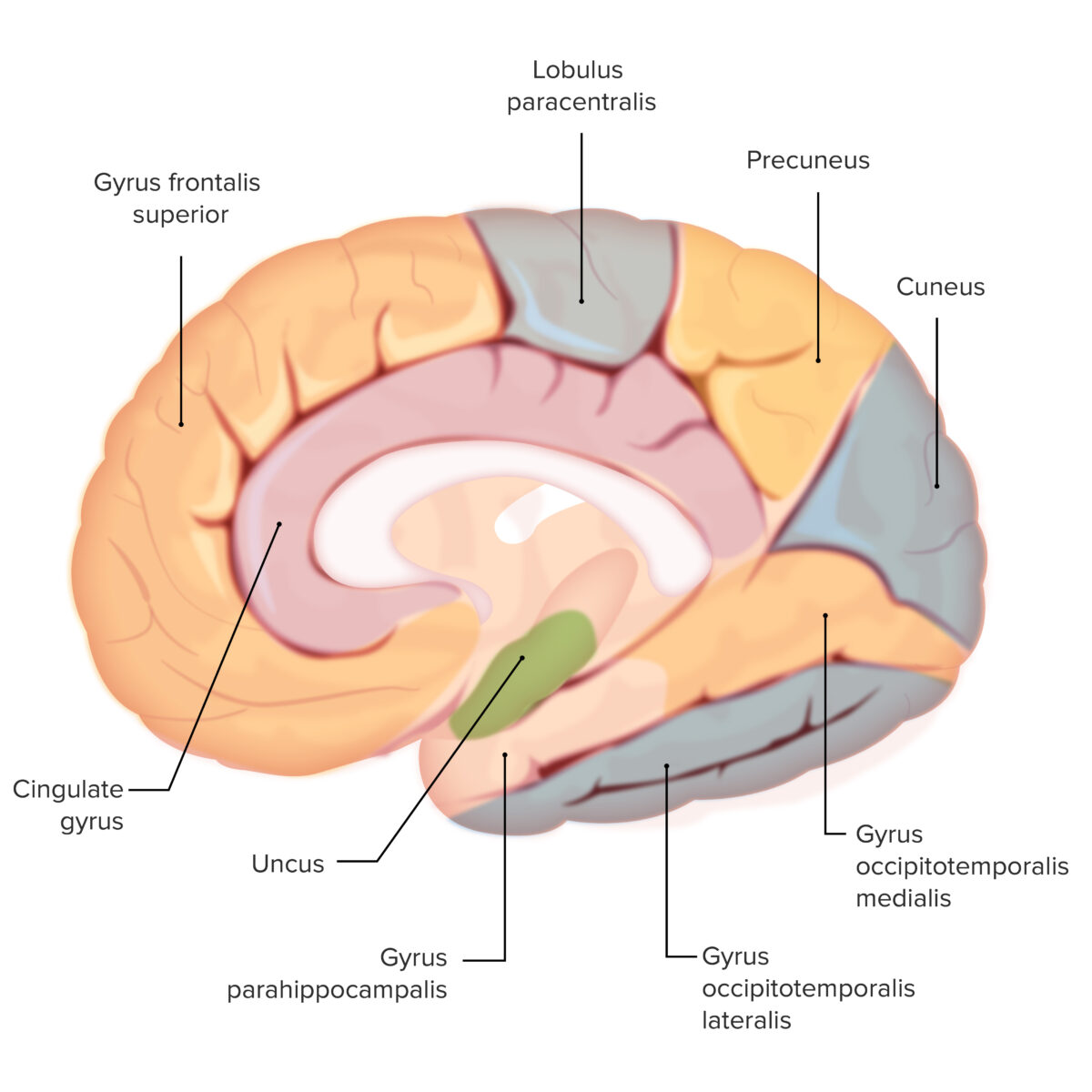
Las distintas circunvoluciones del cerebro: obsérvese el uncus (sombreado en verde)
Esta es una estructura importante para el olfato
Las siguientes estructuras están estrechamente relacionadas con la corteza cerebral por su localización o función: