El coma se define como un estado profundo de inconsciencia y ausencia de respuesta ambiental, caracterizado por una puntuación de ≤ 8 puntos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la GCS GCS A scale that assesses the response to stimuli in patients with craniocerebral injuries. The parameters are eye opening, motor response, and verbal response. Coma (Glasgow Coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma Scale Scale Dermatologic Examination, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). Un estado comatoso puede ser causado por una multitud de afecciones, lo que dificulta determinar la epidemiología precisa y el pronóstico del coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente mediante un examen neurológico completo, incluyendo la evaluación del tronco encefálico para evaluar la presencia de muerte cerebral. El tratamiento definitivo depende de la etiología subyacente.
Last updated: Jan 28, 2026
| Descripción | Puntaje | |
|---|---|---|
| Apertura ocular | Espontánea | 4 |
| Apertura al AL Amyloidosis habla | 3 | |
| Responde al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation | 2 | |
| Ninguna | 1 | |
| Mejor respuesta verbal | Orientado | 5 |
| Confundido | 4 | |
| Palabras inapropiadas | 3 | |
| Palabras incomprensibles | 2 | |
| Ninguna | 1 | |
| Mejor respuesta motora | Obedece órdenes | 6 |
| Localiza el dolor Dolor Inflammation | 5 | |
| Retira al AL Amyloidosis dolor Dolor Inflammation | 4 | |
| Postura de decorticación (flexión) | 3 | |
| Postura de descerebración (extensión) | 2 | |
| Ninguna | 1 |
Difícil de determinar debido a:
| Estructurales | Tóxicos | Metabólicos |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
La secuencia específica de esta afección depende de la etiología subyacente, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum términos generales:
La evaluación y el abordaje puede ocurrir de manera simultánea.
Inicial:
Exploración neurológica (nivel de respuesta a los LOS Neisseria estímulos):
Examen del tronco encefálico (determinación de muerte cerebral):
El resto del examen físico se guía por la sospecha clínica de la etiología subyacente. Por ejemplo, si se sospecha meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, se justifica la prueba de signos de irritación meníngea.
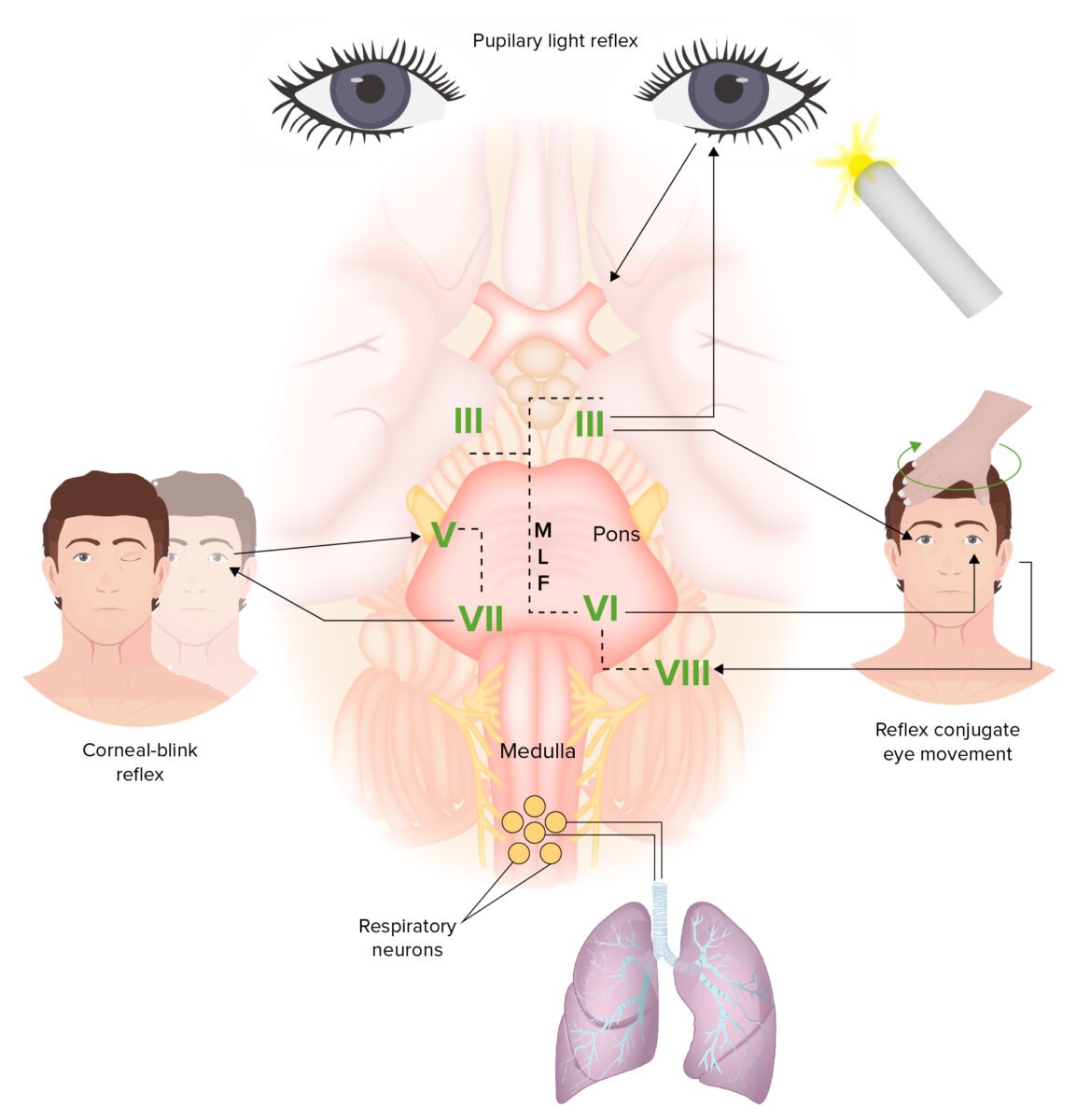
Tronco cerebral y reflejos:
El tronco cerebral conecta las vías entre el cerebro y la médula espinal. Las funciones controladas por el tronco encefálico incluyen el ciclo sueño-vigilia, los reflejos del tronco encefálico y la regulación del ritmo cardíaco y la respiración. La rama aferente del reflejo luminoso pupilar es el nervio óptico (NC II); la rama eferente es el nervio oculomotor (NC III). El reflejo oculocefálico (reflejo del ojo de muñeca) implica la rotación de la cabeza, un movimiento detectado por el nervio vestibular (NC VIII). Las señales llegan al núcleo vestibular. La salida se envía al NC III, que inerva el recto medial, y al nervio abducens (NC VI), que inerva el recto lateral. La coordinación del movimiento ocular se realiza a través del fascículo longitudinal medial (FML), que tiene fibras que conectan el núcleo abducens con el núcleo oculomotor contralateral. Esta conexión es importante para realizar la mirada horizontal conjugada. El reflejo corneal es causado por un bucle a través del nervio trigémino sensorial (NC V) en la córnea, que se proyecta al núcleo facial, y el nervio facial (NC VII), que sale del núcleo facial e inerva el músculo orbicular.
El diagnóstico de coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma es estrictamente clínico y se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un examen neurológico completo. Se llevan a cabo investigaciones adicionales (imagenología y laboratorios) para determinar la etiología.
Los LOS Neisseria estudios de laboratorio a solicitar dependen de la sospecha de la etiología subyacente. Algunos análisis de rutina incluyen:
TC/RM para evaluar:
La recuperación se define como el regreso de la capacidad de seguir órdenes de manera convincente y consistente.